PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934592

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934592
South America Molluscicides - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The South America molluscicides market is expected to grow from USD 120 million in 2025 to USD 127.02 million in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 168.62 million by 2031 at 5.83% CAGR over 2026-2031.
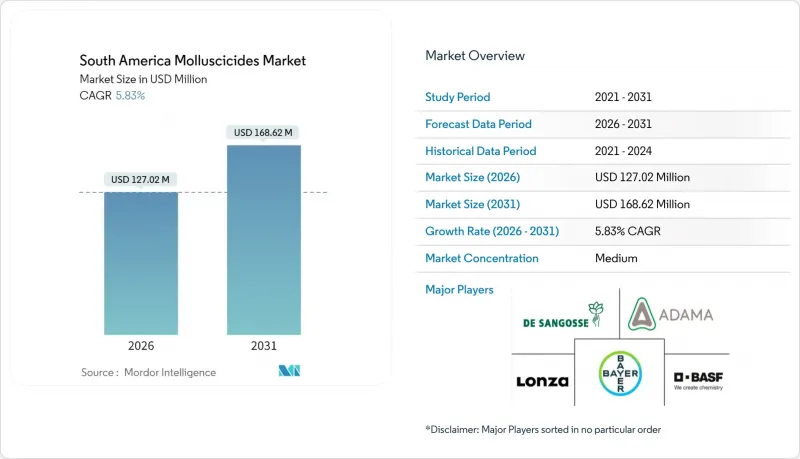
The South America molluscicides market is benefiting from climate-induced humidity spikes that accelerate gastropod breeding cycles, a swift transition toward safer iron-phosphate actives, and public subsidy programs that reward integrated pest management compliance. Brazil retains leadership in large-scale horticulture exports, robust coffee and sugarcane acreage, and government credit lines that link loan eligibility to sustainable pest-control protocols. Colombia's specialty-crop boom and Chile's export-quality mandates further reinforce regional demand while favoring premium, rain-fast pellet innovations. Competitive intensity is moderate, with five suppliers capturing significant revenue share, yet niche local formulators remain relevant by tailoring products to micro-climates and resistance-management needs.
South America Molluscicides Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Slug and Snail Infestations from Climate-Change-Driven Humidity Spikes
Warmer temperatures and heavier rainfall shorten the dormancy period for Deroceras and Pomacea species, intensifying gastropod attacks in soybeans, coffee, and vegetables. Field studies show that a 2 °C temperature increase combined with 20% more precipitation can triple reproductive rates, forcing growers to extend baiting windows well into harvest. Brazilian Cerrado farms now schedule two additional pellet applications per season to protect early-maturing horticulture crops. Similar trends surface in Colombia's Andean valleys, where persistent dew films allow slugs to feed overnight even during traditionally dry months. The expanded pressure elevates per-hectare molluscicide spending, especially on high-potency pellets that survive recurring rain events.
Government Subsidy Programs for Sustainable Coffee, Sugarcane, and Horticulture Production
Brazil's National Program for Strengthening Family Agriculture offers subsidized credit only when growers document integrated pest-management plans that favor ferric-phosphate over metaldehyde. Colombia's coffee-sector modernization grants reimburse up to 30% of molluscicide costs if GPS-guided spreaders are used, spurring adoption of variable-rate pellets. Argentina widened its sustainable-farming tax code in 2025 to credit molluscicide resistance-management plans, indirectly lifting demand for dual-mode baits. These financial carrots shift purchasing decisions away from lowest-cost options toward safer formulations that pass residue audits. As subsidies tie compliance to loan terms, demand remains resilient even when commodity prices soften .
Tightening South American Regulations on Metaldehyde Residues
Brazil's ANVISA harmonized maximum-residue limits with European thresholds in 2024, forcing growers to lower field rates or pivot to ferric-phosphate for export-bound produce. Argentina's SENASA added buffer-zone and timing rules that complicate metaldehyde scheduling during rainy seasons. Compliance audits often coincide with peak harvest, magnifying economic risk if residue fines suspend shipments. Distributors report a 15% drop in metaldehyde volume where coffee and berries are dominant. Regulatory drag, therefore, tempers the expansion of legacy chemistries despite their cost advantage.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in Horticulture Exports Demanding Blemish-Free Produce
- Launch of Rain-Fast, Extended-Residual Pellet Formulations
- High Cost Premium of Iron-Phosphate Active Ingredient
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Metaldehyde held 59.35% of South America's molluscicides market share in 2025, due to decades of cost-effective performance across soybeans, maize, and horticulture. Even so, iron-phosphate revenue is climbing at a 9.26% CAGR as export-certification bodies and domestic regulators impose stricter residue controls. The South America molluscicides market size for iron-phosphate products is forecast to almost double by 2031, with high-value fruit, vegetable, and ornamental segments absorbing the premium. Second-tier actives such as methiocarb maintain pockets of relevance in ornamentals, especially where rapid knockdown is required before shipment to urban retailers.
Combination products linking multiple modes of action are gaining traction as resistance emerges in continuous-cropping systems. Patent filings that pair niclosamide with carbaryl illustrate industry efforts to diversify chemical pressure while meeting evolving safety thresholds . Suppliers also explore biological co-formulants that improve palatability and regulate bait moisture, extending field life in humid micro-climates. These innovations collectively reinforce the perception that robust stewardship and safety compliance will dictate future active-ingredient adoption trajectories across the South America molluscicides market.
Contact formulations generated 40.75% of the South America molluscicides market size in 2025 due to proven broad-spectrum lethality, simple calibration, and compatibility with existing pellet spreaders. Marketing focus now pivots to next-generation repellent chemistries that create protective barriers for 2-3 weeks with minimal re-entry intervals, appealing to specialty-crop growers with high labor costs. Repellent revenues are forecast to expand at a 8.87% CAGR through 2031.
Ingestive baits remain a staple for perimeter defense around greenhouses, while systemic options serve niche aquatic uses where dissolved uptake curbs invasive snails. Regulatory agencies in Brazil and Argentina increasingly encourage rotation among contact, repellent, and ingestive modes to reduce resistance risk. As integrated pest management becomes mainstream, demand tilts toward labeled products that clearly specify mode-of-action groups, enabling growers to plan season-long rotation calendars.
The South America Molluscicides Market Report is Segmented by Active Ingredient (Metaldehyde, Iron Phosphate and More), by Mode of Action (Contact, Ingestive and More), by Formulation (Pellets, Liquids and More), by Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, and More), by Application Method (Agricultural Fields and More), and by Geography (Brazil, Argentina, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Bayer AG
- BASF SE
- Syngenta AG
- De Sangosse Ltd.
- Lonza Group AG
- Adama Ltd.
- American Vanguard Corporation (AMVAC)
- ANASAC
- UPL Ltd.
- Bequisa
- Certis Biologicals
- Nufarm Limited
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating slug and snail infestations from climate-change-driven humidity spikes
- 4.2.2 Government subsidy programs for sustainable coffee, sugarcane, and horticulture production
- 4.2.3 Surge in horticulture exports demanding blemish-free produce
- 4.2.4 Launch of rain-fast, extended-residual pellet formulations
- 4.2.5 Andean shift toward specialty crops increasing mollusk pressure in high-altitude zones
- 4.2.6 EU metaldehyde ban diverting safer iron-phosphate production capacity to Brazil
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Tightening South American regulations on metaldehyde residues
- 4.3.2 High-cost premium of the iron-phosphate active ingredient
- 4.3.3 Rising mollusk resistance to single-mode chemistries
- 4.3.4 Informal trade in counterfeit crop-protection inputs
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Active Ingredient
- 5.1.1 Metaldehyde
- 5.1.2 Iron Phosphate
- 5.1.3 Other Chemical Actives (e.g., Methiocarb)
- 5.2 By Mode of Action
- 5.2.1 Contact
- 5.2.2 Ingestive
- 5.2.3 Systemic
- 5.2.4 Repellent
- 5.3 By Formulation
- 5.3.1 Pellets
- 5.3.2 Granules
- 5.3.3 Liquids
- 5.3.4 Powders
- 5.4 By Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.4.2 Cereals and Grains
- 5.4.3 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.4.4 Ornamentals
- 5.4.5 Forage and Pasture Crops
- 5.5 By Application Method
- 5.5.1 Agricultural Fields
- 5.5.2 Aquatic Areas
- 5.5.3 Industrial and Commercial Premises
- 5.5.4 Residential Gardens
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2 Argentina
- 5.6.3 Chile
- 5.6.4 Colombia
- 5.6.5 Peru
- 5.6.6 Rest of South America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Bayer AG
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Syngenta AG
- 6.4.4 De Sangosse Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Lonza Group AG
- 6.4.6 Adama Ltd.
- 6.4.7 American Vanguard Corporation (AMVAC)
- 6.4.8 ANASAC
- 6.4.9 UPL Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Bequisa
- 6.4.11 Certis Biologicals
- 6.4.12 Nufarm Limited
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




