PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911741

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1911741
India Steel - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
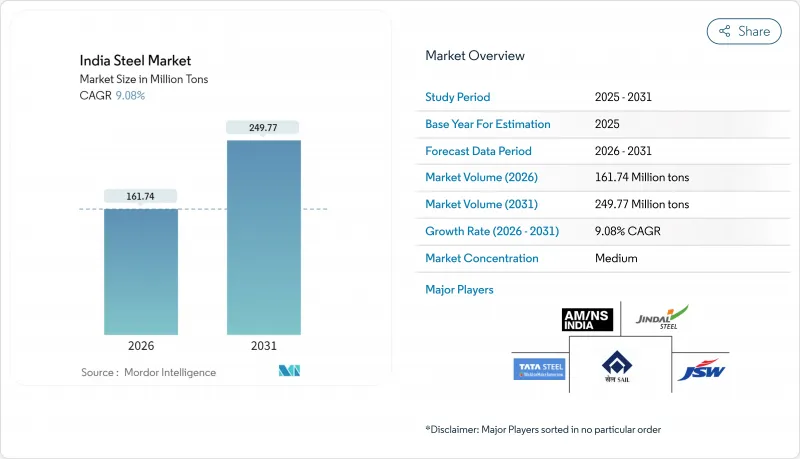
India Steel Market size in 2026 is estimated at 161.74 million tons, growing from 2025 value of 148.28 million tons with 2031 projections showing 249.77 million tons, growing at 9.08% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Expanding capacity targets of 300 million tons by 2030, accelerating infrastructure spending, and policy incentives together anchor this trajectory, positioning the India steel industry as the world's second-largest producer cohort. Government-backed megaprojects such as Bharatmala's 34,800 km highway build-out, PM-AWAS's large-scale housing programs, and Smart Cities 2.0 create durable domestic offtake, while an emerging green-steel policy ecosystem channels investment toward low-carbon technologies. Competitive intensity remains high, as leading producers race to secure brown- and green-field capacity, hedge against import surges, and comply with export-linked environmental mandates, such as the EU's CBAM. Simultaneously, state-level advantages in raw material availability and logistics connectivity spur an eastward production shift, supporting regional economic development and optimizing supply chain costs. Despite rising decarbonization outlays, capital efficiency gains, and value-added product strategies, these help shield operating margins amid volatile raw-material prices, thereby strengthening the overall resilience of the India steel industry.
India Steel Market Trends and Insights
Strong Policy Support
A comprehensive framework, combining the National Steel Policy's 300 million ton capacity target, the PLI scheme for specialty steel, and the mandate for domestically manufactured iron and steel products, underpins demand certainty across the India steel industry. Production-linked incentives worth INR 27,106 crore have already unlocked 7.9 million tons of specialty capacity and nearly 15,000 jobs. Preferential procurement thresholds of 15-50% value-added bolster domestic suppliers in government tenders, while real-time import monitoring via the Steel Import Monitoring System refines trade remedy decisions. Infrastructure integration through PM-Gati Shakti lowers logistics costs by up to 15%, sharpening competitiveness for producers in mineral-rich regions. Finally, the Bureau of Indian Standards enforces quality compliance, ensuring that new capacity delivers globally acceptable product grades that align with export market requirements.
Surge in Domestic and Foreign CAPEX for Brown-/Green-field Capacity
Private and public commitments exceeding USD 25 billion have amplified the India Steel investment cycle, drawing marquee entrants and expanding incumbents. ArcelorMittal Nippon Steel's INR 1.5 lakh crore Andhra Pradesh complex exemplifies technology-transfer driven upgrades in advanced high-strength grades. SAIL's trajectory from 20 million tons to 35.65 million tons capacity by 2031, supported by incremental FY25 capex allocations, highlights public-sector alignment with national targets. Strategic FDI flows embed knowledge of low-carbon technologies, while mineral-rich eastern clusters shorten raw material supply lines and enable economies of scale. Employment multipliers reinforce state support, creating virtuous cycles of skill development and industrial growth across the India Steel industry.
Per-Capita Steel Consumption Still Below Global Average
At 93.44 kg in 2023, India's per-capita steel usage remains far below the 230 kg global mean, signaling untapped potential but also revealing structural bottlenecks. Rural markets, which account for 65% of the population, have disproportionately low demand due to limited infrastructure penetration and income constraints. Consumption disparities complicate capacity-planning decisions, as producers must balance supply expansion with realistic regional demand curves. These patterns underline the need for parallel investments in rural infrastructure to unlock the full potential of the India Steel industry.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Large Infrastructure Pipeline (Bharatmala, PM-AWAS, Smart Cities 2.0)
- Hydrogen-Based DRI Pilots and Scrap Substitution Push
- ESG-Linked Export Carbon Tariffs (EU CBAM)
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The BF-BOF route held 46.12% India Steel industry share in 2025, a level underscoring the entrenched integrated-plant footprint that still delivers cost advantages on large volumes. The India steel market size for BF-BOF output is forecast to compound at an 8.77% CAGR as producers sweat existing assets even while charting decarbonization roadmaps. Declining unit emissions through incremental efficiency gains and partial hydrogen injection illustrate pragmatic transition pacing. Electric-arc furnaces are gaining traction in scrap-rich urban clusters, signaling a future redistribution of capacity toward low-carbon hubs. Emerging hydrogen DRI pilot plants introduce a third vector, although commercial uptake hinges on green-hydrogen cost parity, which is expected only beyond 2030.
In the medium term, BF-BOF complexes evolve through the use of hot-blast stoves, top-pressure recovery turbines, and slag granulation upgrades, thereby enhancing energy recovery and product quality. Technology partnerships accelerate process-control digitalization, widening yield spreads between best- and average-practice plants. Meanwhile, secondary producers leverage EAF flexibility to nimbly supply specialty grades and meet evolving construction standards. The coexistence of multiple routes reflects the India Steel market size and varied regional scrap-availability profiles, suggesting a gradual rather than abrupt technology realignment.
Crude steel constitutes the entire basic-form segment and is forecast to climb at a 7.73% CAGR, mirroring upstream capacity additions across integrated and secondary mills. High utilization rates of roughly 80% underscore latent headroom before extensive green-field builds are required. Iron-ore self-sufficiency across Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Karnataka grants crude-steel producers a sustained raw-material edge compared with import-dependent peers in Southeast Asia, strengthening the india steel industry position in the region.
Enabling policies, such as captive mine allocations and express environmental clearances for expansion projects, expedite throughput gains in the India steel market. Simultaneously, the Steel Scrap Recycling Policy aims to lift scrap use from 25% to 70%, driving process efficiency. Crude steel players are increasingly integrating predictive maintenance analytics and process optimization software, narrowing the gap to best performance and trimming energy intensity. These moves collectively solidify the segment's centrality within the India steel industry.
The India Steel Report is Segmented by Technology (Blast Furnace-Basic Oxygen Furnace, Electric Arc Furnace, and Other Technologies), Basic Form (Crude Steel), Final Form (Finished Steel), and End-User Industry (Automotive and Transportation, Building and Construction, Tools and Machinery, Consumer Goods, Energy, and Other End-User Industries). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Million Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- AM/NS India
- Godawari Power and Ispat
- Jindal Steel & Power Limited
- JSW Steel Limited
- Kalyani Steels
- Mukand Ltd.
- NMDC Steel Limited
- Rashtriya Ispat Nigam Limited
- Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL)
- Tata Steel
- Vedanta Limited
- VISA STEEL
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Strong Policy Support
- 4.2.2 Surge in Domestic and Foreign CAPEX for Brown-/Green-Field Capacity
- 4.2.3 Large Infrastructure Pipeline (Bharatmala, PM-AWAS, Smart Cities 2.0)
- 4.2.4 Auto OEM Pivot to High-Strength AHSS and EV-Grade Steels (Under-Reported)
- 4.2.5 Hydrogen-Based DRI Pilots and Scrap Substitution Push (Under-Reported)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Per-Capita Steel Consumption Still Below Global Average.
- 4.3.2 Volatile Raw-Material and Energy Costs
- 4.3.3 ESG-Linked Export Carbon Tariffs (E.G., EU CBAM) (Under-Reported)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Blast Furnace-Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF)
- 5.1.2 Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
- 5.1.3 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Basic Form
- 5.2.1 Crude Steel
- 5.3 By Final Form
- 5.3.1 Finished Steel
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.4.2 Building and Construction
- 5.4.3 Tools and Machinery
- 5.4.4 Consumer Goods
- 5.4.5 Energy
- 5.4.6 Other End-User Industries
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (MandA, JVs, CAPEX, Green-steel deals)
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level overview, Market-level overview, Core segments, Financials, Strategic information, Market rank/share, Products and Services, Recent developments)
- 6.4.1 AM/NS India
- 6.4.2 Godawari Power and Ispat
- 6.4.3 Jindal Steel & Power Limited
- 6.4.4 JSW Steel Limited
- 6.4.5 Kalyani Steels
- 6.4.6 Mukand Ltd.
- 6.4.7 NMDC Steel Limited
- 6.4.8 Rashtriya Ispat Nigam Limited
- 6.4.9 Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL)
- 6.4.10 Tata Steel
- 6.4.11 Vedanta Limited
- 6.4.12 VISA STEEL
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Circular Economy and Scrap Processing Hubs
- 7.3 Green-steel Premiums and Export Windows




