PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911706

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911706
North America Vegetable Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The North America vegetable seed market was valued at USD 2.03 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 2.14 billion in 2026 to reach USD 2.76 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.22% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
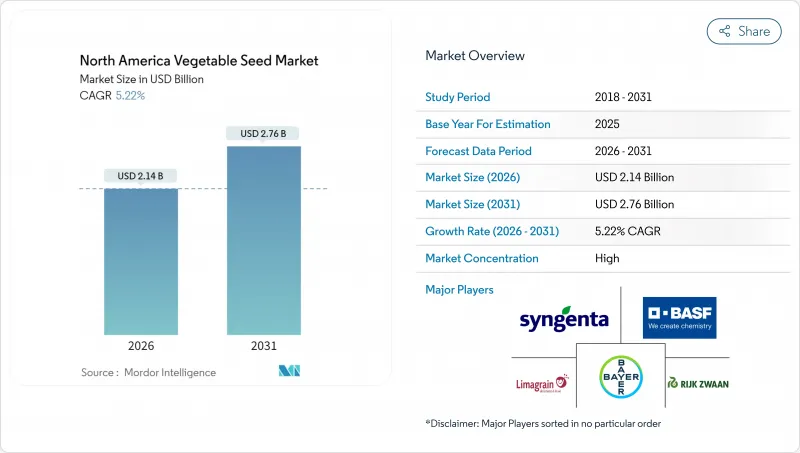
This growth trajectory reflects brisk adoption of hybrid genetics, rapid scaling of controlled-environment agriculture, sharper export orientation in Mexico, and steady policy support for gene-edited crops across the region. Large-scale United States producers continue to anchor demand, yet Mexico's protected-cultivation build-out and Canada's greenhouse modernization add fresh momentum. Capital inflows into breeding infrastructure, exemplified in new research facilities, underscore rising competitive intensity. Meanwhile, climate-driven pest volatility and counterfeit seed trade create operational risks that incentivize resilient trait development and tighter supply-chain oversight.
North America Vegetable Seed Market Trends and Insights
Rising Adoption of Hybrid Varieties
Hybrid seed uptake accelerates as growers prioritize resilience against heat spikes and novel pathogens. Mexico's tomato exporters attain 96% shipment orientation to United States buyers using hybrid lines that sustain quality under long-haul logistics. Public universities complement corporate pipelines; UC Davis released jalapeno hybrids suited to organic systems, while New Mexico State University introduced NuMex Enchantment serrano with heightened sunscald protection. Trait stacking, combining multiple resistance genes with shelf-life enhancers, now anchors most new product launches, reinforcing hybrid dominance within the North America vegetable seed market.
Expansion of Controlled-Environment Agriculture
Protected cultivation infrastructure investment fundamentally reshapes seed demand patterns as growers transition from field-adapted varieties to greenhouse-optimized genetics. Canada's greenhouse vegetable sector spans 23.4 million square meters with production valued at USD 2.0 billion, while Mexico adds over 1,500 hectares of protected cultivation annually. BASF's strategic partnership with Plant Products targets controlled-environment agriculture markets specifically, recognizing that greenhouse production requires fundamentally different genetic profiles than field cultivation. The trend accelerates as climate change increases production risks in traditional growing regions, with Washington State projecting 35 additional days above 90°F heat index by mid-century in Eastern Washington, forcing growers toward protected systems that maintain consistent growing conditions regardless of external weather volatility.
Regulatory Uncertainty for Biotech Traits
Mexico's regulatory framework gaps for gene-edited crops create competitive disadvantages and market fragmentation across North America's integrated seed system. While USDA APHIS provides clear exemptions for CRISPR-edited varieties, Mexico lacks specific legal frameworks for gene editing, creating a regulatory gray area that neither explicitly permits nor prohibits commercial applications. Asociacion Mexicana de Semilleros (AMSAC) advocates for regulatory modernization to align with international standards under UPOV 91, emphasizing that delays create competitive disadvantages relative to Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and other countries that have established clear gene editing pathways. This uncertainty forces seed companies to maintain separate product portfolios for different markets, increasing development costs and slowing trait deployment.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Demand for Organic and Specialty Produce
- USDA Approval of CRISPR-Edited Seeds
- Climate-Driven Pest-Pressure Volatility
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hybrid varieties accounted for 92.55% of the North America vegetable seed market share in 2025, generating reliable revenue that funds long-horizon R&D. The segment's 5.18% CAGR to 2031 indicates sustained, not explosive, expansion, yet market leaders channel steady cash flow into CRISPR-enabled trait stacking that compresses time-to-market. Open-pollinated lines remain relevant for seed-saving farmers and certain organic certifications, but scale economics heavily favor hybrids across export-oriented tomato and pepper chains.
Demand for precise vigor, uniformity, and multi-disease packages secures hybrids' strategic edge. Syngenta's exclusive onion licensing with Emerald Seed underscores how intellectual-property control protects margins. Syngenta's exclusive partnership with Emerald Seed for onion licensing demonstrates how established players leverage hybrid platforms to accelerate trait deployment, while maintaining intellectual property control over valuable genetics. Open-pollinated varieties and hybrid derivatives serve niche markets focused on seed saving, organic production, and specialty applications where genetic uniformity is less critical than adaptability and cost considerations.
The North America Vegetable Seed Market Report is Segmented by Breeding Technology (Hybrids, and Open Pollinated Varieties and Hybrid Derivatives), Cultivation Mechanism (Open Field and Protected Cultivation), Crop Family (Brassicas, Cucurbits, and More), and Geography (Canada, Mexico, United States, and Rest of North America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Syngenta Group
- Bayer AG
- East-West Seed Group
- Bejo Zaden BV
- Groupe Limagrain
- Takii and Co.,Ltd.
- Enza Zaden BV
- BASF SE
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- High Mowing Organic Seeds
- Nong Woo Bio
- Sakata Seeds Corporation
- Johnny's Selected Seeds LLC
- Seedway (GROWMARK Inc.)
- VoloAgri Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
- 1.3 Research Methodology
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.1.1 Vegetables
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.2.1 Cucumber & Cabbage
- 4.2.2 Tomato & Onion
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.3.1 Vegetables
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.6 Market Drivers
- 4.6.1 Rising adoption of hybrid varieties
- 4.6.2 Expansion of controlled-environment agriculture
- 4.6.3 Demand for organic and specialty produce
- 4.6.4 USDA approval of CRISPR-edited seeds
- 4.6.5 Growth of direct-to-farmer e-commerce channels
- 4.6.6 Harmonized Canada-United States phytosanitary rules
- 4.7 Market Restraints
- 4.7.1 Regulatory uncertainty for biotech traits
- 4.7.2 Climate-driven pest-pressure volatility
- 4.7.3 Distributor consolidation squeezing small breeders
- 4.7.4 Counterfeit seed trade in Mexico
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECAST (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Family
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.1.2 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.1.3 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.5.3 Carrot
- 5.3.5.4 Okra
- 5.3.5.5 Peas
- 5.3.5.6 Spinach
- 5.3.5.7 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 Canada
- 5.4.2 Mexico
- 5.4.3 United States
- 5.4.4 Rest of North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.2 Bayer AG
- 6.4.3 East-West Seed Group
- 6.4.4 Bejo Zaden BV
- 6.4.5 Groupe Limagrain
- 6.4.6 Takii and Co.,Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Enza Zaden BV
- 6.4.8 BASF SE
- 6.4.9 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.10 High Mowing Organic Seeds
- 6.4.11 Nong Woo Bio
- 6.4.12 Sakata Seeds Corporation
- 6.4.13 Johnny's Selected Seeds LLC
- 6.4.14 Seedway (GROWMARK Inc.)
- 6.4.15 VoloAgri Group
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEED CEOS




