PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907227

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1907227
North America Food Safety Testing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The North America food safety testing market is expected to grow from USD 8.51 billion in 2025 to USD 8.99 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 11.81 billion by 2031 at 5.61% CAGR over 2026-2031.
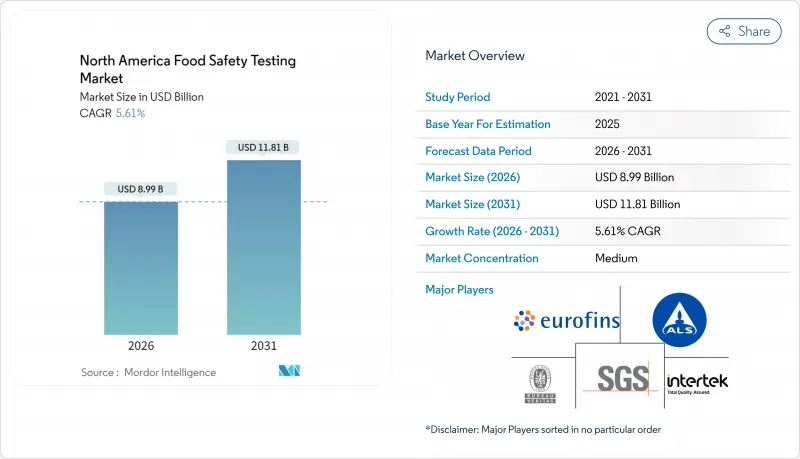
This growth stems from tighter food safety regulations, increased public awareness of foodborne outbreaks through media coverage, and growing consumer interest in transparent food labeling. As companies engage in more international trade of fresh produce, meat, and processed foods, supply chains have become increasingly complex, leading to higher risks of contamination and greater testing requirements. Within the market, large testing laboratories are enhancing their capabilities with high-volume testing equipment, while smaller firms carve out niches through specialized testing services and quick response times. The industry continues to evolve with advancements in chemical residue testing, allergen identification, and digital tracking systems.
North America Food Safety Testing Market Trends and Insights
Stringent Government Regulations Regarding Food Safety Standards
The FDA's Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) has intensified regulatory enforcement across North America, introducing stringent compliance requirements for food manufacturers. The FDA's updated allergen labeling guidance, effective January 2024, requires enhanced testing protocols for nine major allergens, increasing the demand for immunoassay-based detection systems . The USDA-FSIS has implemented a comprehensive Salmonella framework for poultry products, requiring processors to conduct pathogen testing at critical control points throughout production. These regulatory requirements have created a compliance-driven testing market, where laboratories must upgrade their analytical capabilities to meet detection thresholds. Non-compliance penalties can reach millions of dollars, making testing investments crucial for risk management. Health Canada's efforts to align food safety standards with United States requirements further strengthen these regulatory measures across North America.
Increasing Frequency of Foodborne Disease Outbreaks
Recent foodborne illness outbreaks have led to expanded testing protocols across affected supply chains. The October 2024 McDonald's E. coli outbreak, traced to slivered onions and affecting 104 individuals across 14 states, resulted in increased testing requirements for leafy greens and fresh-cut produce. Norovirus outbreaks linked to raw oysters from British Columbia waters prompted enhanced shellfish testing protocols across North American distribution networks . The Salmonella outbreak in charcuterie meats during late 2024 highlighted bacterial contamination risks in processed foods, increasing demand for rapid pathogen detection systems. These incidents drive market growth as food companies implement more frequent testing to prevent contamination. The financial impact of outbreaks, demonstrated by McDonald's stock volatility following the E. coli incident, makes preventive testing more cost-effective than managing contamination aftermath.
High Cost of Advanced Food Safety Testing Procedures
Advanced analytical instrumentation poses substantial financial challenges for smaller food manufacturers striving to implement comprehensive testing protocols. The investment required for pesticide residue analysis systems, including maintenance costs, creates significant financial barriers for mid-market food processors. The industry-wide shortage of qualified technicians amplifies these challenges, as experienced analytical chemists demand considerably higher compensation compared to general laboratory staff, affecting operational budgets for companies expanding their testing programs. The burden of regulatory compliance continues to increase as agencies mandate more sophisticated detection methods, with specialized testing procedures like mycotoxin analysis requiring complex sample preparation techniques that substantially impact testing budgets. Small and medium enterprises frequently turn to external testing laboratories, but capacity constraints during high-demand periods result in production delays and increased inventory costs. This financial pressure is particularly challenging for organic and specialty food producers, who must maintain stringent testing standards while operating with narrower profit margins compared to traditional food manufacturers.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Adoption of Blockchain for Traceability and Data Integrity
- Prevalence and Detection Emphasis on Food Allergens
- Difficulty in Testing for Emerging and Complex Contaminants
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Pathogen testing currently holds the largest market share at 45.20% in 2025, as food manufacturers focus heavily on preventing microbial contamination that could result in health emergencies and facility closures. The GMO testing segment shows promising growth potential with a projected CAGR of 6.44% through 2031, responding to heightened consumer interest in product transparency and the increasing need to verify organic and non-GMO claims.
While companies continue to invest significantly in traditional microbial safety testing, the market is expanding to accommodate new verification requirements that provide testing laboratories with additional business opportunities. The pesticide and residue testing segment maintains steady demand for chemical contamination screening, alongside mycotoxin testing which remains crucial for grain and nut processors. Testing laboratories can charge premium rates for their advanced analytical capabilities, which are essential for meeting FDA aflatoxin limits ranging from 20 ppb in nuts to 0.5 ppb in milk.
The North America Food Safety Testing Market Report is Segmented by Containment Type (Pathogen Testing, Pesticide and Residue Testing, Mycotoxin Testing, and More), Technology (Polymerase Chain Reaction, Immunoassay-Based and More), Application (Pet Food and Animal Feed, and Food), and Geography (United States, Canada, Mexico, and Rest of North America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- SGS SA
- Eurofins Scientific
- Bureau Veritas
- Intertek Group PLC
- ALS Limited
- NSF International
- Merieux NutriSciences
- NEOGEN Corporation
- TUV SUD
- AsureQuality
- Microbac Laboratories
- 3M Company
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Danaher
- Charm Sciences
- IDEXX Laboratories
- Romer Labs
- Genetic ID NA
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Stringent government regulations regarding food safety standards
- 4.2.2 Increasing frequency of foodborne disease outbreaks
- 4.2.3 Growing adoption of blockchain for traceability and data integrity
- 4.2.4 Prevalence and detection emphasis on food allergens
- 4.2.5 Greater incidence of adulteration and toxicity in processed foods
- 4.2.6 Demand for shelf-life extension and reduction of product recalls
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of advanced food safety testing procedures
- 4.3.2 Difficulty in testing for emerging and complex contaminants
- 4.3.3 Shortage of skilled professionals in food safety laboratories
- 4.3.4 Time-consuming nature of conventional testing methods
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Containment Type
- 5.1.1 Pathogen Testing
- 5.1.2 Pesticide and Residue Testing
- 5.1.3 Mycotoxin Testing
- 5.1.4 GMO Testing
- 5.1.5 Allergen Testing
- 5.1.6 Other Contaminant Testing
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Polymerase Chain Reaction
- 5.2.2 Immunoassay-based
- 5.2.3 Chromatography and Spectrometry
- 5.2.4 Others
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Pet Food and Animal Feed
- 5.3.2 Food
- 5.3.2.1 Meat and Poultry
- 5.3.2.2 Dairy
- 5.3.2.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.2.4 Processed Food
- 5.3.2.5 Crops
- 5.3.2.6 Other Foods
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 United States
- 5.4.2 Canada
- 5.4.3 Mexico
- 5.4.4 Rest of North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 SGS SA
- 6.4.2 Eurofins Scientific
- 6.4.3 Bureau Veritas
- 6.4.4 Intertek Group PLC
- 6.4.5 ALS Limited
- 6.4.6 NSF International
- 6.4.7 Merieux NutriSciences
- 6.4.8 NEOGEN Corporation
- 6.4.9 TUV SUD
- 6.4.10 AsureQuality
- 6.4.11 Microbac Laboratories
- 6.4.12 3M Company
- 6.4.13 Bio-Rad Laboratories
- 6.4.14 Agilent Technologies
- 6.4.15 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.4.16 Danaher
- 6.4.17 Charm Sciences
- 6.4.18 IDEXX Laboratories
- 6.4.19 Romer Labs
- 6.4.20 Genetic ID NA
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




