PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906958

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1906958
North America Agricultural Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The North America agricultural machinery market is expected to grow from USD 54.3 billion in 2025 to USD 57.5 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 76.57 billion by 2031 at 5.9% CAGR over 2026-2031.
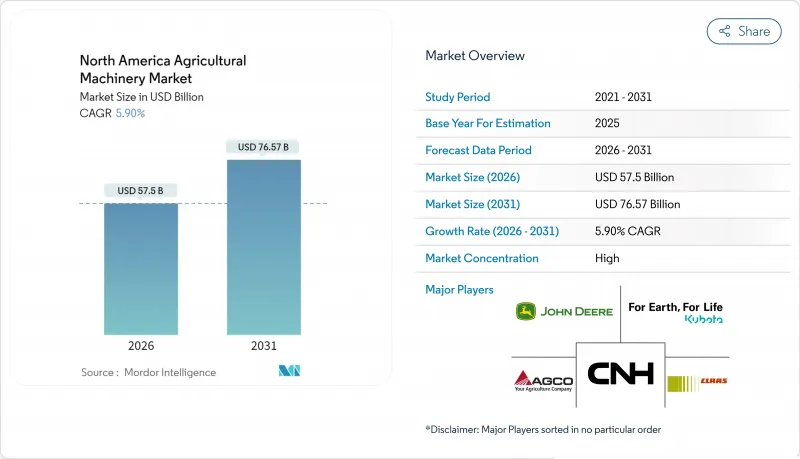
The expansion reflects persistent mechanization demand despite elevated interest rates and commodity price swings that limited capital spending in 2024. Structural labor shortages, federal subsidy programs that encourage fleet renewal, and rapid precision-ag adoption continue to underpin equipment orders. Autonomous capabilities showcased at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2025 are accelerating early replacement cycles because farms now weigh software compatibility on par with horsepower. Simultaneously, irrigation modernization, especially in water-stressed Mexico, widens the addressable base for specialized equipment makers. Competitive dynamics remain intense as leading OEMs bundle embedded finance, software subscriptions, and dealer support to retain customers and stabilize revenue.
North America Agricultural Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Robust Farm-Income Outlook and Subsidy Programs
Federal depreciation allowances and direct grants keep capital budgets resilient. The USDA Climate-Smart Commodities program alone has allocated more than USD 3 billion since 2024 for equipment that lowers emissions and improves efficiency. Section 179 rules allow deductions up to USD 1.16 million per tax year, offsetting higher borrowing costs. Mid-sized growers respond by front-loading purchases to capture both grant and tax benefits. Dealer feedback indicates stronger demand for mid-horsepower tractors equipped with telematics that document sustainability metrics required for grant compliance. As a result, the North America agricultural machinery market enjoys a predictable baseline of subsidized orders that cushions cyclical demand dips.
Rising Labor Scarcity and Wage Inflation
Rural workforce participation keeps falling, which pushes farms to mechanize tasks once handled manually. Mexico's crop yield setbacks in 2024 underscore how labor shortages can throttle production. Autonomous sprayers and robotic harvest aids reduce field crews and curb escalating wages that now outstrip general inflation. OEM demonstrations prove that integrated machine-vision lowers chemical use, which further offsets labor costs. Grain-elevator operators also automate with AI-enabled sensors that let facilities run at night without staff oversight. Persistent worker scarcity, therefore, sustains long-term demand for advanced equipment across the region.
High Upfront and Maintenance Costs of Advanced Machinery
A high-horsepower tractor exceeded USD 400,000 in 2024, while precision retrofits add USD 50,000-100,000 per unit. Total ownership costs climb further because modern engines and software demand specialized technicians that remain scarce. Nearly 87% of dealers struggle to hire qualified service staff. Extended warranties and service contracts ease uncertainty, yet they add another USD 15,000-25,000 to the purchase price. Many producers, therefore, refurbish decade-old machines, which postpones technology upgrades and raises fuel consumption during critical field windows. As a result, small and mid-sized farms often delay purchases until late-season discounting emerges, compressing dealer margins and extending replacement cycles.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Precision-Agriculture Adoption Accelerating Equipment Replacement
- USDA Climate-Smart Grants Driving Low-Emission Equipment
- Volatile Commodity Prices Curbing CAPEX Cycles
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tractors maintained a 47.30% share of the North America agricultural machinery market in 2025, underscoring their central role across crop operations. The segment benefits from autonomous retrofits tested on 50,000 acres, validating real-world uptime and lowering skepticism about driverless tillage. Yet irrigation machinery, supported by water-scarcity mitigation projects, is projected to register a 13.4% CAGR through 2031, outpacing every other equipment class. The North America agricultural machinery market size for irrigation equipment is forecast to show a significant growth during the period as center-pivot conversions accelerate in Mexico.
Secondary categories such as plows and cultivators grow modestly because precision tech shifts demand toward variable-rate applications. In harvesting, integrated grain-quality sensors and yield mapping push farms to upgrade combines earlier than the traditional 6-year cycle. Haying and forage machinery benefits from dairy and beef expansion in the Upper Midwest and Canadian Prairies, while the other types bucket now covers autonomous robots that perform weeding, spot spraying, and soil monitoring. Kubota's KATR robot exemplifies a multifunctional design that blurs traditional equipment lines.
The North America Agricultural Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Type (Tractor, Equipment, Irrigation Machinery, Harvesting Machinery, Haying and Forage Machinery, Other Types) and Geography (United States, Canada, Mexico, Rest of North America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Mahindra & Mahindra Limited
- Netafim USA Inc.
- Lindsay Corporation
- Trimble Inc.
- Horsch Maschinen GmbH
- KUHN SAS
- Bernard Krone Holding SE & Co. KG
- The Toro Company
- Vermeer Corporation
- J.C. Bamford Excavators Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Robust farm-income outlook and subsidy programs
- 4.2.2 Rising labor scarcity and wage inflation
- 4.2.3 Precision-ag adoption accelerating equipment replacement
- 4.2.4 OEM embedded-finance boosting purchasing power
- 4.2.5 Subscription-based machinery access models (under-reported)
- 4.2.6 USDA Climate-Smart grants driving low-emission equipment (under-reported)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront and maintenance costs of advanced machinery
- 4.3.2 Volatile commodity prices curbing CAPEX cycles
- 4.3.3 Interest-rate-driven credit tightening at farm level
- 4.3.4 Battery-grade semiconductor supply constraints for e-tractors (under-reported)
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Tractor
- 5.1.1.1 Less Than 40 HP
- 5.1.1.2 40 to 100 HP
- 5.1.1.3 More than 100 HP
- 5.1.1.4 4WD Tractors
- 5.1.2 Equipment
- 5.1.2.1 Plows
- 5.1.2.2 Harrows
- 5.1.2.3 Cultivators and Tillers
- 5.1.2.4 Other Equipment
- 5.1.3 Irrigation Machinery
- 5.1.3.1 Sprinkler
- 5.1.3.2 Drip
- 5.1.3.3 Other Irrigation
- 5.1.4 Harvesting Machinery
- 5.1.4.1 Combine Harvesters
- 5.1.4.2 Forage Harvesters
- 5.1.4.3 Other Harvesting
- 5.1.5 Haying and Forage Machinery
- 5.1.5.1 Mowers
- 5.1.5.2 Balers
- 5.1.5.3 Other Haying and Forage
- 5.1.6 Other Types
- 5.1.1 Tractor
- 5.2 By Geography
- 5.2.1 United States
- 5.2.2 Canada
- 5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.2.4 Rest of North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Deere & Company
- 6.4.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.4 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.5 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.4.6 Mahindra & Mahindra Limited
- 6.4.7 Netafim USA Inc.
- 6.4.8 Lindsay Corporation
- 6.4.9 Trimble Inc.
- 6.4.10 Horsch Maschinen GmbH
- 6.4.11 KUHN SAS
- 6.4.12 Bernard Krone Holding SE & Co. KG
- 6.4.13 The Toro Company
- 6.4.14 Vermeer Corporation
- 6.4.15 J.C. Bamford Excavators Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




