PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911368

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911368
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
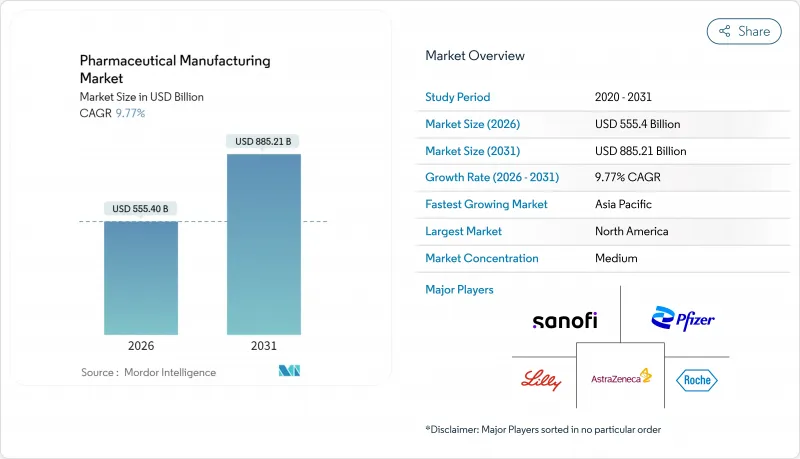
The Pharmaceutical Manufacturing market is expected to grow from USD 505.97 billion in 2025 to USD 555.4 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 885.21 billion by 2031 at 9.77% CAGR over 2026-2031.
The pharmaceutical manufacturing market is moving toward advanced technologies, greater biosimilar capacity, and regionally diversified supply chains that collectively help manufacturers satisfy rising global demand and comply with tighter regulations. Momentum is reinforced by continuous-processing economics, reshoring incentives, and artificial-intelligence-enabled quality control systems that shorten time-to-market cycles and support high-mix, low-volume production strategies. CDMOs are scaling rapidly to meet biologics demand, North American companies are pouring capital into domestic capacity, and Asia-Pacific governments are refining regulatory frameworks, all of which position the pharmaceutical manufacturing market for sustained double-digit growth.
Global Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market Trends and Insights
Rising R&D Investments by Big Pharma
Large pharmaceutical companies are channeling unprecedented funds into research, development, and manufacturing upgrades, with global drug spending projected to reach USD 1.9 trillion by 2032. Biologics alone are set to surpass USD 600 billion in annual revenue, prompting firms to align R&D and manufacturing budgets so that facility design directly supports clinical pipelines. Capital allocations of USD 50 billion or more from Novartis and Roche illustrate how integrated R&D-manufacturing strategies can accelerate radioligand and biologics programs, while AI-enabled process optimization has already boosted throughput by 20% in pilot plants across the pharmaceutical manufacturing market.
Acceleration of Continuous Manufacturing
Continuous-processing adoption cuts facility footprints by 70% and operating costs by up to 50%, providing an immediate economic rationale for transition from batch production within the pharmaceutical manufacturing market. The FDA's implementation of ICH Q13 gives companies a clear regulatory pathway, leading to faster review times for continuous-manufactured drugs and vaccines. Approved products from Pfizer and Eli Lilly validate commercial viability, while emerging platforms now cover nanomaterials and lipid-nanoparticle mRNA products.
Global Drug Pricing Pressures and Cost-Containment Policies
The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act authorizes Medicare negotiations, accelerating a shift toward lower launch prices and higher rebate exposure. On 1 January 2024, regulators recorded 453 brand-price hikes offset by 30 decreases, signaling intense scrutiny that compresses manufacturer margins. European proposals such as the Critical Medicines Act add parallel pressure by incentivizing local production while capping reimbursement, compelling firms to pursue aggressive automation to defend profitability.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Integration of AI, IoT, and Automation across Legacy Facilities
- Biosimilar Surge Following Major Patent Expirations
- Supply-Chain Disruptions for Critical Inputs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Small-molecule drugs controlled 60.58% of pharmaceutical manufacturing market share in 2025, supported by extensive global infrastructure and proven regulatory pathways. Biologics and biosimilars, although smaller in absolute terms, are expected to grow at a 10.22% CAGR, benefiting from patent expirations and rising demand for targeted therapies.
Manufacturing complexity drives capacity differentiation: single-use bioreactors and closed-loop analytics dominate biologics plants, while small molecules increasingly shift to fully-continuous tabletop lines. AI-driven control strategies are a unifying theme, enabling both molecule classes to stabilize yields and reduce batch-failure risk across the pharmaceutical manufacturing market.
In-house sites held 58.79% share in 2025, sustained by legacy capabilities and intellectual-property considerations. Yet CDMOs, growing at 10.69% CAGR, have become central for cell-and-gene therapy, mRNA platforms, and high-potency APIs. As biosimilars and advanced modalities multiply, sponsors are outsourcing analytical development, fill-finish, and packaging to partners that can flex capacity quickly.
Hybrid approaches combine core in-house lines for flagship assets with outsourced manufacturing for variable-demand products, allowing companies to limit fixed-cost exposure. This strategy positions the pharmaceutical manufacturing market for balanced growth while enabling CDMOs to innovate in modular plant design and digital integration.
The Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Market Report is Segmented by Molecule Type (Biologics & Biosimilars (Large Molecules), Conventional Drugs (Small Molecules)), Manufacturing Mode (In-House, CMO/CDMO), Formulation (Tablets, Capsules, and More), Manufacturing Technology, Application, Prescription Type, and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 37.25% market share in 2025, anchored by more than USD 200 billion in announced capacity expansions from Roche, Eli Lilly, and Johnson & Johnson, each committing USD 50 billion-plus to U.S. projects. Executive Order 14293 streamlines domestic approvals, while continuous-processing pilots showcase innovation leadership. Canada and Mexico complement the regional network through pathway harmonization and cost-competitive API sites.
Europe maintains a strong position through established clusters in Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom. The proposed Critical Medicines Act aims to improve supply security and sustainability standards, driving investments in green chemistry and circular-manufacturing pilots. EMA guidance on continuous and modular plants helps align national authorities and accelerates market entry for advanced therapies across the continent.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region at 12.4% CAGR to 2031, led by India's expanding CRDMO ecosystem and China's mRNA and monoclonal antibody capacity additions. Japan, South Korea, and Australia supply high-purity biologics, while Singapore and Vietnam attract fill-finish projects that benefit from skilled labor pools and pro-investment policies. Regulatory convergence initiatives and government subsidies for automation position the pharmaceutical manufacturing market for sustained regional momentum.
- Pfizer
- Roche
- Novartis
- Merck
- Sanofi
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Abbvie
- AstraZeneca
- Takeda Pharmaceuticals
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Amgen
- Novo Nordisk
- Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Cipla
- Lonza Group
- Catalent
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising R&D Investments by Big Pharma
- 4.2.2 Acceleration of Continuous Manufacturing
- 4.2.3 Integration of AI, IoT, and Automation across Legacy Facilities
- 4.2.4 Biosimilar Surge Following Major Patent Expirations
- 4.2.5 Reshoring and Localization of API Production
- 4.2.6 Sustainability and Circular Manufacturing Initiatives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Global Drug Pricing Pressures and Cost Containment Policies
- 4.3.2 Supply Chain Disruptions for Critical Inputs
- 4.3.3 Regulatory Complexity for Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
- 4.3.4 Skilled Workforce Shortage in Biotech Manufacturing
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Molecule Type
- 5.1.1 Biologics & Biosimilars (Large Molecule)
- 5.1.2 Conventional Drugs (Small Molecule )
- 5.2 By Manufacturing Mode
- 5.2.1 In-house
- 5.2.2 CMO/CDMO
- 5.3 By Formulation
- 5.3.1 Tablets
- 5.3.2 Capsules
- 5.3.3 Injectables
- 5.3.4 Topical & Transdermal
- 5.3.5 Nasal & Pulmonary Sprays
- 5.3.6 Others
- 5.4 By Manufacturing Technology
- 5.4.1 Batch
- 5.4.2 Continuous
- 5.4.3 Single-Use
- 5.5 By Application
- 5.5.1 Oncology
- 5.5.2 Diabetes
- 5.5.3 Cardiovascular
- 5.5.4 Neurology
- 5.5.5 Respiratory
- 5.5.6 Others
- 5.6 By Prescription Type
- 5.6.1 Prescription Drugs
- 5.6.2 Over-the-Counter (OTC)
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Mexico
- 5.7.2 Europe
- 5.7.2.1 Germany
- 5.7.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.2.3 France
- 5.7.2.4 Italy
- 5.7.2.5 Spain
- 5.7.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.3.1 China
- 5.7.3.2 Japan
- 5.7.3.3 India
- 5.7.3.4 Australia
- 5.7.3.5 South Korea
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.7.4.1 GCC
- 5.7.4.2 South Africa
- 5.7.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.7.5 South America
- 5.7.5.1 Brazil
- 5.7.5.2 Argentina
- 5.7.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.2 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.3.3 Novartis AG
- 6.3.4 Merck & Co.
- 6.3.5 Sanofi
- 6.3.6 GSK
- 6.3.7 Eli Lilly and Company
- 6.3.8 AbbVie
- 6.3.9 AstraZeneca
- 6.3.10 Takeda
- 6.3.11 Bristol Myers Squibb
- 6.3.12 Amgen
- 6.3.13 Novo Nordisk
- 6.3.14 Sun Pharma
- 6.3.15 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 6.3.16 Teva
- 6.3.17 Cipla
- 6.3.18 Lonza Group AG
- 6.3.19 Catalent
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




