PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906129

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906129
Rocket Propulsion - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The rocket propulsion market was valued at USD 6.99 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 7.48 billion in 2026 to reach USD 10.48 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 6.98% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
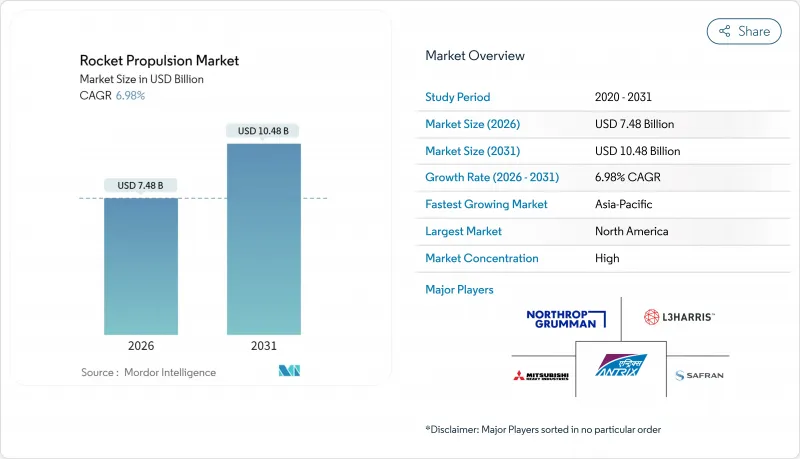
Cost savings from reusable launch systems, the cadence required for mega-constellation roll-outs, and stepped-up defense spending collectively reshape demand and supply priorities. Liquid engines retain primacy because their higher specific impulse and throttling precision enable accurate orbital insertions. Yet, hybrid solutions are gaining traction as manufacturers seek lower-cost blends of liquid and solid technologies. North America currently dominates the volume, but the Asia-Pacific region shows the steepest trajectory as China and India expand their launch infrastructure. Across the ecosystem, additive manufacturing cuts component counts by up to 98%, redirecting competitive advantage toward vertically integrated producers with in-house printers.
Global Rocket Propulsion Market Trends and Insights
Reusable Launch Vehicle Economics
Successful booster recovery programs, such as Falcon 9, have already cut launch costs by more than 50% and shifted propulsion priorities toward rapid refurbishment rather than single-use, peak performance. Engines now require robust turbopumps, advanced chamber cooling, and built-in health-monitoring sensors, allowing turn-time between flights to drop from months to days. Manufacturers respond with modular subsystems that technicians can swap on the pad, a design philosophy spilling over to satellite propulsion, where constellation operators benefit from lower deployment budgets. The economic ripple encourages smaller launch providers to enter the market with reusable micro-launchers. Component suppliers consequently invest in high-cycle fatigue testing and automated non-destructive inspection lines to validate re-flown hardware within compressed schedules.
Rapid Mini-sat and Mega-constellation Deployment
Constellation plans involving thousands of spacecraft force propulsion factories to scale well beyond historic lot sizes. High-rate upper-stage engine production supports steady weekly launch rhythms, while electric thrusters for in-orbit station-keeping move toward automotive-style production cells. Standardized engine families reduce qualification burdens and enable multi-launch contracts that secure bulk pricing. Satellite makers simultaneously request propellant combinations with fewer ground-handling hazards to streamline integration flows. The boom fuels secondary demand for test stands, cryogenic storage tanks, and avionics, creating an expansive industrial loop that maintains high capacity utilization across the rocket propulsion market.
Cryogenic Supply Chain Bottlenecks
Liquid-hydrogen (LH2) and liquid-oxygen (LOX) production have not kept pace with launch tempo, causing scheduling conflicts at shared pads and driving demand for costly mobile storage farms. Smaller launch companies feel the pinch most acutely because existing suppliers prioritize high-volume anchor customers. Infrastructure expansion often faces lengthy permitting timelines and scrutiny from local communities. Boil-off losses translate to stranded costs and emissions that conflict with emerging environmental regulations, prompting some operators to consider methane or green monopropellants. Until production capacity catches up, propulsion scheduling flexibility will continue to be a competitive differentiator.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Deep-space and Lunar-mission Funding Spike
- Hypersonic-Weapons Propulsion Race
- Stringent Export-control Regimes (ITAR, MTCR)
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Liquid engines captured 63.22% of the rocket propulsion market share in 2025 and are expected to hold leadership as the segment's inherent throttling accuracy remains indispensable for precise orbital insertions. Innovations such as 3D-printed copper chambers reduce part counts by 98%, significantly slashing build times and costs. Hybrid propulsion, however, is projected to grow at a 8.91% CAGR, aligning with new launchers that blend solid fuel grains and liquid oxidizers to balance simplicity with restart capability. Solid motors remain relevant for tactical missiles and long-term storage needs, where shelf-life reliability takes precedence over specific impulse.
The rocket propulsion market continually rebalances as methane-oxygen combinations gain favor for their lower toxicity and ease of reloading on reusable stages. Hybrid engines utilize advanced swirl injectors to enhance combustion efficiency, while solid motors benefit from high-energy propellant chemistries that extend range without increasing airframe size. Liquid systems also utilize closed-cycle turbopumps fabricated through additive manufacturing, which reduces mass and improves thrust-to-weight ratios. Regulatory pushes toward cleaner emissions will further elevate green bipropellants, giving liquid suppliers a head start in certification pathways.
Civil and commercial customers maintained 58.95% of the rocket propulsion market size in 2025, yet military and government programs exhibit an 7.86% CAGR that now outpaces the broader market. Hypersonic glide vehicles, missile defense interceptors, and responsive-space initiatives consume large numbers of solid motors and upper-stage engines. Defense budgets favor contractors that can stand up surge lines during crises, prompting investments in modular plants across Virginia, Arkansas, and Alabama.
Commercial operators, meanwhile, focus on cost per kilogram and launch cadence. Their procurement policies reward engine families offering commonality across multiple vehicle classes. Government agencies remain pivotal to technology breakthroughs, underwriting nuclear-electric and nuclear-thermal demonstrations that will ultimately benefit commercial deep-space logistics. As defense customers prioritize robustness against peer threats, propulsion makers must partition product lines to meet divergent durability versus affordability benchmarks within the rocket propulsion market.
The Rocket Propulsion Market Report is Segmented by Propulsion Type (Solid, Liquid, and Hybrid), End User (Civil and Commercial, and Military and Government), Component (Motor Casing, Nozzle, Propellant, and Other Components), Type (Rocket Motor and Rocket Engine), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America commands the largest slice of revenue, driven by mature manufacturing clusters and substantial US Department of Defense (DoD) outlays. L3Harris's new facilities aim to produce 25,000 solid rocket motors annually by 2029, ensuring sufficient inventory for both strategic missiles and interceptors. SpaceX's vertically integrated engine lines in California and Texas exemplify cost efficiencies that ripple through the launch services value chain. Export-control regimes concentrate advanced know-how inside domestic borders, sustaining high utilization rates for US test stands and cryogenic suppliers.
The Asia-Pacific region exhibits the fastest growth, underpinned by China's state-backed launch manifest and India's deregulated space economy, which opens orbital slots to private operators. Indigenous propulsion start-ups benefit from government procurement quotas that favor homegrown technology. Australia has begun seeding composite-motor research centers, and Japan directs R&D subsidies toward high-strength ceramic matrix nozzles. The regional race for capacity also triggers cooperative agreements on liquid-oxygen plants and test ranges, distributing investment across multiple nations.
Europe maintains a diversified supplier base that prioritizes environmental stewardship. ArianeGroup's shift toward recoverable stages dovetails with EU climate directives, positioning methalox and green monopropellants as differentiators. National agencies in France and Germany co-fund additive-manufacturing centers to strengthen autonomy from non-EU metals. Smaller European states participate via subsystem specialization, supplying valves and sensors for large engine families. Although launch volume remains modest compared to North America, the continent's emphasis on advanced materials and stringent certification standards allows premium pricing.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- Safran SA
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- IHI Corporation
- Antrix Corporation Limited
- Ursa Major Technologies, Inc.
- Avio S.p.A (General Electric Company)
- Thales Alenia Space (Thales Group)
- Relativity Space, Inc.
- ABL Space Systems
- Moog Inc.
- Busek Co. Inc.
- HyImpulse Technologies GmbH
- Exotrail
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Reusable launch vehicle economics
- 4.2.2 Rapid mini-sat and mega-constellation deployment
- 4.2.3 Government deep-space and lunar-mission funding spike
- 4.2.4 Hypersonic weapons propulsion race
- 4.2.5 Additive manufacturing cost breakthroughs
- 4.2.6 Methalox and green-propellant adoption push
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cryogenic-supply-chain bottlenecks
- 4.3.2 Stringent export-control regimes (ITAR, MTCR)
- 4.3.3 Solid propellant raw-material shortages
- 4.3.4 Infrastructure limitations in emerging space nations
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Propulsion Type
- 5.1.1 Solid
- 5.1.2 Liquid
- 5.1.3 Hybrid
- 5.2 By End User
- 5.2.1 Civil and Commercial
- 5.2.2 Military and Government
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Motor Casing
- 5.3.2 Nozzle
- 5.3.3 Propellant
- 5.3.4 Other Components
- 5.4 By Type
- 5.4.1 Rocket Motor
- 5.4.2 Rocket Engine
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 Germany
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.3 Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.4 Safran SA
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- 6.4.7 IHI Corporation
- 6.4.8 Antrix Corporation Limited
- 6.4.9 Ursa Major Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.10 Avio S.p.A (General Electric Company)
- 6.4.11 Thales Alenia Space (Thales Group)
- 6.4.12 Relativity Space, Inc.
- 6.4.13 ABL Space Systems
- 6.4.14 Moog Inc.
- 6.4.15 Busek Co. Inc.
- 6.4.16 HyImpulse Technologies GmbH
- 6.4.17 Exotrail
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




