PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851872

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851872
Intracranial Pressure Monitoring - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
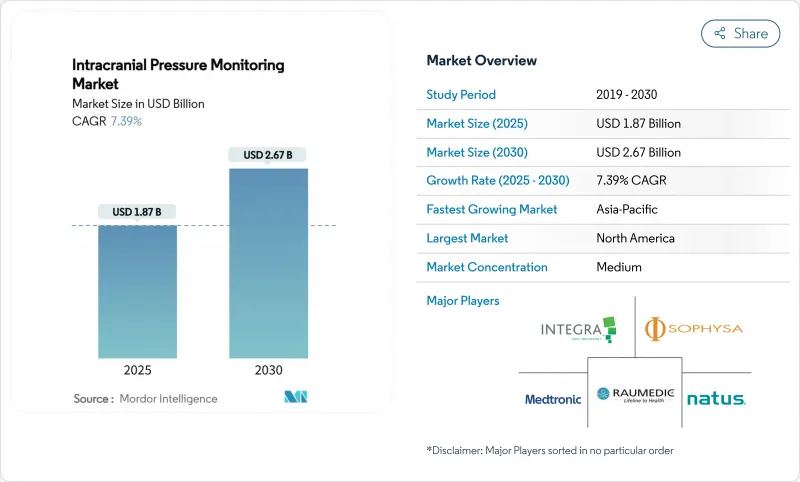
The intracranial pressure monitoring market stood at USD 1.87 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 2.67 billion by 2030, advancing at a 7.4% CAGR.
Growth rests on the pairing of artificial intelligence with conventional neurocritical care, letting clinicians predict pressure surges well before a patient shows clinical decline. Hospitals are adopting wireless micro-sensors that deliver accuracy within 1.0 mm Hg of invasive systems, while predictive analytics platforms cut intervention time and lower complication rates. Traumatic brain injury keeps demand steady, but infectious conditions and space medicine add fresh revenue streams. Vendors that integrate cybersecurity, data analytics and biocompatible materials now command premium pricing.
Global Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Market Trends and Insights
Rising Incidence of Traumatic Brain Injury
Traffic collisions, sports mishaps and falls among seniors sustain a high caseload that requires continuous monitoring in intensive care units. Updated Brain Trauma Foundation guidelines recommend pressure tracking for every severe case with a Glasgow Coma Scale below 8, increasing the eligible patient cohort. Military conflicts and adventure sports widen demographic exposure, while value-based care models reward early detection that prevents secondary damage.
Growing Prevalence of Hydrocephalus & Neuro-Degenerative Disorders
Hydrocephalus affects 1 in 1,000 newborns and appears more often among aging adults. Programmable shunt systems now include embedded sensors that fine-tune drainage in real time, trimming revision surgeries. Alzheimer's and Parkinson's patients also benefit from sustained monitoring when cerebrospinal dynamics fluctuate.
High Device and Procedure Cost; Reimbursement Gaps
Capital equipment costs range from USD 15,000 to USD 50,000, and each implantation adds another USD 5,000-15,000 in patient charges. Annual maintenance, single-use sensors and software licences inflate lifetime ownership costs. Reimbursement remains patchy; some insurers cover only invasive systems or demand prior authorization, leaving newer non-invasive options unfunded. Hospitals must compile cost-effectiveness dossiers before purchase, so many low-resource centers postpone adoption despite clinical need.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Adoption of Minimally Invasive Micro-Sensor Technologies
- Demand from Space-Medicine & High-Altitude Expeditions
- Shortage of Trained Neuro-Critical-Care Staff
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Invasive devices delivered 73.5% of intracranial pressure monitoring market revenue in 2024. External ventricular drains remain indispensable when cerebrospinal fluid diversion is required, while fiber-optic probes offer high fidelity for continuous readings. The segment benefits from standardised clinical protocols and widespread physician familiarity. Non-invasive platforms are growing at 10.1% CAGR, propelled by transcranial Doppler and optic-nerve ultrasonography that achieve clinically acceptable accuracy. Diffuse correlation spectroscopy narrows mean error to 1.0 mm Hg, edging closer to catheter precision.
Continued research funds mobile ultrasound solutions that frontline responders can use before hospital arrival, reinforcing non-invasive momentum. Yet the intracranial pressure monitoring market size for invasive systems is projected to preserve a strong base through 2030 because neurosurgeons still prefer direct readings for complex trauma cases. Hybrid models, where a patient begins with invasive surveillance and shifts to cuff-less optical sensors for step-down care, illustrate convergence across techniques.
The Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Market Report is Segmented by Technique (Invasive [External Ventricular Drainage and More] and Non-Invasive [Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography and More]), Application (Traumatic Brain Injury, Intracerebral Hemorrhage, and More), End User (Hospitals & Trauma Centres, Neuro-Intensive Care Units and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America held 39.8% of global revenue in 2024 on the back of trauma networks, ample reimbursement and early AI adoption. The United States leads through FDA clearance processes that favour iterative sensor upgrades, while Canada leverages a universal system to implement standardized protocols. Mexico's device manufacturing clusters add supply resilience, though budget constraints temper hospital uptake. Cyber-security mandates increase compliance costs, yet they also create barriers that protect incumbent vendors.
Asia-Pacific is growing the fastest at 9.5% CAGR thanks to hospital build-outs, rising accident rates and government push for med-tech self-reliance. China subsidises domestic sensor production, and India's private clinics deploy advanced monitors to serve medical tourists. Japan's rapidly aging society fuels hydrocephalus applications, whereas South Korea positions trauma facilities as regional centres of excellence. Australia and New Zealand use portable kits to serve mining and remote communities.
Europe shows steady expansion anchored in evidence-based practice and robust data-privacy legislation. Germany and the United Kingdom finance multi-centre trials to validate non-invasive algorithms, while France and Italy refine paediatric protocols. GCC countries invest in neurotrauma capacity, and South Africa pilots tele-neurocritical care to bridge rural gaps. As regulators harmonise rules, market entry becomes simpler yet cyber-security standards tighten, elevating development requirements.
- Medtronic
- Integra LifeSciences Corp.
- Natus Medical
- Raumedic
- Sophysa SA
- Codman Neuro (J&J)
- Spiegelberg GmbH & Co.KG
- Headsense Medical
- Sense Neuro Diagnostics
- Vittamed Corporation
- Branchpoint Technologies
- Longeviti Neuro Solutions
- NeurOptics
- Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics
- G.Tec Medical Engineering
- B. Braun
- Shenzhen Kinglove Medical
- Moor Instruments
- Terumo
- Koninklijke Philips
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Incidence Of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- 4.2.2 Growing Prevalence Of Hydrocephalus & Neuro-Degenerative Disorders
- 4.2.3 Rapid Adoption Of Minimally-Invasive Micro-Sensor Technologies
- 4.2.4 AI-Driven Personalised ICP Thresholds & Predictive Analytics
- 4.2.5 Demand From Space-Medicine & High-Altitude Expeditions
- 4.2.6 Paediatric ICU Protocols Mandating Continuous ICP Monitoring
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Device & Procedure Cost; Reimbursement Gaps
- 4.3.2 Shortage Of Trained Neuro-Critical-Care Staff
- 4.3.3 Cyber-Security & Data-Privacy Risks With Wireless Systems
- 4.3.4 Supply-Chain Fragility For Sensor-Grade Piezo Materials
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technology Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value-USD)
- 5.1 By Technique
- 5.1.1 Invasive
- 5.1.1.1 External Ventricular Drainage (EVD)
- 5.1.1.2 Micro-transducer ICP Monitoring
- 5.1.2 Non-invasive
- 5.1.2.1 Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography
- 5.1.2.2 Tympanic Membrane Displacement
- 5.1.2.3 Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter
- 5.1.2.4 MRI / CT-based ICP Estimation
- 5.1.2.5 Other Non-invasive Techniques
- 5.1.1 Invasive
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Traumatic Brain Injury
- 5.2.2 Intracerebral Haemorrhage
- 5.2.3 Meningitis
- 5.2.4 Other Applications
- 5.3 By End-User
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Trauma Centres
- 5.3.2 Neuro-intensive Care Units (NICUs)
- 5.3.3 Ambulatory Surgical Centres
- 5.3.4 Military & Space Health Facilities
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Medtronic plc
- 6.3.2 Integra LifeSciences Corp.
- 6.3.3 Natus Medical Inc.
- 6.3.4 RAUMEDIC AG
- 6.3.5 Sophysa SA
- 6.3.6 Codman Neuro (J&J)
- 6.3.7 Spiegelberg GmbH & Co.KG
- 6.3.8 Headsense Medical
- 6.3.9 Sense Neuro Diagnostics
- 6.3.10 Vittamed Corporation
- 6.3.11 Branchpoint Technologies
- 6.3.12 Longeviti Neuro Solutions
- 6.3.13 NeurOptics Inc.
- 6.3.14 Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics
- 6.3.15 G.Tec Medical Engineering
- 6.3.16 B. Braun
- 6.3.17 Shenzhen Kinglove Medical
- 6.3.18 Moor Instruments
- 6.3.19 Terumo Corporation
- 6.3.20 Koninklijke Philips N.V.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




