PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1852204

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1852204
Molecular Breeding - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
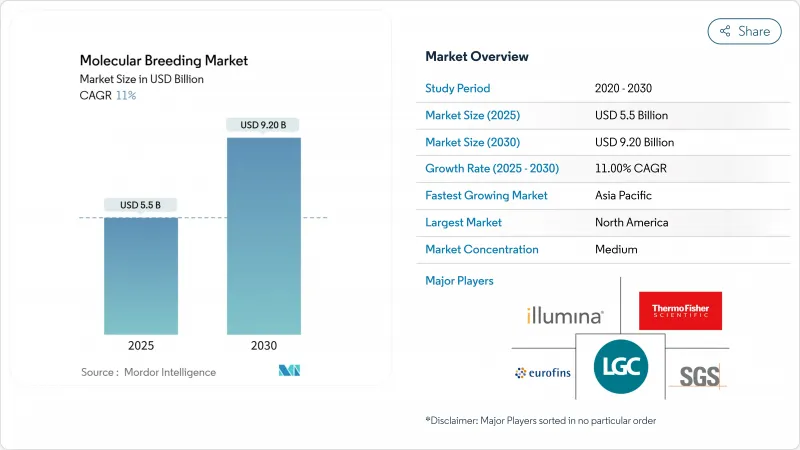
The molecular breeding market attained USD 5.5 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 9.2 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 11.0%.
The incorporation of artificial intelligence with genomic selection has reduced breeding cycles from years to months, enhancing product development efficiency. Government initiatives, including the U.S. Vision for Adapted Crops and Soils and India's National Action Plan on Food Security, are driving demand for climate-resilient crop varieties. Market expansion is facilitated by high-throughput phenotyping, decreased sequencing costs, and accessible genotyping services. While North America retains its advantage in research infrastructure, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates substantial growth potential due to regulatory reforms and food security requirements.
Global Molecular Breeding Market Trends and Insights
Expanding Biotechnology Research and Development Funding
Private and public spending in the market is increasing rapidly. Thermo Fisher invested USD 1.3 billion in research and development in 2023 to advance next-generation sequencing and reagent innovation, reducing entry costs for midsized breeders. The U.S. Department of Agriculture's data-standards programs are harmonizing genomic datasets, preventing redundant trials, and reducing time-to-market. These capital investments have decreased compliance barriers for smaller firms, enabling novel trait developers to navigate regulatory requirements. Additionally, multilateral initiatives, such as CGIAR's USD 400 million nutrition-focused portfolio, are attracting donor funds and accelerating biofortification outcomes.
Growing Demand for High-Yield, Climate-Resilient Crops
India's release of 100-day wheat varieties capable of withstanding record temperatures has enabled heat- and drought-tolerant genotypes to advance from pilot to commercial scale. Japanese research centers are developing quinoa and soybean varieties adapted to saline and water-stress conditions to maintain production levels in climate-vulnerable countries. Plant breeding priorities now extend beyond yield optimization to include multistress tolerance, necessitating the use of multiplexed molecular markers that integrate productivity with environmental resilience. The financial implications are significant, as extreme weather events currently cause crop losses worth billions of USD per season, increasing the return on investment for climate-resilient seed portfolios.
Stringent, Slow-Moving Regulatory Approvals
The compliance cost per new trait can reach USD 15 million, consuming approximately half of the total development budgets and deterring smaller innovators. The European Union's regulation of gene-edited crops under GMO legislation drives companies to focus on markets with favorable regulations, such as the United States and Brazil. While Argentina, Uruguay, and Thailand updated their regulations in 2024 to simplify approvals, regulatory uncertainty continues to extend timelines and increase financing costs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid Adoption of Precision Breeding and Phenotyping Platforms
- Government-Backed Food Security Initiatives
- High Capital Cost of Sequencing and Genotyping Infrastructure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Plant applications accounted for 63% of the molecular breeding market in 2024, primarily through genomic selection implementation in maize, wheat, and soybean breeding programs. The livestock segment is experiencing growth at a 13.1% CAGR, driven by genomic breeding values that demonstrate superior performance compared to traditional estimates in dairy cattle and CRISPR-based disease-resistant pig development. Tools such as Angus SteerSELECT have demonstrated prediction accuracies exceeding 0.72 for critical carcass traits, enhancing feedlot profitability and attracting investment.
The poultry sector is implementing precision editing of fertility and growth genes to reduce generation intervals. Furthermore, integrated metabolomic and genomic models in swine breeding demonstrate potential for improving average daily gain, despite current modest outcomes. These developments indicate that the livestock segment may substantially increase its contribution to the molecular breeding market by 2030.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) accounted for 42% of the molecular breeding market size in 2024 and maintain a 13.2% CAGR due to their compatibility with high-throughput platforms and enhanced genome-wide association outputs. The reduction in unit costs has diminished the price advantage previously held by simple sequence repeats, prompting developing-country programs to adopt SNP solutions directly. The implementation of functional-variant panels from RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data has improved breeding accuracies by 3 percentage points in dairy-protein traits, demonstrating the technology's reliability.
The standardization of SNP workflows has positioned express sequence tags and other traditional markers primarily in specialized applications such as expression profiling. The increased adoption of SNPs enhances data interoperability, which is fundamental for developing AI-enabled breeding systems.
The Molecular Breeding Market Report is Segmented by Application (Plant, Livestock, and More), by Marker Type (Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR), and More), by Breeding Process (Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS), and More), by Trait Target (Yield Enhancement, and More), by End-User (Seed and Crop-Protection Companies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America holds 36% of the molecular breeding market share in 2024, supported by advanced research infrastructure and efficient regulatory frameworks. Illumina reported USD 4.33 billion revenue in 2024 and has partnered with LGC Biosearch Technologies to increase targeted genotyping-by-sequencing capabilities for row-crop and livestock segments. The USDA's SECURE rule streamlines the approval process for gene-edited products, maintaining the region's market leadership.
Asia-Pacific demonstrates the highest growth potential with a projected 12.1% CAGR through 2030. China approved disease-resistant gene-edited wheat in 2024, while India's regulatory updates streamline approvals for specific genome edits, accelerating private breeding initiatives. Japan's tiered regulatory system and focus on crop-stress research establishes it as a key regional hub. The combination of government funding and private venture capital is strengthening the region's breeding infrastructure to address food security needs.
Europe maintains significant market presence despite regulatory constraints. The EU Environment Committee's approval of new genomic technology legislation in late 2024 indicates movement toward risk-based assessment. The UK implemented the Precision Breeding Act, establishing a two-tier safety review system to expedite gene-edited crop trials. Switzerland is implementing similar regulatory changes. Market growth depends on policy developments, with substantial demand for varieties meeting European Green Deal sustainability requirements.
- Illumina, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- LGC Limited (Cinven)
- Eurofins Scientific
- SGS SA
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- DanBred P/S
- LemnaTec GmbH (Nynomic AG)
- Charles River Laboratories
- Intertek Group plc
- KeyGene NV
- Syngenta AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- Bayer AG
- BASF SE
- Sequentia Biotech SL
- Hudson Alpha
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expanding Biotechnology Research and Development Funding
- 4.2.2 Growing Demand for High-Yield, Climate-Resilient Crops
- 4.2.3 Rapid Adoption of Precision Breeding and Phenotyping Platforms
- 4.2.4 Government-Backed Food Security Initiatives
- 4.2.5 Convergence of AI and Genomic Selection
- 4.2.6 Carbon-Credit Incentives for Low-Input Cultivars
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent, Slow-Moving Regulatory Approvals
- 4.3.2 High Capital Cost of Sequencing and Genotyping Infrastructure
- 4.3.3 Limited Breeder Access to Interoperable Data Platforms
- 4.3.4 Public Perception Concerns Over "Molecular-Modified" Seeds
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Plant
- 5.1.2 Livestock
- 5.1.3 Other Application
- 5.2 By Marker Type
- 5.2.1 Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR)
- 5.2.2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP)
- 5.2.3 Expressed Sequence Tags (EST)
- 5.2.4 Other Markers
- 5.3 By Breeding Process
- 5.3.1 Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS)
- 5.3.2 Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping
- 5.3.3 Marker-Assisted Back-Crossing
- 5.3.4 Genomic Selection
- 5.4 By Trait Target
- 5.4.1 Yield Enhancement
- 5.4.2 Disease and Pest Resistance
- 5.4.3 Abiotic Stress Tolerance
- 5.4.4 Quality and Nutritional Traits
- 5.5 By End-User
- 5.5.1 Seed and Crop-Protection Companies
- 5.5.2 Livestock Breeding Firms
- 5.5.3 Academic and Government Research Institutes
- 5.5.4 Independent Breeding Service Providers
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Russia
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Illumina, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.3 LGC Limited (Cinven)
- 6.4.4 Eurofins Scientific
- 6.4.5 SGS SA
- 6.4.6 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.7 DanBred P/S
- 6.4.8 LemnaTec GmbH (Nynomic AG)
- 6.4.9 Charles River Laboratories
- 6.4.10 Intertek Group plc
- 6.4.11 KeyGene NV
- 6.4.12 Syngenta AG
- 6.4.13 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.14 Bayer AG
- 6.4.15 BASF SE
- 6.4.16 Sequentia Biotech SL
- 6.4.17 Hudson Alpha
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




