PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910646

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910646
Medical Suction Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Medical Suction Devices Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 19.59 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 18.59 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 25.44 billion, growing at 5.37% CAGR over 2026-2031.
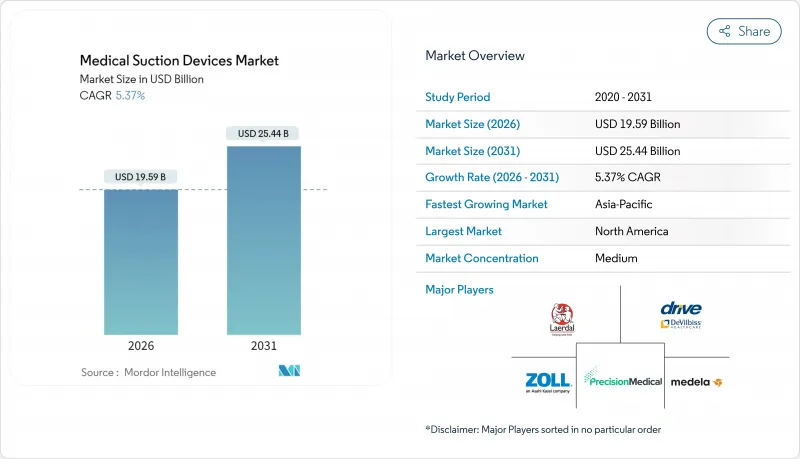
Robust demand for airway management solutions in emergency medicine, critical care, and operating rooms underpins this expansion. Battery and pump efficiency gains are enabling lighter, quieter, and more powerful portables, supporting the shift of care toward ambulatory centers and the home environment. North America retains leadership with 39.34% revenue share, aided by strict quality standards and supportive reimbursement, while Asia-Pacific posts the fastest growth at 6.97% CAGR on the back of rising surgical volumes and expanded hospital capacity. Competitive intensity remains moderate: global incumbents emphasize product differentiation through noise suppression and smart sensors, and regional manufacturers pursue cost-optimized offerings that suit price-sensitive buyers. Heightened scrutiny of single-use plastic canisters is already steering design roadmaps toward reusable or recyclable options and may create incremental compliance costs for some suppliers.
Global Medical Suction Devices Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Global Surgical Procedure Volume Driving Device Adoption
Expanding elective and trauma surgery volumes, especially minimally invasive approaches that require precise fluid evacuation to keep the field clear. Robotic and computer-assisted systems now dominate many spine, urology, and abdominal procedures, and their success hinges on medical suction devices market solutions that deliver steady negative pressure without vibration for camera stability. Surgeons also request programmable flow rates that synchronize with electrosurgical tools, reducing smoke and blood contamination. Hybrid operating rooms in leading North American hospitals routinely outfit each tower with dual high-vacuum pumps to meet these needs. Asia-Pacific facilities redeveloping cardiovascular theaters similarly standardize on multiport collectors so that perfusionists and surgeons can operate simultaneously. Manufacturers therefore integrate digital controllers that adjust vacuum within 0.1 seconds, improving hemodynamic visibility and shortening operative time.
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Respiratory Diseases Necessitating Advanced Airway Management
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and bronchiectasis continue to exert profound mortality and morbidity burdens directly expanding demand across the medical suction devices market. Acute exacerbations commonly lead to mucus hypersecretion and airway obstruction, and first-line management in emergency departments still includes aggressive suctioning. Home-based clearance regimens are equally critical: pulmonologists prescribe portable devices capable of -600 mmHg vacuum so that patients can self-manage secretions and avoid rehospitalization. Latin American public insurers piloting remote monitoring programs now reimburse for Bluetooth-enabled aspirators that relay usage patterns to respiratory therapists. These data streams help clinicians titrate bronchodilators and detect adherence gaps, further embedding suction equipment into chronic-care pathways.
High Maintenance Costs Limiting Adoption in Resource-Constrained Settings
Advanced suction pumps require routine calibration, filter replacement, and periodic servicing by trained technicians to keep vacuum performance within safe limits. These maintenance steps add recurring costs that can exceed the original purchase price over the equipment's life cycle, straining budgets in small hospitals and rural clinics. When parts or skilled labor are unavailable locally, facilities must ship devices to urban service centers, causing downtime that interrupts patient care. A U.S. Department of Homeland Security evaluation found wide variation in maintainability among portable units and noted that some models demand specialized tools that many low-resource providers do not possess. Faced with these hurdles, administrators often choose simpler manual devices or postpone upgrades, slowing penetration of modern systems in emerging markets and moderating growth of the medical suction devices market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Home Healthcare Adoption Accelerating Portable Device Innovation
- Stringent Infection-Control Regulations Driving Closed-System Adoption
- Reimbursement Limitations Creating Market Access Barriers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The AC-powered class generated 44.52% of the medical suction devices market share in 2025, retaining primacy because surgical and intensive-care teams cannot tolerate runtime limits. In tertiary hospitals expanding neurosurgical suites across India and China, installers continue to favor wall-outlet units rated to -750 mmHg sustained vacuum with dual-pump redundancy. The medical suction devices market size for AC-powered models is projected to grow from USD 8.27 billion in 2025 to USD 12.11 billion by 2031 at 6.55% CAGR, reflecting the parallel construction of higher-acuity beds.
Battery-powered systems, while smaller today, are winning preference among ambulance operators aiming for ergonomic upgrades. The AIRO Suction Unit weighs 0.9 kg yet holds charge for 30 minutes of peak draw. Emergency medical technicians note 24% faster scene turnover because disposable hydrophobic filters reduce post-use cleanup. Manufacturers now bundle USB-C fast-charge adaptors so devices recharge during transfer to hospitals, aligning with international EMS asset-tracking protocols that log battery cycles.
Wall-mounted systems maintained 45.48% of the medical suction devices market size in 2025 owing to embedded installation across operating rooms, birthing centers, and ICUs. Retrofit programs in U.S. community hospitals are upgrading analog gauges to digital LEDs that alert staff when negative pressure dips below set points. Simultaneously, ventilation specialists adjust flows remotely from central dashboards, enhancing responsiveness during high census periods.
Conversely, the hand-held/portable segment is forecast to post an 7.84% CAGR through 2031, reflecting paramedic and home-care demand for compact tools. The NAR Tactical Suction Device produces 100 mmHg vacuum via pistol-grip pump and weighs under 400 g, facilitating single-handed airway clearance in confined spaces. Asia-Pacific humanitarian agencies routinely keep such devices in disaster kits due to minimal maintenance requirements and absence of electrical components, a factor accelerating unit sales during cyclone and flood seasons.
The Medical Suction Devices Market Report is Segmented by Type (AC-Powered, Battery-Powered, and More), Portability (Hand-Held/Portable, Wall-Mounted, and Trolley/Cart-Mounted), Application (Airway Clearance, Surgical Applications, and More), End User (Hospitals, Home Healthcare Settings, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America leads with 39.12% revenue thanks to rigorous standards that require continuous suction availability at every critical bed. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services reimburse 80.0% of DME invoice amounts after deductibles, widening access to portable pumps for home ventilator users. U.S. ambulance services upgrading fleets under federal grants are standardizing on lithium-battery units that integrate with onboard telematics, further expanding the regional installed base.
Asia-Pacific is projected to record a 6.91% CAGR through 2031. The Indian Production Linked Incentive scheme offers 5%-10% subsidies on domestic suction equipment, spurring plant investments in Andhra Pradesh MedTech. China's county-level trauma centers add dedicated ENT suites, each requiring dual vacuum regulators, boosting volume throughput for local assemblers. Japan faces rapidly aging demographics; municipal health insurers thus fund portable aspirators for at-home COPD management, supporting premium-priced models with HEPA exhaust.
Europe maintains strong demand, driven by environmental regulation that penalizes PVC waste and encourages polypropylene canisters with integrated solidifiers. German hospitals adopting closed-liner systems reduced staff exposure incidents by 23.0%, accelerating tender conversions. United Kingdom NHS trusts emphasize sustainability, favoring pumps with recyclable housings and energy-saving standby modes.
Middle East & Africa offers mixed prospects: Gulf Cooperation Council states import high-specification devices for new trauma centers, while sub-Saharan regions prioritize rugged battery-free pumps to offset grid unreliability. South America's moderate expansion is led by Brazil, where public-private partnerships fund surgical capacity growth in state hospitals, driving upgrades from manual foot-operated to electric units.
- Laerdal Medical AS
- Labconco
- ZOLL Medical Corporation (Asahi Kasei)
- Precision Medical
- Medela
- Amsino International
- Integra Biosciences AG
- Olympus
- Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare
- MG Electric Ltd.
- Allied Healthcare Products
- ATMOS MedizinTechnik
- Smiths Group
- Cardinal Health
- Pennine Healthcare
- Ambu
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Global Surgical Procedure Volume, Especially MIS
- 4.2.2 Rising Prevalence of Chronic Respiratory Diseases Requiring Long-term Airway Management
- 4.2.3 Growing Adoption of Home Healthcare & Telemedicine Boosting Portable Device Demand
- 4.2.4 Stringent Infection-Control Regulations Mandating Closed Canister Systems
- 4.2.5 Advances in Battery & Pump Efficiency Enabling High-Performance Portables
- 4.2.6 Expansion of EMS Infrastructure and Ambulance Fleet Modernization Worldwide
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Maintenance and Calibration Costs in Low-Resource Settings
- 4.3.2 Reimbursement Limitations for Capital Equipment in Ambulatory & Home Care
- 4.3.3 Availability of Alternative Airway-Clearance Methods Reducing Device Utilization
- 4.3.4 Environmental & Disposal Concerns over Single-Use Plastic Canisters
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 AC-Powered
- 5.1.2 Battery-Powered
- 5.1.3 Dual (AC & Battery) Powered
- 5.1.4 Manually Operated
- 5.2 By Portability
- 5.2.1 Hand-Held / Portable
- 5.2.2 Wall-Mounted
- 5.2.3 Trolley / Cart-Mounted
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Airway Clearance
- 5.3.2 Surgical Applications
- 5.3.3 Obstetrics & Gynecology
- 5.3.4 Research & Diagnostics
- 5.3.5 Other Applications
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Home Healthcare Settings
- 5.4.3 Dental Clinics
- 5.4.4 Other End Users
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Laerdal Medical AS
- 6.4.2 Labconco Corporation
- 6.4.3 ZOLL Medical Corporation (Asahi Kasei)
- 6.4.4 Precision Medical Inc.
- 6.4.5 Medela AG
- 6.4.6 Amsino International Inc.
- 6.4.7 Integra Biosciences AG
- 6.4.8 Olympus Corporation
- 6.4.9 Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare
- 6.4.10 MG Electric Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Allied Healthcare Products Inc.
- 6.4.12 ATMOS MedizinTechnik GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.13 Smiths Medical (ICU Medical)
- 6.4.14 Cardinal Health Inc.
- 6.4.15 Pennine Healthcare
- 6.4.16 Ambu A/S
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




