PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906137

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906137
RF Components - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The RF components market was valued at USD 44.41 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 50.07 billion in 2026 to reach USD 91.19 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 12.74% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
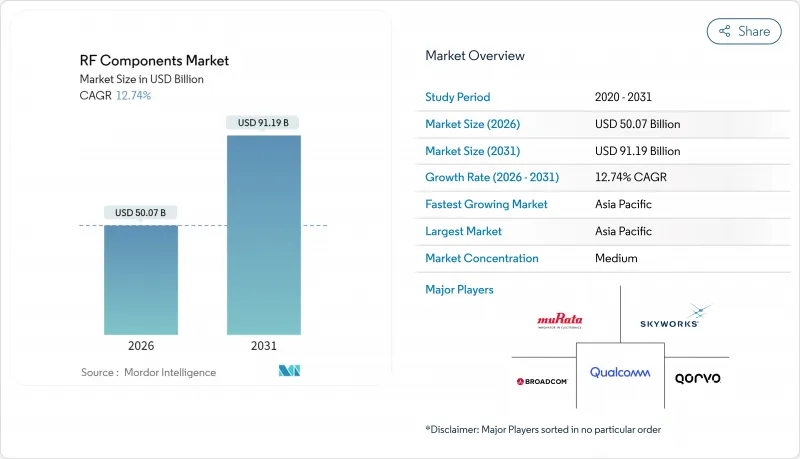
The growth path reflects surging deployments of 5G base stations, radar-centric autonomous vehicles, and space-based communications platforms. Government programs that localize semiconductor supply chains, breakthroughs in frequencies above 40 GHz, and rising content per smartphone collectively reinforce demand momentum. Competitive strategies emphasize vertical integration, AI-assisted design automation, and advanced thermal packaging, opening opportunities for suppliers able to balance performance and cost while navigating geopolitical headwinds. The RF components market also benefits from policy-driven investments in Open RAN, low-Earth-orbit (LEO) constellations, and edge-AI industrial automation, all of which require frequency-agile, power-efficient architectures.
Global RF Components Market Trends and Insights
5G Infrastructure Densification Drives Macro-Cell RF Dem
Mobile operators continue to densify 5G macro-cell networks, requiring high-efficiency power amplifiers, low-loss filters, and beam-steering switches that can withstand elevated thermal loads. The strategy is reinforced by Open RAN programs, notably the USD 450 million Public Wireless Supply Chain Innovation Fund, which incentivizes multi-vendor interoperability software-defined architectures. Partnerships, such as MaxLinear RFHIC's 55.2% efficiency GaN power amplifier, underline the focus on energy savings for large-scale deployments. As macro cells deliver higher power than small cells, suppliers with a mature GaN process gain a competitive edge. Policy support through 2027 ensures sustained demand, giving the RF components market a strong anchor for mid-term revenue visibility.
Automotive Radar Integration Accelerates V2X Ecosystem Development
Each Level-3-ready vehicle now features multiple 77-81 GHz radar sensors, alongside dedicated V2X transceivers, which doubles the RF content per unit compared to 2023 models. North American and European regulators require advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to meet functional safety norms, nudging OEMs toward fully qualified automotive-grade RF suppliers. ISO 26262 certification and FCC Part 15 compliance further restrict sourcing to vendors with proven reliability records. The dual use of radar and V2X intensifies design complexity, increasing demand for integrated front-end modules that balance isolation and coexistence. Lead times for high-Q dielectric materials remain elevated, posing short-term supply risks yet reinforcing premium pricing for qualified inventories.
High CAPEX Requirements Limit GaN/GaAs Fab Expansion
A new compound-semiconductor line can cost USD 2-5 billion, underscored by TSMC's Arizona outlay that eclipses USD 165 billion when fully built. Even with CHIPS Act incentives, smaller entrants struggle to secure financing for molecular-beam epitaxy MOCVD tools. MACOM's USD 180 million expansion, subsidized by federal backing, illustrates how government aid can offset but not erase capital hurdles. The multiyear build--qualify cycle delays market entry, encouraging consolidation, and favoring incumbents with depreciated assets.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Space Funding Catalyzes LEO Constellation RF Innovation
- mmWave Thermal Management Creates Technical Differentiation
- Shortage of High-Q Dielectric Materials Constrains Production
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Power amplifiers generated the largest slice of the RF components market in 2025, accounting for USD 16.23 billion. Their entrenched role in macro-cell radios, radar modules, home-gateway equipment anchors volume demand, even as efficiency mates intensify. Meanwhile, RF tunable devices compound at 13.74% annually through 2031. Enterprises adopt these components to enable seamless cross-b transition, especially in Open RAN LEO terminals, where software-defined architectures streamline network upgrades. Qualcomm's X85 modem-RF platform integrates an AI engine that dynamically tunes filters and switches, highlighting the march toward smarter front ends. Suppliers that merge power amps, low-noise amps, and tuners into single modules help customers shrink board area while easing thermal budgets, a trend visible in Qorvo's latest Wi-Fi 7 front-end modules.
Second-order effects reinforce this trajectory. Higher-order MIMO topologies in 5G NR Release 18 boost the number of signal paths per base station, multiplying power-amplifier sockets even when per-path wattage tapers. In smartphones, antenna-switch multiplexing rises with 5G STBY modes that leverage non-contiguous carrier aggregation, driving RF switch shipments. Integrated filter-switch banks support coexistence across Sub-6 GHz spectra, preserving linearity while containing BOM costs.
The Sub-6 GHz domain still owns 62.10% of the RF components market share thanks to the sheer footprint of LTE early 5G radios. However, the 40-100 GHz band grows the fastest at a 13.63% CAGR, favored by enterprise fixed-wireless access (FWA), backhaul links, and emerging 6G research corridors. NTIA's public consultation on 6G use cases underscores governmental intent to leverage these higher bands for next-generation gigabit services. Suppliers adept at thermal-conscious packaging position themselves to capitalize on this incremental wave. The 24-40 GHz class observes steady, yet slower, adoption in dense urban mmWave 5G-thermal design, siting logistics, and backhaul costs temper mass rollout velocity.
Technical maturation drives competitive behavior. Beam-steering ICs with embedded phase shifters shrink the antenna aperture needed for data-center roof links, while GaN-on-SiC power amplifiers unlock higher EIRP at manageable drain voltages. Regulatory alignment, such as the FCC's millimeter-wave service rules, fosters certainty but still demands sophisticated coexistence management with satellite incumbents.
The RF Components Market Report is Segmented by Component Type (Power Amplifiers, RF Filters, Antenna Switches, and More), Frequency Band (Sub-6 GHz, 6-24 GHz, and More), Semiconductor Material (GaAs, Silicon, Gan, Sige), End-User Industry (Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, Automotive, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2025, Asia-Pacific dominated the RF components market, claiming a 55.85% share. This surge was largely fueled by the inauguration of 18 new fabs in China alone. Government subsidies have effectively reduced unit costs, and the region's proximity to key OEMs has bolstered visibility. While South Korea and Japan continue to lead in substrate materials and filter ceramics, Taiwan's foundries are at the forefront, providing advanced packaging for multichip modules. India's push for 5G, backed by the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, is drawing backend assembly operations, though the country currently lacks a significant wafer-fab scale. Even with rising trade restrictions, Asia-Pacific's cost advantages ensure it anchors over half of the global shipments for the foreseeable decade.
North America is riding the wave of the CHIPS Act. TSMC's facility in Arizona is not only introducing 4-nanometer class processes but also bringing advanced RF packaging closer to U.S. clients. This move significantly reduces logistics risks, bolstering the security of defense supply chains. Additionally, federal grants amounting to USD 117 million, sourced from the wireless innovation fund, are championing domestic Open RAN radio development, steering business towards American RF specialists. While Canada is upgrading its telco infrastructure for mid-band 5G, it predominantly relies on U.S. component imports. Meanwhile, Mexico's EMS sector is capitalizing on low-cost assembly contracts for customer premises equipment (CPE) devices. Europe, eyeing a 20% share of the global semiconductor market by 2030, is positioning itself for strategic autonomy through the European Chips Act. In Germany and France, automotive OEM clusters are anchoring radar modules to meet Euro NCAP safety standards, boosting local fab utilization. The UK's GBP 16 million LEO program is backing Ka-band component R&D, nurturing a nascent space supply chain. Nordic nations are experimenting with millimeter-wave fixed wireless access for rural broadband, procuring GaN front-end equipment from U.S. and Japanese suppliers. However, regulatory challenges, such as the REACH chemistry rules, are extending part qualification cycles, inadvertently benefiting established players with a history of European compliance.
- Broadcom Inc.
- Skyworks Solutions Inc.
- Qorvo Inc.
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- Qualcomm Incorporated
- Analog Devices, Inc.
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Renesas Electronics Corporation
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Cree Wolfspeed Inc.
- Knowles Corporation
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- MediaTek Inc.
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- Teledyne Technologies Incorporated
- Cobham Advanced Electronic Solutions
- Amphenol RF Division
- Airgain Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 5G infrastructure densification
- 4.2.2 Surge in RF front-end content per smartphone
- 4.2.3 Rising automotive radar and V2X deployments
- 4.2.4 Government funding for Space and LEO constellations
- 4.2.5 Rapid adoption of RF energy-harvesting PMICs
- 4.2.6 Edge-AI mmWave sensing in smart-factory cobots
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX for GaN/GaAs wafer fabs
- 4.3.2 Thermal-management challenges above 28 GHz
- 4.3.3 Export-control tightening on ultra-wideband chips
- 4.3.4 Shortage of high-Q dielectric materials
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Pricing Analysis
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Component Type
- 5.1.1 Power Amplifiers
- 5.1.2 RF Filters
- 5.1.3 Antenna Switches
- 5.1.4 Low-Noise Amplifiers
- 5.1.5 RF Tunable Devices
- 5.2 By Frequency Band
- 5.2.1 Sub-6 GHz
- 5.2.2 6-24 GHz (C/X/Ku)
- 5.2.3 24-40 GHz (mmWave 1)
- 5.2.4 40-100 GHz (mmWave 2)
- 5.3 By Semiconductor Material
- 5.3.1 Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
- 5.3.2 Silicon (CMOS/SOI)
- 5.3.3 Gallium Nitride (GaN)
- 5.3.4 Silicon-Germanium (SiGe)
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.2 Telecommunication
- 5.4.3 Automotive
- 5.4.4 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.4.5 Industrial Automation
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 South Korea
- 5.5.4.4 India
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.6 Africa
- 5.5.6.1 South Africa
- 5.5.6.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Broadcom Inc.
- 6.4.2 Skyworks Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.3 Qorvo Inc.
- 6.4.4 Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- 6.4.6 Qualcomm Incorporated
- 6.4.7 Analog Devices, Inc.
- 6.4.8 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 6.4.9 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.10 Renesas Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.11 Infineon Technologies AG
- 6.4.12 Cree Wolfspeed Inc.
- 6.4.13 Knowles Corporation
- 6.4.14 Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- 6.4.15 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 MediaTek Inc.
- 6.4.17 ON Semiconductor Corporation
- 6.4.18 Teledyne Technologies Incorporated
- 6.4.19 Cobham Advanced Electronic Solutions
- 6.4.20 Amphenol RF Division
- 6.4.21 Airgain Inc.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




