PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906147

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906147
Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Market was valued at 19.27 Million tons in 2025 and estimated to grow from 19.83 Million tons in 2026 to reach 22.89 Million tons by 2031, at a CAGR of 2.92% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
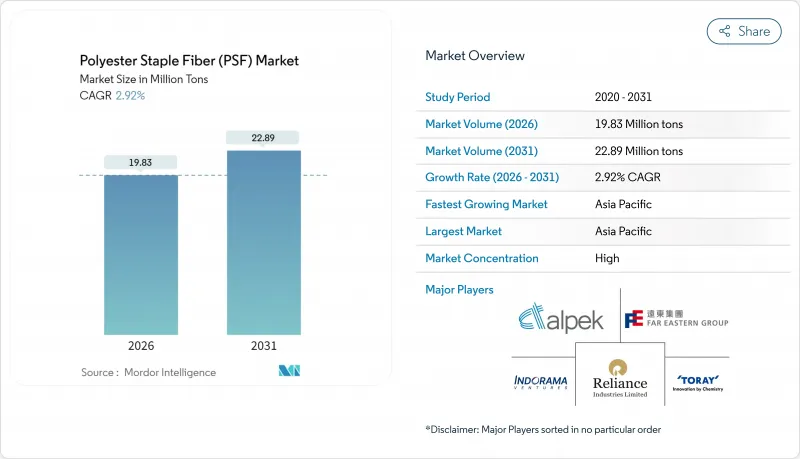
This steady rise mirrors the material's expanding footprint in apparel, home furnishings, non-woven hygiene products, automotive noise-control parts, and a growing range of technical uses. Rising demand for cost-effective synthetics, the structural shift away from cotton, and investment in closed-loop recycling are reinforcing the market's resilience even as oil-linked raw-material costs and trade barriers add volatility. Competition is intensifying around recycled grades as global fashion retailers, automakers, and hygiene converters move sustainability spending downstream into fiber supply contracts. Producers able to blend scale, chemistry innovation, and traceable feedstocks are positioned to strengthen margins over the decade.
Global Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Market Trends and Insights
Surge in Demand for Recycled PSF from Fast-Fashion Brands
Mounting consumer scrutiny and new European Digital Product Passports are compelling global retailers to replace virgin polyester with textile-to-textile recycled alternatives. H&M has committed USD 600 million to Syre for closed-loop polymer regeneration, signalling a permanent shift away from bottle-based feedstock. Shein has introduced a proprietary depolymerisation process and intends to license it to partner mills once pilot output scales to 3,000 tons per year. Brands are also locking multi-year offtake agreements, which is tightening supply of high-quality recycled staple and encouraging expansion of advanced chemical recycling hubs in Europe and Asia. As traceability becomes non-negotiable, fiber producers able to validate chain-of-custody data stand to win long-term volume contracts and price premiums, lifting overall growth in the polyester staple fiber market.
Substitution of Cotton with Polyester amid Price Volatility
Persistent swings in cotton prices have sharpened apparel makers' focus on synthetic alternatives that guarantee predictable cost and supply. USDA's 2024 and 25 outlook shows U.S. mill cotton use at multi-year lows even as global cotton crops rise, underscoring polyester's relative economic security. Fiber converters are capturing share in denim blends, athleisure and mass-market fashion by offering polyester yarns that mimic cotton's hand feel while resisting shrinkage. The shift is most pronounced in India and China where fabric mills are scaling draw-texturised yarn lines dedicated to knitted t-shirt and polo production. This structural migration lifts baseline demand, underpinning the polyester staple fiber market through 2030.
Raw-Material Price Volatility Linked to Crude-Oil Swings
Paraxylene and PTA prices mirror Brent movements, exposing polyester economics to energy market turbulence. In 2024 North American PX traded at premiums to Asia because of refinery dynamics referred to as the "gasoline effect," widening delivered-cost gaps. Although Sinopec's 3 million-ton PTA unit in Jiangsu eases supply pressure, price spikes compel fiber makers to juggle inventory cover and hedging, often deferring capacity upgrades when margins compress. Volatility therefore subtracts an estimated 0.6 percentage points from the polyester staple fiber market CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Urbanisation-Led Home-Textile Boom in India & China
- Growth of Lightweight NVH Automotive Components
- Anti-Dumping Duties on PSF in United States and European Union
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Solid fibers accounted for 59.35% of volume in 2025, underpinned by broad usage in apparel, home textiles and stuffing materials. In the same year hollow grades captured the remaining share yet are predicted to expand 5.62% annually to 2031-well above the overall polyester staple fiber (PSF) market. Performance stems from the thermal-insulation value of hollow cores and their ability to wick moisture, essential for athleisure, sleeping bags and quilt fillings.
Production advances now prevent fiber collapse, allowing higher loft at lower weight. Automotive interior trims, air filters and hygiene topsheets are specifying bi-component hollow products designed with hydrophilic finishes that speed liquid transport. Thermal-bonded webs between 13-100 gsm supplied by Asian non-woven converters demonstrate the breadth of end-use possibilities. As technical customers prioritize weight savings and energy efficiency, hollow variants are set to capture a larger slice of the polyester staple fiber market size for insulation and filtration sub-segments.
The Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Market Report Segments the Industry by Product Type (Solid, Hollow), Origin (Virgin, Blended, Recycled), Application (Textile, Home Furnishing, Automotive, Filtration, Construction, Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Tons).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominated global volume with a 72.40% share in 2025, propelled by China's integrated PTA, MEG and fiber assets and India's expanding knitwear hub in Tamil Nadu. Region-wide adoption of draw-texturised yarns and hollow variant lines positions APAC to grow at a 5.18% CAGR, the fastest regional rate. Sinopec's megascale 3 million-ton PTA plant improves upstream security, lowering break-even costs for downstream spinners.
India continues to leverage the Performance-Linked Incentive scheme to boost man-made fiber exports while domestic urbanisation lifts household textile consumption. Vietnam, Indonesia, and Thailand attract hygiene-non-woven investments, drawing resin imports and sparking new staple lines co-located with spunbond units. Together, these trends inject momentum into the regional polyester staple fiber market.
North America and Europe account for a smaller volume, yet fibre engineered for automotive, furniture, and filtration draws premium margins. Anti-dumping cases in both regions alter trade flows: Latin America and Turkiye receive redirected Asian shipments while European producers target technical customers less sensitive to price. Over the forecast horizon, incremental investments in recycling infrastructure-such as chemical depolymerisation plants in Spain, France and the eastern United States, will taper virgin volume growth but raise recycled penetration within the polyester staple fiber (PSF) market.
- Alpek Polyester
- Barnet
- Bombay Dyeing
- BoReTech Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
- Diyou Fibre (M) Sdn Bhd
- Far Eastern Group
- Hang Zhou Benma Chemfibre and Spinning Co.,Ltd.
- Huvis Corp
- Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited.
- Komal Fibres
- Nirmal Fibres (P) Ltd.
- Reliance Industries Limited
- Sanfame Group
- Shubhalakshmi
- SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEMICAL FIBRE LIMITED
- Thai polyester Co., Ltd.
- Tongkun Holding Group
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
- XINDA
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in Demand for Recycled PSF from FastFashion Brands
- 4.2.2 Expansion of Nonwoven Hygiene Capacity in Southeast Asia
- 4.2.3 Substitution of Cotton with Polyester amid Price Volatility
- 4.2.4 Growth of Lightweight NVH Automotive Components
- 4.2.5 UrbanisationLed Home Textile Boom in India & China
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 RawMaterial Price Volatility Linked to CrudeOil Swings
- 4.3.2 Anti Dumping Duties on PSF in United States & EU
- 4.3.3 Stringent Legal and Political Regulations
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Solid
- 5.1.2 Hollow
- 5.2 By Origin
- 5.2.1 Virgin
- 5.2.2 Blended
- 5.2.3 Recycled
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Textile
- 5.3.2 Home Furnishing
- 5.3.3 Automotive
- 5.3.4 Filtration
- 5.3.5 Construction
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.1.1 China
- 5.4.1.2 India
- 5.4.1.3 Japan
- 5.4.1.4 South Korea
- 5.4.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.4.1.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.2 North America
- 5.4.2.1 United States
- 5.4.2.2 Canada
- 5.4.2.3 Mexico
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 Asia Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank / Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Alpek Polyester
- 6.4.2 Barnet
- 6.4.3 Bombay Dyeing
- 6.4.4 BoReTech Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Diyou Fibre (M) Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.6 Far Eastern Group
- 6.4.7 Hang Zhou Benma Chemfibre and Spinning Co.,Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Huvis Corp
- 6.4.9 Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited.
- 6.4.10 Komal Fibres
- 6.4.11 Nirmal Fibres (P) Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Reliance Industries Limited
- 6.4.13 Sanfame Group
- 6.4.14 Shubhalakshmi
- 6.4.15 SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEMICAL FIBRE LIMITED
- 6.4.16 Thai polyester Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Tongkun Holding Group
- 6.4.18 TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
- 6.4.19 XINDA
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 Whitespace & UnmetNeed Assessment
- 7.2 Growing Awareness Regarding Recycled Polyester Staple Fiber




