PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851575

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851575
Computer Numerical Controls (CNC) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
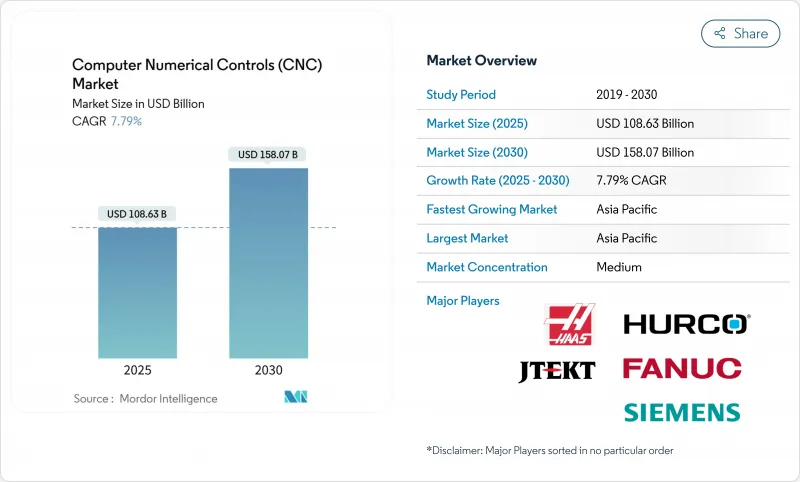
The global CNC machine market stands at USD 108.63 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 158.07 billion by 2030, reflecting a 7.79% CAGR.
Persistently tight labor markets, near-shoring of production, and the push for Industry 4.0 automation are converging, so manufacturers are accelerating investments in multi-axis and digitally connected equipment. Reshoring legislation in the United States and Europe is shifting capital away from low-cost regions toward flexible machining assets that support short lead-time production. Cybersecurity risk is rising in parallel with connectivity, motivating vendors to embed security-by-design features in new controllers. At the same time, sustained high steel and aluminum prices are driving demand for precision processes that minimize scrap. Together these forces keep the CNC machine market on a solid growth trajectory even as component shortages create near-term supply friction.
Global Computer Numerical Controls (CNC) Market Trends and Insights
Reshoring-led Demand for Flexible CNC Equipment in North America and Europe
U.S. imports of finished goods from China fell 13% in 2023 while domestic factory investment rose sharply after infrastructure and semiconductor incentives. Incoming work is highly variable, so buyers prefer adaptable 5-axis machines and modular robot cells that handle diverse part families. Near-market production justifies higher capital outlays because freight risks fall and delivery speed improves. Vendors that offer rapid re-tooling and digital setup features gain a competitive edge. This reshoring vector directly enlarges the CNC machine market by converting decades of outsourced volumes into local capacity growth.
Industry 4.0-Driven Adoption of Digital-Twin-Enabled CNC Controllers
Digital twins let programmers validate tool paths virtually, cutting physical setup time by 20% with Siemens Sinumerik 828D hardware. Studies show 14.53% productivity gains and 13.9% lower energy use when machines run in closed-loop coordination with their virtual counterparts. Adoption is strongest in aerospace and automotive sectors that need real-time compensation for thermal drift and tool wear. Controller suppliers embed cloud connectivity and AI analytics, turning the CNC machine market into a software-centric arena. As license revenues grow, machine builders look to recurring income rather than one-time hardware margin.
Semiconductor Motion-Control Chip Shortages Constraining Supply
Precision servo drives rely on specialty ASICs that remain in short supply, stretching lead times for premium machines beyond nine months. Some builders redesign around available chips, but that demands costly re-qualification. OEMs with secured allocations win share while latecomers lose backlog. The bottleneck suppresses the near-term CNC machine market volume despite solid order books.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- EV Power-train Complexity Boosting Multi-Axis CNC Orders in Asia
- Government Incentives for Aerospace Precision Machining (Japan, France)
- High CAPEX of 5-Axis and Hybrid Additive-Subtractive Machines
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
CNC lathes held 23.4% of CNC machine market share in 2024 and remain indispensable for round parts such as shafts and hubs. Continuing EV power-train development raises tolerance demands, so many shops retrofit live tooling and Y-axis capability to conventional turning centers. Milling machines form the next largest slice of the CNC machine market, serving complex mold cavities for aerospace and medical implants. Laser and plasma cutters grow as sheet-metal designs multiply in battery enclosures, and EDM stays relevant for hardened tool steels. The CNC machine market size for 5-axis platforms is poised to grow 10.8% CAGR because single-setup capability slashes fixture time and eliminates reposting errors. Grinding and welding machines add niche depth: friction-stir welding joins battery shells without filler metal, while grinding delivers mirror finishes on turbine discs.
The 5-axis and above category illustrates why value is shifting toward flexibility rather than raw spindle horsepower. Integrated tool changers allow several hundred cutters that handle aluminum, titanium, and composites in one cycle. Probing routines verify geometry in situ, reducing scrap despite high material costs. Early adopters report 18% throughput gains once operators master simultaneous axis commands. Component suppliers therefore treat multi-axis as a strategic hedge against labor risk, pushing the CNC machine market toward higher complexity tiers regardless of plant size.
Three-axis units still anchor the installed base with a 46% share and attractive price-performance ratios for simple work. Yet part programs with undercuts and helical flutes drive shops to add rotary tables or invest in full five-axis machines. The 5-axis and above segment posts a 10.8% CAGR because it merges milling and turning, enabling machining from all directions without reclamping. Improved CAM software plus training subsidies make the technology accessible to mid-market buyers, widening the CNC machine market size for advanced axis counts.
Rotary-tilt tables on 4-axis systems bridge the gap and allow affordable entry into positional machining. However, aerospace primes increasingly require simultaneous motion capability that only true 5-axis delivers. FANUC's 500i-A controller, with 2.7 times CPU power, optimizes axis interpolation for complex tool paths. As OEMs validate shorter cycle times and better surface finishes, even conservative job shops reconsider equipment roadmaps. This dynamic ensures a steady migration that enlarges the CNC machine market beyond conventional formats.
CNC Market Report is Segmented by Machine Type (CNC Lathe Machines, CNC Milling Machines, and More), Axis Type (3-Axis, and More), Component (CNC Controller, Servo Motor Drive, and More), Control System (Open-Loop, Closed-Loop), Deployment (Stand-Alone CNC Machines, Integrated Production Cells), End User (Automotive, Aerospace and Defense, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific leads the CNC machine market with a 52% revenue share, anchored by China's vast supplier ecosystem and Japan's trail-blazing multi-axis technology. Beijing's dual-circulation policy encourages local content, spurring demand for domestic spindle makers and feedback encoders. Tokyo's investment in magnesium alloy machining for space launch widens its leadership in lightweight materials. South Korea's state-funded drive system advances cut reliance on imported servos, underlining a regional strategy toward self-sufficiency. ASEAN countries benefit from supply-chain diversification, attracting greenfield plants that require entry-level yet upgradeable equipment.
North America gains momentum as reshoring projects proliferate under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the CHIPS Act. Siemens earmarked over USD 10 billion to expand U.S. production lines for electrification hardware, adding 900 skilled roles. FANUC's USD 110 million campus in Michigan trains thousands of technicians annually, alleviating talent shortages. Canadian aerospace clusters in Quebec adopt high rpm titanium cutters, while Mexican automotive hubs invest in flexible machining to service near-term EV assembly demand. The CNC machine market thus benefits from synchronized policy and private investment.
Europe shows steady growth amid sustainability mandates and push for electric mobility. French aerospace subsidies accelerate hybrid additive-subtractive machine trials, boosting local OEM competitiveness. Germany's Mittelstand firms retrofit legacy mills with closed-loop drives to cut energy use, aligning with EU Green Deal goals. FANUC's Iberia office expansion signals rising demand in Spain and Portugal for robotized machining cells. Eastern European countries capture overflow work from Western plants, driving orders for mid-range 3-axis centers. Despite macro headwinds, Europe remains a technology testbed that shapes future CNC machine market specifications.
- Fanuc Corporation
- Siemens AG
- DMG Mori Seiki Co., Ltd.
- Haas Automation, Inc.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Okuma Corporation
- Yamazaki Mazak Corporation
- Hurco Companies, Inc.
- JTEKT Corporation
- Dr. Johannes Heidenhain GmbH
- Trumpf Group
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- GSK CNC Equipment Co., Ltd.
- Dalian Machine Tool Group
- Makino Milling Machine Co., Ltd.
- Hyundai Wia Corporation
- Fagor Automation
- Brother Industries, Ltd.
- Amera-Seiki, Inc.
- Fair Friend Group (FFG)
- Doosan Machine Tools Co., Ltd.
- Hardinge Inc.
- TAKISAWA Machine Tool Co., Ltd.
- Protomatic Inc.
- Metal Craft AMS
- Micromedical LLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Reshoring-led Demand for Flexible CNC Equipment in North America and Europe
- 4.2.2 Industry 4.0-Driven Adoption of Digital-Twin-Enabled CNC Controllers
- 4.2.3 EV Power-train Complexity Boosting Multi-Axis CNC Orders in Asia
- 4.2.4 Government Incentives for Aerospace Precision Machining (Japan, France)
- 4.2.5 Automated CNC Cells Addressing Global Skilled-Labor Shortages
- 4.2.6 Micro-CNC Demand from High-Growth Medical Device Segment
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Semiconductor Motion-Control Chip Shortages Constraining Supply
- 4.3.2 High CAPEX of 5-Axis and Hybrid Additive-Subtractive Machines
- 4.3.3 Cyber-Security Concerns with Networked CNC Systems
- 4.3.4 Volatile Steel and Aluminum Prices Impacting SME ROI
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Investment Trends and Capital Expenditure Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Machine Type
- 5.1.1 CNC Lathe Machines
- 5.1.2 CNC Milling Machines
- 5.1.3 CNC Laser Cutting Machines
- 5.1.4 CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
- 5.1.5 CNC Electric Discharge Machines (EDM)
- 5.1.6 CNC Grinding Machines
- 5.1.7 CNC Winding Machines
- 5.1.8 CNC Welding Machines
- 5.1.9 Other Machine Types
- 5.2 By Axis Type
- 5.2.1 3-Axis
- 5.2.2 4-Axis
- 5.2.3 5-Axis and Above
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 CNC Controller
- 5.3.2 Servo Motor Drive
- 5.3.3 Sensors and Feedback
- 5.3.4 Others
- 5.4 By Control System
- 5.4.1 Open-loop
- 5.4.2 Closed-loop
- 5.5 By Deployment
- 5.5.1 Stand-alone CNC Machines
- 5.5.2 Integrated Production Cells (CNC + Robotics)
- 5.6 By End User
- 5.6.1 Automotive (incl. EV)
- 5.6.2 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.6.3 Power and Energy
- 5.6.4 Industrial Machinery
- 5.6.5 Medical Devices
- 5.6.6 Electronics and Semiconductor
- 5.6.7 Other End Users
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.2 Latin America
- 5.7.2.1 Mexico
- 5.7.2.2 Brazil
- 5.7.2.3 Argentina
- 5.7.2.4 Rest of Latin America
- 5.7.3 Europe
- 5.7.3.1 Germany
- 5.7.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3.3 France
- 5.7.3.4 Italy
- 5.7.3.5 Spain
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.5 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.5.1 China
- 5.7.5.2 Japan
- 5.7.5.3 South Korea
- 5.7.5.4 India
- 5.7.5.5 Australia
- 5.7.5.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global?level Overview, Market level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Fanuc Corporation
- 6.4.2 Siemens AG
- 6.4.3 DMG Mori Seiki Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Haas Automation, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.6 Okuma Corporation
- 6.4.7 Yamazaki Mazak Corporation
- 6.4.8 Hurco Companies, Inc.
- 6.4.9 JTEKT Corporation
- 6.4.10 Dr. Johannes Heidenhain GmbH
- 6.4.11 Trumpf Group
- 6.4.12 Bosch Rexroth AG
- 6.4.13 GSK CNC Equipment Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Dalian Machine Tool Group
- 6.4.15 Makino Milling Machine Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Hyundai Wia Corporation
- 6.4.17 Fagor Automation
- 6.4.18 Brother Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Amera-Seiki, Inc.
- 6.4.20 Fair Friend Group (FFG)
- 6.4.21 Doosan Machine Tools Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.22 Hardinge Inc.
- 6.4.23 TAKISAWA Machine Tool Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.24 Protomatic Inc.
- 6.4.25 Metal Craft AMS
- 6.4.26 Micromedical LLC
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




