PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906279

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906279
Indonesia Construction Equipment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Indonesia Construction Equipment Market was valued at USD 3.41 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 3.62 billion in 2026 to reach USD 4.89 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 6.18% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
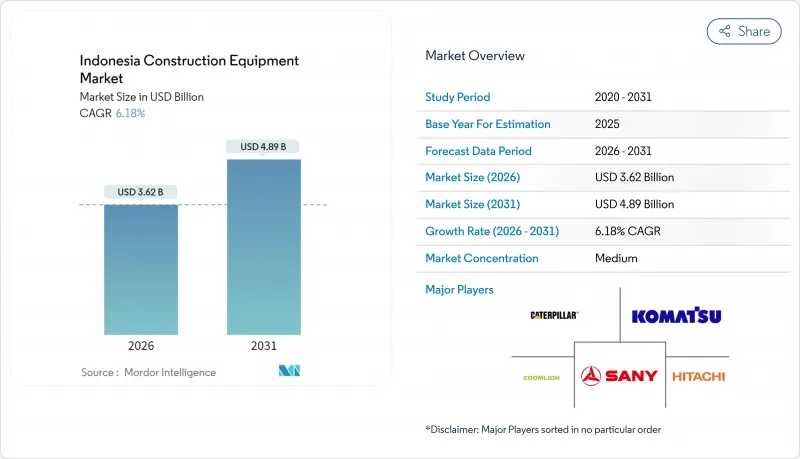
Continued implementation of the Proyek Strategis Nasional (PSN) pipeline, the USD 35 billion New Capital City (IKN) program, and resilient mining investment jointly anchors demand across earth-moving, material-handling, and specialized machinery categories. Suppliers that blend local assembly, flexible financing, and telematics services are best positioned to capitalize on utilization rates in Jakarta-centric fleets.
Indonesia Construction Equipment Market Trends and Insights
Surging Public-Sector Spend on Indonesia's 2030 Infrastructure Vision
Indonesia's 41 final-stage PSN schemes require uninterrupted equipment deployment across toll roads, dams, ports, and industrial parks. Every rupiah spent on infrastructure has generated 1.9 rupiah in economic value, reinforcing procurement budgets for contractors and rental houses. The multiplier appears strongest in economic zones and power projects, prompting nationwide demand peaks rather than the historical Java concentration. North Sumatra and South Sulawesi have posted the sharpest output lifts, turning each province into a regional rental hotspot. Longer project pipelines permit suppliers to structure five- to seven-year maintenance contracts, locking in parts and service revenue throughout machine life cycles.
Rapid Urban Rail & Toll-Road Build-Outs Driving Earth-Moving Fleet Renewal
Completed in 2024, the Cimanggis-Cibitung Toll Road exemplifies high earth-moving intensity, with significant deployment of excavators and dump trucks during peak construction. On-site digital monitoring at the Karangjoang-Kariangau Section 3A helped reduce equipment idle time significantly while improving utilization rates-highlighting the growing importance of telematics integration. Contractors adopting precision guidance systems are seeing notable gains in fuel efficiency and operational speed. These practices are now being extended by provincial authorities to infrastructure corridors like Parapat in North Sumatra, indicating that technology-driven upgrades are expanding beyond Java. With stricter emission norms tightening around aging Tier 2 equipment, contractors are increasingly turning to cleaner, low-hour Tier 3 and hybrid machines.
Volatile Rupiah Elevating Imported Equipment Prices & Financing Costs
Capital-goods imports form a significant share of Indonesia's trade basket, exposing contractors to foreign-exchange swings that erode purchasing budgets by quarter-points in weeks. Letters of credit add cost buffers, while local content mandates complicate specification choices for global brands. Trade Ministerial Regulation No. 8/2024 streamlines port clearance, yet currency risk persists, prompting equipment financiers to tighten loan-to-value ratios for smaller firms. Dealers increasingly bundle dollar-indexed parts contracts with rupiah-denominated machine loans, reducing mismatch but raising documentation overheads. Local assembly in Batam and Cikarang mitigates exposure, though Tier 4F engine imports remain priced in USD.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- E-Commerce Warehousing Boom Lifting Demand for Material-Handling Equipment
- Commodity Super-Cycle Fueling Mining-Sector Capex in Kalimantan
- Project Execution Delays Tied to Land-Acquisition Bureaucracy
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Earth-moving machinery generated more than a billion USD within the Indonesian construction equipment market in 2025, translating into a 48.12% share amid a surge of PSN and mining groundwork. Motor graders, crawler excavators, and articulated haulers form the backbone of toll-road and dam packages, while batching plants and crushing units round out larger EPC scopes. Advanced telematics now track idle fuel-burn and undercarriage wear, nudging contractors to upgrade older Tier 2 models ahead of emission mandates.
Material-handling equipment contributed significant share and is expanding at a 7.32% CAGR, propelled by warehouse automation and port modernization. Forklifts with lithium-ion packs enable triple-shift operations without battery swaps, cutting downtime by 25%. At Tanjung Priok, remote-operated quay cranes improve berth productivity, driving follow-on orders from Tanjung Perak and Kijing.
Hydraulic platforms captured 84.55% revenue in 2025, underpinned by cost-performance equilibrium and familiarity among Indonesian operators. Suppliers refine spool-valve tuning and energy-recovery circuits to cut fuel consumption by 8% without shifting working habits. Remote drilling projects value hydraulic robustness over electrical complexity, sustaining replacement demand in 100 km-plus radius mines.
Electric and hybrid variants, although only 4,200 units on rent today, post a 6.45% CAGR backed by carbon-credit incentives and 10% VAT discounts on locally contented EVs. Pilot retrofits on 20-tonne excavators show operating-cost drops of 30 basis points per cubic meter moved. Contractors adopting hybrids often secure preferential scoring in public tenders aligned with CCS/CCUS compliance. Financing bundles include green-label asset-backed securities, trimming coupon spreads versus conventional loans, and nudging adoption into mainstream bids for 2027 onward.
The Indonesia Construction Equipment Market Report is Segmented by Equipment Type (Earth-Moving Equipment, Road Construction Equipment, and More), Drive Type (Hydraulic and Electric/Hybrid), Power Output (Less Than 100 KW and More), End-User (Infrastructure & Real-Estate Contractors and More), Application (Residential Construction and More), and Region. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Komatsu Ltd.
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- J.C. Bamford Excavators Ltd. (JCB)
- HD Hyundai Construction Equipment
- SANY Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.
- Xuzhou Construction Machinery Group (XCMG)
- Zoomlion Heavy Industry Sci & Tech
- Liebherr Group
- Kubota Corporation
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- Takeuchi Mfg. Co., Ltd.
- Kobelco Construction Machinery
- Manitou Group
- Toyota Material Handling
- Volvo Construction Equipment
- Doosan Bobcat
- Sumitomo Construction Machinery
- CNH Industrial (CASE Construction)
- Shantui Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging Public-Sector Spend on Indonesia's 2030 Infrastructure Vision
- 4.2.2 Rapid Urban Rail & Toll-Road Build-Outs Driving Earth-Moving Fleet Renewal
- 4.2.3 E-Commerce Warehousing Boom Lifting Demand for Material-Handling Equipment
- 4.2.4 Commodity Super-Cycle Fueling Mining-Sector Capex in Kalimantan
- 4.2.5 Carbon-Credit Incentives Pushing Contractors Toward Electric/Hybrid Fleets
- 4.2.6 ASEAN-Wide Supply-Chain Re-Shoring into Indonesia Expanding Construction Pipelines
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Volatile Rupiah Elevating Imported Equipment Prices & Financing Costs
- 4.3.2 Project Execution Delays Tied to Land-Acquisition Bureaucracy
- 4.3.3 Fragmented Rental Ecosystem Limiting Nationwide Fleet Utilisation
- 4.3.4 Persistent Skills Gap in Advanced Machine-Control Operation
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value & Volume)
- 5.1 By Equipment Type
- 5.1.1 Earth-moving Equipment
- 5.1.1.1 Excavators
- 5.1.1.2 Backhoe Loaders
- 5.1.1.3 Motor Graders
- 5.1.1.4 Bulldozers
- 5.1.2 Road Construction Equipment
- 5.1.2.1 Road Rollers
- 5.1.2.2 Asphalt Pavers
- 5.1.3 Material-Handling Equipment
- 5.1.3.1 Cranes
- 5.1.3.2 Forklifts & Telescopic Handlers
- 5.1.3.3 Articulated Boom Lifts
- 5.1.4 Other Construction Equipment
- 5.1.1 Earth-moving Equipment
- 5.2 By Drive Type
- 5.2.1 Hydraulic
- 5.2.2 Electric / Hybrid
- 5.3 By Power Output (kW)
- 5.3.1 Less than 100 kW
- 5.3.2 101 to 200 kW
- 5.3.3 201 to 400 kW
- 5.3.4 More than 400 kW
- 5.4 By End-user
- 5.4.1 Infrastructure & Real-estate Contractors
- 5.4.2 Mining & Quarrying Companies
- 5.4.3 Manufacturing & Industrial Facilities
- 5.4.4 Agriculture & Plantation Sector
- 5.5 By Application
- 5.5.1 Residential Construction
- 5.5.2 Commercial Construction
- 5.5.3 Industrial Construction
- 5.5.4 Transportation & Infrastructure Projects
- 5.5.5 Energy & Utilities Projects
- 5.6 By Region
- 5.6.1 Java
- 5.6.2 Sumatra
- 5.6.3 Kalimantan
- 5.6.4 Sulawesi
- 5.6.5 Papua & Maluku
- 5.6.6 Rest of Indonesia
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Caterpillar Inc.
- 6.4.2 Komatsu Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 J.C. Bamford Excavators Ltd. (JCB)
- 6.4.5 HD Hyundai Construction Equipment
- 6.4.6 SANY Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Xuzhou Construction Machinery Group (XCMG)
- 6.4.8 Zoomlion Heavy Industry Sci & Tech
- 6.4.9 Liebherr Group
- 6.4.10 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.11 Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Takeuchi Mfg. Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Kobelco Construction Machinery
- 6.4.14 Manitou Group
- 6.4.15 Toyota Material Handling
- 6.4.16 Volvo Construction Equipment
- 6.4.17 Doosan Bobcat
- 6.4.18 Sumitomo Construction Machinery
- 6.4.19 CNH Industrial (CASE Construction)
- 6.4.20 Shantui Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




