PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911349

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911349
Middle East Edible Meat - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
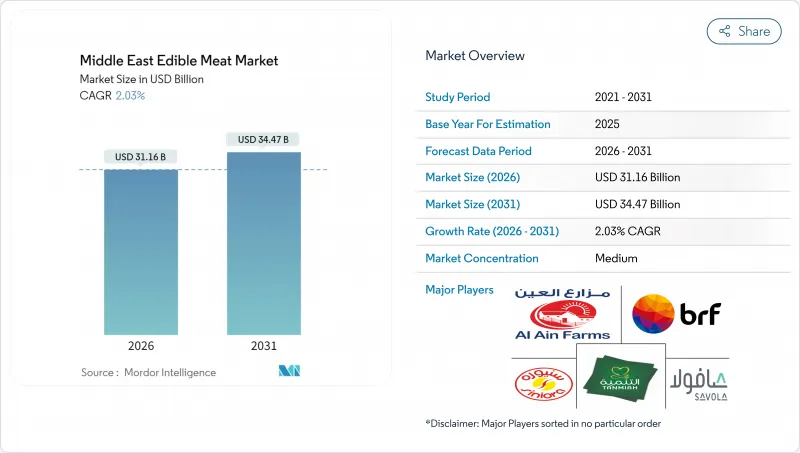
The Middle East edible meat market was valued at USD 30.54 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 31.16 billion in 2026 to reach USD 34.47 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 2.03% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Backed by robust government initiatives and bolstered by rising disposable incomes, the Middle East's edible meat market is witnessing steady growth. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 and Qatar's National Food Security Strategy are channeling billions into vertically integrated livestock projects, aiming for import substitution. These strategies not only fortify the region's meat market but also shield it from global supply chain fluctuations, ensuring a more self-reliant and sustainable supply of edible meat. Modern retail and e-commerce platforms are expanding consumer access to premium proteins, catering to the growing demand for high-quality meat products. Simultaneously, upgrades to the cold chain across the region are reducing post-harvest losses, preserving product quality, and further fueling market growth. Moreover, the adoption of advanced technologies, ranging from AI-driven poultry management systems that optimize production to blockchain solutions ensuring halal verification, is enhancing resource efficiency, improving traceability, and ensuring stringent quality standards in the Middle East's edible meat market.
Middle East Edible Meat Market Trends and Insights
Rising per-capita meat consumption in GCC economies
By 2031, per-capita meat intake in the GCC is set to rise by 6.1%, reaching 25.7 kg. This uptick mirrors the region's ongoing urbanization trend, with a notable 83% of residents now calling cities home. The demand from these bustling metropolitan centers fuels a steady flow of hypermarkets and quick-service restaurants, driving volume efficiencies in the Middle East's edible meat market. Urbanization not only increases access to modern retail formats but also enhances consumer exposure to diverse meat products, further driving demand. With 60% of the population under 30, the region's youthful demographic leans towards protein-rich convenience foods. This trend is bolstering premiumization in poultry, beef, and value-added products, as younger consumers increasingly seek high-quality and ready-to-cook options. In Saudi Arabia and Qatar, government consumer-subsidy schemes play a pivotal role in maintaining price stability. These initiatives ensure that households can afford meat, even amidst commodity price fluctuations, thereby safeguarding consistent consumption levels. Collectively, these factors not only bolster consumption resilience but also provide scale advantages for vertically integrated producers in the Middle East's edible meat market.
Expansion of local livestock capacity through import-substitution agendas
In 2024, Saudi Arabia reached a poultry self-sufficiency rate of 72% and aims for 90% by 2030 as part of its Vision 2030 initiative, which focuses on reducing reliance on imports and strengthening domestic production capabilities. Meanwhile, Qatar, through its National Food Security Strategy, is pushing for complete self-sufficiency in dairy and fresh chicken, while also targeting a 30% increase in red-meat production by 2030. This strategy aligns with the broader goal of enhancing food security and reducing dependency on external markets. A unified roadmap from the GCC is directing a substantial USD 3.8 billion into agri-tech ventures, with projections suggesting a potential saving of USD 30.5 billion on import bills. These investments aim to foster innovation and scalability in agricultural practices, thereby intensifying projects in the Middle East's edible meat market. Launched in 2024 with an initial seed funding of over OMR 10 million, Oman's Food Security Lab has established a pipeline exceeding OMR 1 billion, focusing on expanding capacity in poultry and red meat. These investments are enhancing finishing farms, hatcheries, and slaughterhouses, leading to reduced lead times, improved operational efficiency, and fresher products in domestic supply chains.
Complex halal certification and trade-compliance costs
India's Integrated Certification and Accreditation System has expanded its reach to 15 export destinations, encompassing all GCC states. This move imposes additional documentation requirements and third-party audits on exporters. According to the GCC's unified guide for imported foods, only approved slaughterhouses can provide the necessary accreditation. As a result, smaller suppliers are now required to navigate dual inspection regimes and manage increased logistics paperwork. For new entrants, the cumulative costs of certification fees, regular audits, and potential shipping delays can diminish gross margins by 3-5 percentage points. In a retail landscape sensitive to pricing, the ability to pass on these costs is limited. This constraint not only dissuades firms that aren't integrated but also strengthens the trend of consolidation within the Middle East's edible meat market. While digitized approval portals are in the works to simplify these processes, their widespread adoption remains a work in progress.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growth of modern retail and cold-chain logistics
- Government food-security funds driving vertical integration
- Volatile global feed-grain prices
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2025, poultry dominated the Middle East's edible meat market, seizing a 64.45% share. Regional governments are championing chicken production as a key strategy for achieving food-security independence. With its modest land and water needs, chicken production is rapidly expanding, positioning Saudi Arabia on track to meet its ambitious 90% self-sufficiency target by 2030. Investments in advanced flock genetics are boosting daily weight gains, and widespread vaccine use is curbing mortality rates. This scalability, bolstered by supportive policies, is solidifying the market stance of integrated poultry operators. The ongoing USD 533 million bidding for Al Watania Poultry underscores the strategic value of expansive broiler assets in fulfilling regional demands. Rising compliance mandates, from halal stun-free slaughter to digital traceability, are steering advantages toward well-capitalized industry leaders adept at navigating these challenges.
While beef contributes less to the overall meat volume, it emerges as the fastest-growing segment, projected to achieve a 2.07% CAGR through 2031. Urban centers, witnessing a surge in consumer wealth, are driving demand for premium steak cuts in upscale dining. Yet, producers grapple with challenges like water scarcity and fluctuating feed prices, leading to a heavy reliance on imports from Sudan and South America. To counter production limitations, modern beef integrators are channeling investments into cold-chain infrastructure and precision feed management. Supply chains are evolving under regulatory pressures, with heightened animal welfare standards and stringent quality certifications becoming the norm. Despite these challenges, the segment's premium allure and increasing disposable incomes present lucrative opportunities for specialized producers committed to delivering top-tier products to an astute market.
The Middle East Edible Meat Market Report is Segmented by Type (Beef, Mutton, Poultry, Other Meat), Form (Canned, Fresh/Chilled, Frozen, Processed), Distribution Channel (HoReCa, Retail), and Geography (Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of Middle East). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Al Ain Farms
- Al Islami Foods
- Americana Group
- BRF S.A.
- Golden Gate Meat Company
- JBS S.A.
- Najmat Taiba Foodstuff LLC
- Qatar Meat Production Company
- Siniora Food Industries Company
- Sunbulah Group
- Tanmiah Food Company
- The Savola Group
- Al Munajem Foods
- Halwani Brothers Co.
- Al Kabeer Group
- Qatar National Import & Export Co.
- Al Faisal Holding
- Ghadeer Foods
- Al Watania Poultry
- Choithrams Meat Division
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Price Trends
- 4.2.1 Beef
- 4.2.2 Mutton
- 4.2.3 Poultry
- 4.3 Production Trends
- 4.3.1 Beef
- 4.3.2 Mutton
- 4.3.3 Poultry
- 4.4 Market Drivers
- 4.4.1 Rising per-capita meat consumption in GCC economies
- 4.4.2 Expansion of local livestock capacity through import-substitution agendas
- 4.4.3 Growth of modern retail and cold-chain logistics
- 4.4.4 Government food-security funds driving vertical integration
- 4.4.5 Adoption of precision-livestock farming suited to arid climates
- 4.4.6 Product innovation in value-added/processed meat
- 4.5 Market Restraints
- 4.5.1 Complex halal certification and trade-compliance costs
- 4.5.2 Volatile global feed-grain prices
- 4.5.3 Water scarcity limiting pasture expansion
- 4.5.4 Urban shift toward plant-based alternatives
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.8 Trade Analysis
- 4.8.1 Import Analysis
- 4.8.2 Export Analysis
- 4.9 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.9.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.9.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.9.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.9.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.9.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.10 Key Strategic Questions for Meat-industry CEOs
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Beef
- 5.1.2 Mutton
- 5.1.2.1 Goat
- 5.1.2.2 Sheep
- 5.1.3 Poultry
- 5.1.3.1 Chicken
- 5.1.3.2 Other Poultry
- 5.1.4 Other Meat
- 5.2 By Form
- 5.2.1 Canned
- 5.2.2 Fresh/Chilled
- 5.2.3 Frozen
- 5.2.4 Processed
- 5.2.4.1 Nuggets
- 5.2.4.2 Sausages
- 5.2.4.3 Meatballs
- 5.2.4.4 Deli Meats
- 5.2.4.5 Marinated/Tenders
- 5.2.4.6 Other Processed Meat
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 HoReCa
- 5.3.1.1 Hotels
- 5.3.1.2 Restaurants
- 5.3.1.3 Catering
- 5.3.2 Retail
- 5.3.2.1 Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
- 5.3.2.2 Convenience/Grocery Stores
- 5.3.2.3 Online Retail Stores
- 5.3.2.4 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.3.1 HoReCa
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Bahrain
- 5.4.2 Kuwait
- 5.4.3 Oman
- 5.4.4 Qatar
- 5.4.5 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.6 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.7 Rest of Middle East
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Al Ain Farms
- 6.4.2 Al Islami Foods
- 6.4.3 Americana Group
- 6.4.4 BRF S.A.
- 6.4.5 Golden Gate Meat Company
- 6.4.6 JBS S.A.
- 6.4.7 Najmat Taiba Foodstuff LLC
- 6.4.8 Qatar Meat Production Company
- 6.4.9 Siniora Food Industries Company
- 6.4.10 Sunbulah Group
- 6.4.11 Tanmiah Food Company
- 6.4.12 The Savola Group
- 6.4.13 Al Munajem Foods
- 6.4.14 Halwani Brothers Co.
- 6.4.15 Al Kabeer Group
- 6.4.16 Qatar National Import & Export Co.
- 6.4.17 Al Faisal Holding
- 6.4.18 Ghadeer Foods
- 6.4.19 Al Watania Poultry
- 6.4.20 Choithrams Meat Division
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




