PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906273

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906273
Eye Infection Treatment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The eye infection treatment market is expected to grow from USD 8.16 billion in 2025 to USD 8.47 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 10.17 billion by 2031 at 3.74% CAGR over 2026-2031.
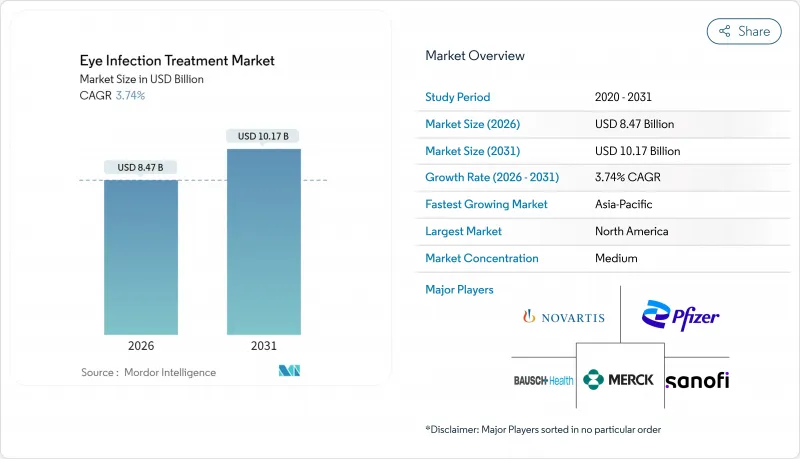
This moderate expansion occurs while established antibiotics confront growing generic pressure, yet innovations in sustained-release delivery and a rising pool of elderly and diabetic patients support incremental growth. Ongoing efforts to contain antimicrobial resistance elevate demand for new mechanisms of action and combination regimens, while premium pricing opportunities emerge for drugs that cut dosing frequency and improve adherence. Surgical volumes continue increasing worldwide, creating larger prophylactic segments and sustaining premium prophylactic therapy uptake. Competitive intensity is defined by patent expiries, corporate acquisitions that consolidate intellectual property, and faster regulatory pathways for breakthrough designations.
Global Eye Infection Treatment Market Trends and Insights
Rising Global Burden of Ocular Infections
Incidence of infectious eye disease now rises in tandem with digital device use that weakens the tear film and creates entry points for pathogens. Climate variability changes pathogen distribution, pushing fungal keratitis into previously temperate regions. Demodex blepharitis, once under-diagnosed, affects 57.7% of patients visiting specialist clinics and fuels demand for novel acaricidal therapies. Contact lens wear climbs across emerging economies were hygiene education trails adoption, raising bacterial keratitis cases. Growing cataract and refractive surgery volumes enlarge postoperative prophylaxis segments, while mobile ophthalmology camps in rural areas reveal previously hidden infection backlogs.
Increasing Geriatric and Diabetic Populations
Global aging adds millions of immune-compromised consumers prone to ocular infection, while diabetes prevalence enlarges the surgical and injection-exposed cohort. Worldwide blindness linked to diabetic retinopathy reached 1.07 million persons in 2024 and visually impaired cases hit 3.28 million, with South America and the Caribbean bearing the highest 6.95% prevalence. Medicare records show anti-VEGF usage for diabetic macular edema climbing from 16% to 35% between 2009-2018. Repeated intraocular procedures heighten infection risk and expand prophylactic antibiotic demand. Projected rise to 14 million age-related macular degeneration cases by 2050 widens the patient base needing stringent infection prevention.
Patent Cliffs and Intensifying Generic Competition
Blockbuster antibiotic patents expired between 2022-2024, and generics now account for 91% of ophthalmic prescriptions in the United States. Consolidated generic manufacturing has triggered shortages, as seen with dorzolamide-timolol, disrupting care continuity. FDA product-specific guidance accelerates additional generic approvals, squeezing price realization for innovators. Brand owners respond with sustained-release and fixed-dose combinations but face scrutiny over incremental innovation claims.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Accelerating R&D Investments in Ophthalmic Anti-Infectives
- Growing Adoption of Topical Combination Therapies
- Escalating Antimicrobial Resistance Concerns
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Antibiotics accounted for 43.02% of 2025 revenue in the eye infection treatment market, reflecting entrenched use in bacterial conjunctivitis and keratitis. Concurrently, antivirals are forecast to register a 5.54% CAGR to 2031, the fastest among classes, as polymerase-chain-reaction diagnostics more reliably detect viral etiologies and as herpes keratitis prophylaxis becomes routine. Antifungals retain a niche, yet they remain indispensable in tropical belts where fungal keratitis imposes high blindness risk. Antihistamines and corticosteroids serve inflammatory comorbidities; recent approval of once-daily Alesion cream targets compliance limitations. Segment innovation favors fixed combinations that suppress infection and inflammation together, a theme expected to bolster antivirals and corticosteroid-laden hybrids alike. The eye infection treatment market size for antibiotics is expected to grow modestly, but antivirals will contribute disproportionate incremental value despite a lower base.
Clinical adoption trends indicate that lipoglycopeptides and cyclic peptides under investigation may enter practice circles by late decade, creating fresh product categories. In tandem, peptide-bound nanoparticle platforms could lift ocular bioavailability and marginally expand the antibiotic share within the eye infection treatment market. Portfolio strategies now emphasize resistance-breaking structural classes, especially in hospital-acquired keratitis, while topical immunomodulators aim to modulate host response, further diversifying revenue streams across the eye infection treatment industry.
The Eye Infection Treatment Market Report is Segmented by Drug Class (Antibiotics, Antivirals, and More), Indication (Conjunctivitis, Keratitis, and More), Dosage Form (Eye Drops, Tablets/Capsules, Ophthalmic Ointments, and Other Dosage Forms), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America captured 38.40% of 2025 revenue in the eye infection treatment market, reflecting robust insurance coverage, high surgical throughput, and rapid uptake of breakthrough approvals like lotilaner. Medicare claims data show rising intravitreal injection numbers, which intensify prophylactic antibiotic usage and open the door for novel sustained-release devices. However, payer pressure and aggressive generic entry restrain price elasticity, even as antimicrobial resistance forces costlier second-line options.
Asia-Pacific is expected to deliver the highest 4.51% CAGR through 2031, buoyed by aging populations, escalating diabetes prevalence, and expanding middle-class access to elective eye care. China and India drive surgical volume gains; Indian high-throughput cataract centers demonstrate scalable care models that amplify prophylactic drug demand. However, practitioner shortages-only 46.2% of regional countries meet the 1:10,000 optometrist ratio-create latent demand for remote diagnosis and pharmacy-led dispensing, an ecosystem supportive of combination over-the-counter therapies.
Europe posts steady growth as universal healthcare encourages broad access, but fiscal discipline favors generics. EU antimicrobial stewardship limits broad-spectrum use, yet it simultaneously accelerates interest in narrow-spectrum or pathogen-targeted drugs. Latin America and the Caribbean record the highest diabetic retinopathy blindness prevalence worldwide, generating above-average infection prophylaxis demand, though economic constraints temper premium adoption.
The Middle East & Africa and South America remain under-penetrated but represent long-term upside as tele-ophthalmology and portable surgical units expand reach. Local production incentives in Saudi Arabia and Brazil could shift generic sourcing patterns and lower acquisition costs. Multinational firms entering via co-marketing or contract-manufacturing arrangements may capture early share by tailoring packaging sizes and dosing to local compliance behavior.
- Novartis
- Alcon
- Pfizer
- Bausch Health
- Santen Pharmaceuticals
- Merck
- Sanofi
- Allergan Plc (AbbVie)
- Johnson & Johnson Vision Care
- Gilead Sciences
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- Roche
- Leadiant Biosciences
- Xellia Pharmaceuticals
- Aurolab
- Aerie Pharmaceutical
- Sun Pharma Industries Ltd.
- Akorn Operating Co. LLC
- Nicox S.A.
- Kala Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope Of The Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Global Burden of Ocular Infections
- 4.2.2 Increasing Geriatric and Diabetic Populations
- 4.2.3 Accelerating R&D Investments in Ophthalmic Anti-Infectives
- 4.2.4 Growing Adoption of Topical Combination Therapies
- 4.2.5 Expanding Access to Eye Care In Emerging Economies
- 4.2.6 Advancements in Sustained-Release Drug Delivery Platforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Patent Cliffs and Intensifying Generic Competition
- 4.3.2 Adverse Effects And Contraindications Of Ocular Anti-Infectives
- 4.3.3 Escalating Antimicrobial Resistance Concerns
- 4.3.4 Stringent Regulatory Hurdles And Pricing Pressures
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat Of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power Of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat Of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Intensity Of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Drug Class
- 5.1.1 Antibiotics
- 5.1.2 Antivirals
- 5.1.3 Antifungals
- 5.1.4 Antihistamines
- 5.1.5 Corticosteroids
- 5.1.6 Glucocorticoids
- 5.2 By Indication
- 5.2.1 Conjunctivitis
- 5.2.2 Keratitis
- 5.2.3 Endophthalmitis
- 5.2.4 Blepharitis
- 5.2.5 Stye (Hordeolum)
- 5.2.6 Uveitis
- 5.2.7 Cellulitis
- 5.2.8 Ocular Herpes
- 5.3 By Dosage Form
- 5.3.1 Eye Drops
- 5.3.2 Tablets / Capsules
- 5.3.3 Ophthalmic Ointments
- 5.3.4 Other Dosage Forms
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials As Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Novartis AG
- 6.3.2 Alcon AG
- 6.3.3 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.4 Bausch Health Companies Inc.
- 6.3.5 Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.6 Merck & Co., Inc.
- 6.3.7 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.8 Allergan Plc (AbbVie)
- 6.3.9 Johnson & Johnson Vision Care
- 6.3.10 Gilead Sciences Inc.
- 6.3.11 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.12 Roche Holding AG
- 6.3.13 Leadiant Biosciences
- 6.3.14 Xellia Pharmaceuticals
- 6.3.15 Aurolab
- 6.3.16 Aerie Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.17 Sun Pharma Industries Ltd.
- 6.3.18 Akorn Operating Co. LLC
- 6.3.19 Nicox S.A.
- 6.3.20 Kala Pharmaceuticals Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




