PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934701

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934701
Space Mining - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The space mining market was valued at USD 2.58 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 3.07 billion in 2026 to reach USD 7.39 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 19.18% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
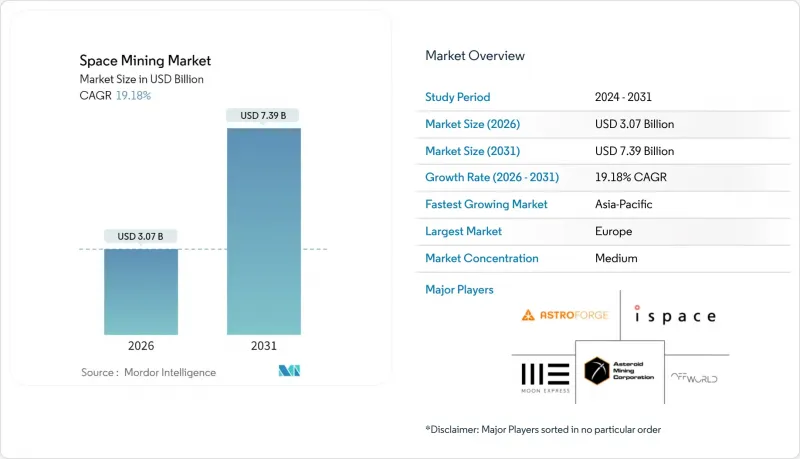
Robust growth is encouraged by sharply falling launch costs enabled by reusable rockets, rising shortages of critical minerals on Earth, and multibillion-dollar government programs that treat off-planet resources as strategic assets. A steady shift from pure research missions to early-stage extraction trials widens the commercial funnel. At the same time, improved in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) technologies shorten payback horizons for capital-intensive projects. Policy clarity under the Artemis Accords and compatible national regulations further reduces investor uncertainty, supporting the next wave of private-sector participation.
Global Space Mining Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Decline in Launch Costs
Reusable heavy-lift vehicles have reduced average orbital launch prices by more than 60% since 2020, with leading systems targeting costs of around USD 100 per kilogram for high-flight-rate scenarios. These economics enable high-value asteroid mining missions to transition from theoretical models to credible business cases, particularly for the retrieval of platinum group metals. The lower threshold attracts smaller operators that previously relied on ride-shares, spurring competition and additional price declines. National space agencies benefit by shifting fixed-price contracts to commercial providers, redirecting public funds toward lunar infrastructure and ISRU demonstrations. The resulting demand flywheel reinforces the growth trajectory of the space mining market.
Rising Demand for PGMs and Rare-Earths in Clean Tech
Fuel-cell vehicles, electrolyzers, and high-capacity batteries require substantial volumes of irreplaceable metals. Forecast supply gaps for platinum group metals exceed 500,000 oz annually through 2028, while rare-earth requirements may quadruple by 2050 to meet global climate goals. Terrestrial production remains geographically concentrated and vulnerable to geopolitical tensions, exposing manufacturers to price fluctuations and supply disruptions. Celestial metal deposits offer a diversification path that could relieve tightness in terrestrial markets and stabilize input costs for clean-tech manufacturers. Early-stage off-planet sourcing aligns with corporate sustainability mandates by lowering land-based ecological footprints.
Extremely High CAPEX and Technology Risk
Complex thermal, mechanical, and robotic challenges raise mission budgets into the hundreds of millions of dollars, with cash flows delayed until resources are processed and transported. Engineering unknowns in abrasive regolith environments or low-gravity asteroid fields create binary success-failure outcomes, increasing the cost of capital. Insurance premiums for deep-space assets remain elevated, and conventional project finance structures seldom accommodate multi-year, non-revenue-generating periods. Investors, therefore, demand hybrid equity-grant models or government milestone payments that dilute overall returns, tempering the pace at which the space mining market can scale.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government ISRU Funding and Artemis Accords
- Expansion of Private Ride-Share Launch Services
- Space-Debris Collision Hazards
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
3D printing corresponds to 42.12% of the space mining market size for applications. This dominance stems from the immediate value of on-orbit manufacturing, which reduces the need to loft bulky spare parts from Earth. Utilizing local feedstock for structural repair and tool fabrication reduces logistics costs and facilitates rapid mission turnaround. Construction applications have the fastest-growing outlook, with a 25.85% CAGR. Emerging concepts for inflatable habitats reinforced with in-situ metal frameworks underpin this momentum by demonstrating a cost-effective approach to the rollout of a lunar base. Human-life-support systems form a third pillar, drawing specialized attention to water recycling and oxygen generation units that depend on reliably mined volatiles. Fuel-refueling services are showing steady progress, leveraging cryogenic depots that establish a closed-loop trade between resource nodes and transportation corridors. Collectively, these threads reinforce the core premise that the space mining market supplies the material backbone of sustainable off-planet economies.
Follow-on growth hinges on integrating additive manufacturing tool chains and autonomous excavation platforms. Machine learning (ML) algorithms enhance sintering accuracy in microgravity, while metal-polymer composite techniques expand the range of usable feedstocks. Demonstrations aboard the International Space Station (ISS) validate print quality, accelerating acceptance in crewed missions beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Regulatory agencies have begun codifying part-qualification standards, giving operators confidence to deploy printed components in load-bearing roles. As infrastructure scales, the application mix within the space mining market will likely shift toward higher-end fabrication, such as pressure vessels and radiation-shielding panels, further boosting demand for refined metals and ceramic precursors.
Water and volatile compounds hold 47.55% of the 2025 revenue. Their primacy reflects universal utility as a drinkable fluid, a radiation shield, and an electrolysis feedstock for hydrogen-oxygen propellant. Permanently shadowed lunar craters host ice reserves reachable by hopping landers, offering early cash flow before complex metal refineries come online. Rare-earth elements and platinum group metals are expected to hold the highest upside, with a 23.52% CAGR, driven by clean-energy supply pressures. Sample-return missions have confirmed the presence of palladium, iridium, and neodymium in M-type asteroids, thereby validating resource models for these asteroids. Structural metals such as aluminum and titanium trail in gross margins but fill essential construction demand, especially as molten-regolith electrolysis achieves pilot-plant status.
Technology maturation is steadily translating orbital assays into reserve classifications akin to terrestrial JORC or NI-43-101 standards. Spectroscopy, combined with neutron-gamma loggers, provides real-time grade control, reducing exploration risk. Simultaneously, improved high-vacuum furnaces now approach 85% metal recovery factors using only solar power concentrators, reducing energy imports. This convergence tightens the cost curve and supports a diversified resource slate, ensuring that the space mining market is not overly reliant on a single commodity cycle.
The Space Mining Market Report is Segmented by Application (Extraterrestrial Commodity, Construction, and More), Resource Type (Water and Volatiles, and More), Extraction Target Body (Near-Earth Asteroids, and More), Mission Phase (Spacecraft Design and Engineering, Launch Services, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained its top position, accounting for 36.12% of global revenue. Federal procurement of lunar propellant and export-credit support for private landers underpins this lead. The Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Act ensures that mined resources are recognized as private property, giving entrepreneurs legal certainty. Flagship Artemis missions serve as anchor tenants for propellant and construction feedstock, while a deep venture-capital ecosystem funds hardware spin-offs ranging from regolith conveyors to vacuum metallurgy units.
Asia-Pacific is projected to deliver the fastest regional CAGR of 23.62% through 2031. China's interagency program pairs university-led technology clusters with comprehensive state contracts that cover prospecting, excavation, and sample analysis. The launch of a multifunctional asteroid- and lunar-mining robot in March 2025 validated indigenous anchoring mechanisms suitable for microgravity. Japan's USD 6.4 billion Space Strategy Fund channels subsidies into ISRU robotics, while India's next phase of Chandrayaan leverages its low-cost launch niche to piggyback prospecting payloads.
Europe benefits from ESA's cohesive regulatory environment, which streamlines cross-border procurement. The Moonlight initiative envisions a secure satellite network offering private miners standardized navigation and communication services. Cooperative participation in the NASA-led Gateway will grant European firms preferential access to delivering construction materials. Countries in the Middle East and Latin America are exploring sovereign wealth investments and bilateral partnerships to secure the supply of helium-3 and strategic metals, suggesting broader geographical diversification for the space mining market by the end of the decade.
- Moon Express
- ispace, Inc.
- Asteroid Mining Corporation
- Off-World, Inc.
- Trans Astronautica Corporation
- Karman+
- Momentus Inc.
- AstroForge
- Helios Project Ltd.
- Bradford Engineering B.V.
- Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- Interlune Corporation
- Aganitha Space Technologies Pvt Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid decline in launch costs
- 4.2.2 Rising demand for PGMs and rare-earths in clean tech
- 4.2.3 Government ISRU funding and Artemis Accords
- 4.2.4 Expansion of private ride-share launch services
- 4.2.5 Micro-gravity additive manufacturing adoption
- 4.2.6 Emerging off-earth ESG/carbon-credit schemes
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Extremely high CAPEX and technology risk
- 4.3.2 Uncertain legal and regulatory framework
- 4.3.3 Commodity-price volatility and ROI risk
- 4.3.4 Space-debris collision hazards
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Extraterrestrial Commodity
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Human Life Sustainability
- 5.1.4 Fuel Mining
- 5.1.5 3D Printing
- 5.2 By Resource Type
- 5.2.1 Water and Volatiles
- 5.2.2 Rare-Earth and Platinum Group Metals
- 5.2.3 Structural Elements
- 5.3 By Extraction Target Body
- 5.3.1 Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs)
- 5.3.2 Main-Belt Asteroids
- 5.3.3 Lunar Regolith
- 5.3.4 Mars Moons (Phobos, Deimos)
- 5.4 By Mission Phase
- 5.4.1 Spacecraft Design and Engineering
- 5.4.2 Launch Services
- 5.4.3 Mining Operations and Logistics
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Moon Express
- 6.4.2 ispace, Inc.
- 6.4.3 Asteroid Mining Corporation
- 6.4.4 Off-World, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Trans Astronautica Corporation
- 6.4.6 Karman+
- 6.4.7 Momentus Inc.
- 6.4.8 AstroForge
- 6.4.9 Helios Project Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Bradford Engineering B.V.
- 6.4.11 Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- 6.4.12 Interlune Corporation
- 6.4.13 Aganitha Space Technologies Pvt Ltd.
- 6.5 Space Agencies
- 6.5.1 Asteroid Mining Corporation
- 6.5.2 Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
- 6.5.3 China National Space Administration
- 6.5.4 National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- 6.6 Emerging Startups
- 6.6.1 Terra Luna Resources Inc.
- 6.6.2 Aganitha Space Technologies Pvt Ltd.
- 6.6.3 Astrum Drive Technologies
- 6.6.4 Orbital Mining Corporation
- 6.6.5 Solid State Propulsion (SSP)
- 6.6.6 PLANETES INT Pte. Ltd.
- 6.6.7 ELO2 Consortium
- 6.6.8 Ethos Space
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




