PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851908

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851908
Hospital Infection Therapeutics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market size is estimated at USD 11.91 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 14.02 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.32% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
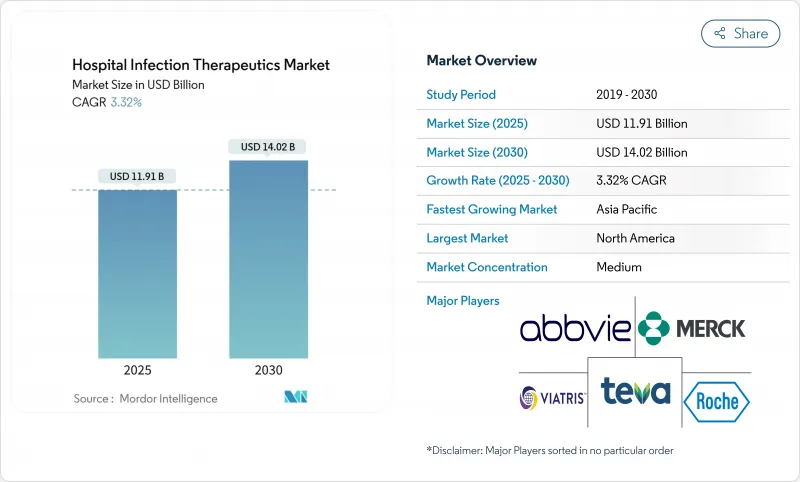
Demand continues to track rising healthcare-associated infection (HAI) incidence, although wider adoption of infection-prevention technologies tempers growth potential. Mortality linked to carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii now exceeds 40% in intensive-care settings, intensifying clinical urgency for effective agents. Governments are injecting fresh capital into antimicrobial pipelines; BARDA alone committed more than USD 500 million to resistance countermeasures in 2024. Parallel advances in artificial-intelligence (AI) drug discovery accelerate asset identification, while subscription-style reimbursement proposals such as the PASTEUR Act promise steadier revenue visibility for innovators.
Global Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Prevalence of HAIs
Roughly 1 in 31 hospitalized U.S. patients acquires an HAI daily, and bloodstream infections alone account for more than 71,000 deaths each year. Hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains now infect both immunocompromised and healthy individuals, challenging conventional antibacterial regimens. In developing neurosurgical centers, spine-surgery infection rates reach 11.7%, lengthening median hospital stay to 36.5 days from 23 days for uninfected patients and directly raising therapeutic demand. Tertiary hospitals in Southwest China report the highest HAI incidence in hematology, cardiology, and neurology wards, where Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli predominate. Collectively, these patterns reinforce consistent global need for potent, broad-spectrum agents within the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Growing Surgical Procedure Volume
Ambulatory surgery centers handle millions of outpatient operations under CDC-mandated surveillance protocols that heighten early detection of surgical site infections (SSIs). Asia-Pacific records the sharpest procedure growth, buoyed by infrastructure expansion and ageing populations pursuing complex interventions. Evidence links lumbar and thoracolumbar surgeries to elevated SSI risk, particularly when patients are admitted within 48 hours pre-operatively. Multimodal interventions across Sub-Saharan Africa have lowered SSI rates by as much as 95%, highlighting scope to curb downstream drug volumes when preventive protocols mature. Nonetheless, absolute procedure expansion still underpins steady unit sales in the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Accelerating AMR Eroding Drug Efficacy
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus remain entrenched threats in intensive-care units. Many pipeline candidates do not address WHO priority pathogens, leaving treatment gaps. Resistance to recently launched combinations such as ceftazidime-avibactam has already emerged within a few years of market entry. Rising failure rates prompt combination regimens that raise toxicity and procurement costs. This erosion pressures sustainable growth in the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Antimicrobial Resistance Crisis
- Government Subscription Incentives for Novel Antibiotics
- High Development Costs and Lengthy Trials
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Antibacterials held 72.21% of global revenue. Intravenous agents such as ceftobiprole address Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia with 79.1% composite response rates, reinforcing the clinical dominance of B-lactam classes. Chinese sponsors now control 20 antibacterial programs in clinical evaluation, deepening supply resilience and competitive intensity. Generous NIAID grants targeting carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas further stimulate antibacterial innovation.
Antivirals, though smaller today, are projected to grow at a 3.83% CAGR, reflecting broadened adoption of hospital-focused antivirals and immunomodulators. Precision-medicine workflows now match viral resistance genotypes with tailored therapy, improving outcomes and justifying price premiums. Antifungals meanwhile benefit from rezafungin approval for candidemia, filling a longstanding gap for once-weekly dosing in critical care. Bacteriophage and monoclonal-antibody therapies in the "others" cluster could add differentiated revenue streams, though manufacturing and regulatory complexities must be resolved before significant contributions accrue to the hospital infection therapeutics market.
The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market Report is Segmented by Drug Class (Antibacterial Drugs, Antifungal Drugs, Antiviral Drugs, Others), Infection Type (Blood Stream Infections, Urinary Tract Infections, Surgical Site Infections, Pneumonia (HAP/VAP), Others), Route of Administration (Oral, Intravenous, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America held 37.83% of global revenue of hospital infection therapeutics market in 2024. The CDC's National Healthcare Safety Network entrenches mandatory HAI-reporting policies that sustain high therapeutic vigilance. BARDA funding underpins rapid translation of pipeline assets, culminating in recent FDA approvals such as ceftobiprole and cefepime-enmetazobactam. Pfizer is investing USD 150 million to modernize an Australian plant intended to supply more than 60 export markets, illustrating regional leadership in responsible manufacturing upgrades. The pending PASTEUR Act may further stabilize cashflows, shaping procurement strategies across hospitals.
Asia-Pacific is forecasted to post a 4.53% CAGR to 2030, the fastest among major regions. China's regulatory reforms and the National Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs have propelled 17 companies with 20 antibacterial trials, contributing pipeline breadth and domestic pricing competition. India is enforcing a code of conduct for medical device marketing that strengthens infection-control standards, yet pharmaceutical effluent management remains a pressing challenge, with high antibiotic residues detected in industrial wastewater. Varied infrastructure maturity across ASEAN and South Asia yields heterogeneous demand, though rising procedure volumes create broad upward momentum within the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Europe benefits from coordinated AMR initiatives such as GSK's £45 million Fleming Centre partnership. The European Medicines Agency's positive opinion on aztreonam-avibactam marks the first B-lactam/B-lactamase inhibitor combination targeting metallo-B-lactamase producers, filling a therapeutic void. The Aurobac joint venture among Boehringer Ingelheim, Evotec, and bioMerieux adds diagnostic-therapeutic integration capabilities that may shorten time-to-effective therapy. Stringent environmental discharge rules and joint procurement initiatives help harmonize supply chain quality, though they also elevate compliance costs for entrants into the hospital infection therapeutics market.
- Abbvie
- Merck
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Viatris
- Roche
- Bayer
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Aurobindo Pharma Ltd (Eugia)
- Sanofi
- Pfizer
- Melinta Therapeutics
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals
- Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd.
- Shionogi & Co., Ltd.
- Paratek Pharmaceuticals
- Spero Therapeutics Inc.
- Iterum Therapeutics plc
- Theravance Biopharma, Inc.
- Cipla
- Seres Therapeutics Inc.
- Venatorx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating Prevalence of HAIs
- 4.2.2 Growing Surgical Procedure Volume
- 4.2.3 Rising Antimicrobial Resistance Crisis
- 4.2.4 Government Subscription Incentives for Novel Antibiotics
- 4.2.5 AI-Enabled Rapid Antibiotic Discovery
- 4.2.6 Infection-Surveillance Analytics Adoption
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Accelerating AMR Eroding Drug Efficacy
- 4.3.2 High Development Costs and Lengthy Trials
- 4.3.3 Preventive Technologies Curbing Drug Demand
- 4.3.4 Tight Discharge Rules on Antibiotic Manufacturing
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Pipeline Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Drug Class
- 5.1.1 Antibacterial Drugs
- 5.1.2 Antifungal Drugs
- 5.1.3 Antiviral Drugs
- 5.1.4 Others
- 5.2 By Infection Type
- 5.2.1 Blood Stream Infections
- 5.2.2 Urinary Tract Infections
- 5.2.3 Surgical Site Infections
- 5.2.4 Pneumonia (HAP/VAP)
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 By Route of Administration
- 5.3.1 Oral
- 5.3.2 Intravenous
- 5.3.3 Others
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.2 Merck & Co., Inc.
- 6.3.3 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- 6.3.4 Viatris Inc.
- 6.3.5 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.3.6 Bayer AG
- 6.3.7 GlaxoSmithKline plc
- 6.3.8 Aurobindo Pharma Ltd (Eugia)
- 6.3.9 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.10 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.11 Melinta Therapeutics
- 6.3.12 Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC
- 6.3.13 Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- 6.3.14 Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd.
- 6.3.15 Shionogi & Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.16 Paratek Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.17 Spero Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.18 Iterum Therapeutics plc
- 6.3.19 Theravance Biopharma, Inc.
- 6.3.20 Cipla Ltd.
- 6.3.21 Seres Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.22 Venatorx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




