PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851931

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851931
Maize - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
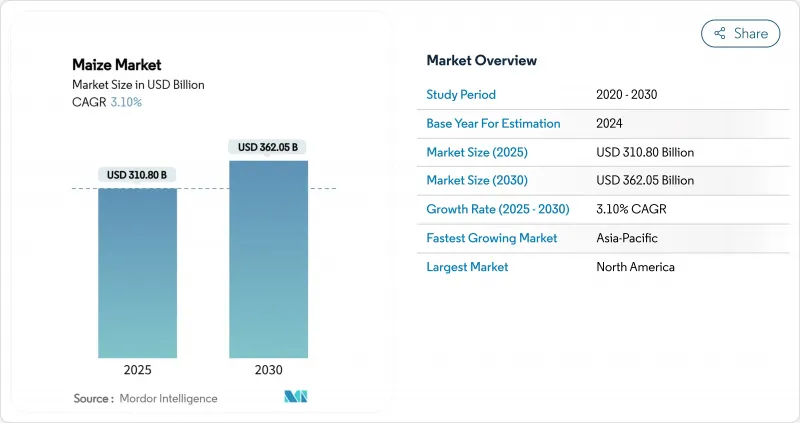
The maize market size is estimated at USD 310.80 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 362.05 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.1% during the forecast period.
Sustained demand from animal feed, biofuel blending mandates, and starch-based industrial applications underpins this momentum, even as climate volatility and trade frictions introduce short-term price swings. Structural tailwinds include the worldwide shift toward higher-protein diets, rapid innovation in high-yield hybrids, and an accelerating build-out of on-farm grain storage that improves marketing flexibility. Competitive intensity is rising as leading traders streamline portfolios and seed companies commercialize short-stature hybrids that support denser plantings and mechanized harvesting. Meanwhile, policy resolutions such as the February 2025 lifting of Mexico's biotech import ban underscore the pivotal role of trade frameworks in safeguarding uninterrupted grain flows.
Global Maize Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Animal Feed
Animal protein consumption is climbing sharply in emerging economies, and livestock rations rely on maize as the primary energy ingredient. Brazil domestic corn use jumped 53% over the past decade as meat packers scaled production, drawing 2.539 billion bushels in 2024-2025 alone. Asia's aquaculture operators are also turning to maize-based gluten meals that lower formulation costs and improve pellet stability. These parallel demand streams lift the maize market's baseline and cushion it from cyclical softness in any single end use. As urbanization and income gains continue, the maize market will capture further upside from protein-centric dietary transitions.
Growing Biofuel Blending Mandates
Mandatory blending targets anchor a sizable share of annual corn offtake, creating relatively inelastic demand in the maize market. The United States keeps ethanol production near 1.05 million barrels per day, translating to 5.5 billion bushels of corn each marketing year under the Renewable Fuel Standard. Emerging sustainable aviation fuel pathways promise additional structural demand as producers pursue Inflation Reduction Act credits through carbon-intensity reductions. Blending mandates therefore insulate portions of the maize market from short-term price gyrations while catalyzing investment in processing capacity.
Climate Change-Driven Yield Volatility
Heat waves and erratic precipitation already disrupt planting and pollination windows, pushing yield variability higher in the maize market. Research indicates each 1 °C temperature rise can shave 7.4% off global maize yields, while modeling shows the probability of crop-insurance claims in the U.S. Corn Belt could double by mid-century. Sub-Saharan countries face even steeper risks. Burkina Faso could see 40% yield losses in core growing zones under high-emission scenarios. Producers are adopting climate-smart hybrids and shifting acreage, yet extreme weather brings added costs for irrigation, crop insurance, and replanting. This volatility dampens long-term capital planning and tempers the maize market's growth trajectory.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Favorable Trade Policies and Tariff Reductions
- Rapid Build-Out of High-Capacity Grain Storage Infrastructure
- Mycotoxin Contamination Tightening Safety Rules
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The Maize Market Report is Segmented by Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa). The Report Includes Production Analysis (Volume), Consumption Analysis (Value and Volume), Export Analysis (Value and Volume), Import Analysis (Value and Volume), and Price Trend Analysis. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
Geography Analysis
North America retained a commanding 35.2% maize market share in 2024. The region's productivity edge derives from widespread precision-agriculture adoption, genetically advanced hybrids, and well-capitalized farm structures. The maize market benefits from coordinated logistics that move grain efficiently from Midwest farms to Gulf loading terminals, while policy stability around ethanol blending provides a predictable demand floor.
South America offers a contrasting picture of rapid acreage expansion coupled with infrastructure catch-up. Brazil is commissioning new corn-ethanol plants and twin-track rail lines that shorten travel times from Mato Grosso to Atlantic ports, thereby boosting farmer gate prices and reinforcing the region's competitiveness in the maize market. Brazil's domestic corn consumption climbed 53% in the past decade, supported by surging meat and ethanol sectors that collectively underpin South America's growing influence.
Asia-Pacific posted the quickest gains, and its 5.1% CAGR positions the region to widen its slice of the maize market size through 2030. Asia-Pacific's consumption outpaces local production in several populous economies, necessitating large import programs and heightened exposure to freight and basis swings. Governments respond through strategic stockpiling and targeted support for domestic hybrid seed industries. India's decision to raise corn-based ethanol procurement prices by 29% is accelerating local usage and incentivizing acreage gains. Meanwhile, storage investments across North Africa and the Middle East mitigate import-timing risks and stabilize domestic milling margins. Africa, though still a net importer, is narrowing its shortfall via yield-boosting initiatives and better post-harvest infrastructure. Europe remains supply-constrained by environmental regulations, but expanded feed-grade corn imports help bridge protein demand, underscoring the interconnected nature of the maize market.
- Market Overview
- Market Drivers
- Market Restraints
- Regulatory Landscape
- Technological Outlook
- Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- List of Stakeholders
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for animal feed
- 4.2.2 Growing biofuel blending mandates
- 4.2.3 Technological advancements in high-yield GM hybrids
- 4.2.4 Favorable trade policies and tariff reductions
- 4.2.5 Rapid build-out of high-capacity grain storage infrastructure
- 4.2.6 Booming demand for corn-based sweeteners and starches
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Climate change-driven yield volatility
- 4.3.2 Escalating fertilizer and agro-input prices
- 4.3.3 Geopolitical export restrictions and quotas
- 4.3.4 Mycotoxin contamination tightening safety rules
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Geography (Production Analysis (Volume), Consumption Analysis (Volume and Value), Import Analysis (Volume and Value), Export Analysis (Volume and Value), and Price Trend Analysis)
- 5.1.1 North America
- 5.1.1.1 United States
- 5.1.1.2 Canada
- 5.1.1.3 Mexico
- 5.1.2 South America
- 5.1.2.1 Brazil
- 5.1.2.2 Argentina
- 5.1.3 Europe
- 5.1.3.1 Spain
- 5.1.3.2 Italy
- 5.1.3.3 France
- 5.1.3.4 Germany
- 5.1.3.5 Russia
- 5.1.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.1.4.1 India
- 5.1.4.2 China
- 5.1.4.3 Vietnam
- 5.1.5 Middle East
- 5.1.5.1 Turkey
- 5.1.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.1.6 Africa
- 5.1.6.1 South Africa
- 5.1.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.1.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 List of Stakeholders
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




