PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934725

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934725
Agricultural Biologicals - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
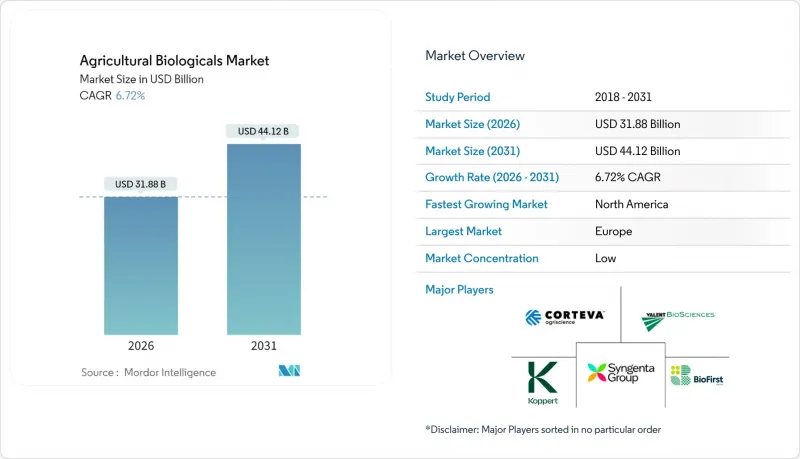
The agricultural biologicals market is expected to grow from USD 29.87 billion in 2025 to USD 31.88 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 44.12 billion by 2031 at 6.72% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Escalating regulatory scrutiny of synthetic residues, farmer demand for soil health solutions, and the acceleration of artificial intelligence-enabled strain discovery collectively propel growth. Large food retailers are tightening residue standards, widening the addressable base beyond certified-organic farms. Rapid microbial research and development (R&D) cycles now deliver commercial candidates in months instead of years, compressing time-to-market and intensifying competitive churn. Corporate capital commitments to local manufacturing and on-farm fermentation lower logistics costs and widen geographic reach.
Global Agricultural Biologicals Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Organic, Residue-Free Produce
Organic food sales in the United States rose 4.6% to USD 67.2 billion in 2024, reflecting shoppers' heightened vigilance over pesticide residues. Premium pricing for certified produce incentivizes conventional growers to adopt biological inputs that help them clear stringent retailer tests. Similar patterns unfold in expanding middle-income segments of Asia, where food safety ranks high among household concerns. As supermarkets tighten private residue standards, biological solutions move from optional to compulsory within many supply contracts. The pull effect boosts recurring demand across biofertilizer, biostimulant, and biopesticide categories.
Stringent Global Curbs on Synthetic Agro-Chemicals
The European Union has banned more than 70 active ingredients since 2020 under its Farm to Fork Strategy, whereas the United States Environmental Protection Agency allows fast-track registration for eligible microbial pesticides. Tighter maximum residue limits shorten the commercial life of many synthetic products. Farmers now face fewer chemical options, raising the strategic value of biological substitutes that clear regulatory hurdles in roughly 18 months, half the timeline of conventional actives. Policymakers' alignment on risk-reduction amplifies the long-run demand floor for biologicals.
Short Shelf Life and Cold-Chain Dependence Of Many Formulations
Many live-culture formulations require storage between 2 °C and 8 °C, which can increase distribution costs by up to 40% where refrigerated trucking is limited. Heat exposure during last-mile delivery can significantly reduce viable colony counts and compromise field performance, eroding farmer confidence. Tropical markets in Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa experience the highest spoilage rates, which constrain volume growth unless shelf-stable formulations scale rapidly.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Integration of Biologicals into Corporate IPM Programs
- Carbon-Credit Revenue from Regenerative Farming Practices
- Complex, Non-Harmonized Registration Pathways
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Crop nutrition maintained a commanding 63.55% share of the agricultural biologicals market in 2025 as growers prioritized soil microbiome resilience and nutrient-use efficiency. The segment's leadership reflects tangible cost savings from reduced synthetic fertilizer demand and improved carbon-credit earnings. Within this category, biofertilizers that fix nitrogen deliver up to 50 pounds per acre equivalence, directly lowering input purchases. Biostimulants extend benefits by enhancing abiotic stress tolerance, a valued trait amid widening climate variability.
Crop nutrition is growing at a robust pace, outpacing all other functions with a 6.78% CAGR. In addition, the maturity of crop nutrition ensures continued volume dominance. However, portfolio diversification into combined nutrition-protection products is rising as manufacturers pursue cross-functional value propositions.
Beyond volume metrics, innovation intensity differentiates players. AI-guided strain selection now underpins next-generation inoculants that deliver precise metabolite profiles, cutting trial-and-error costs while elevating field consistency. Nutrient formulations are increasingly integrating carrier chemistries that shield microbes from UV radiation and desiccation, extending shelf life to 18 months without refrigeration.
The Agricultural Biologicals Market Report is Segmented by Function (Crop Nutrition Into Organic Fertilizers, Biofertilizers, and Biostimulants); (Crop Protection Into Biopesticides and Biocontrol Agents), by Crop Type (Row Crops, Horticultural Crops, Cash Crops), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
Geography Analysis
Europe held a 34.05% share of the agricultural biologicals market in 2025, underpinned by the European Union's combination of chemical bans and financial stimuli for organic transitions. Member states reimburse up to 25% of biological input costs within eco-scheme payments, shortening grower payback horizons. Despite its scale, expansion moderates as penetration nears 100% in high-value fruit sectors, prompting European suppliers to pivot outward and export regulatory expertise and formulations through technology partnerships.
North America registered the fastest 8.55% CAGR by 2031. The Coordinated Framework for Biotechnology simplifies microbial approvals to an 18-month median, catalyzing product pipeline throughput. Capital spending on domestic fermentation plants by Corteva and BASF exceeds USD 700 million, signaling a long-term commitment. Cross-border regulatory alignment with Canada further enlarges the contiguous addressable market, while Mexico's export-oriented fruit sector adopts biologicals to meet European residue limits.
The Asia-Pacific region stands as the emerging frontier, driven by India's expedited clearance of 15 biological pesticides in 2024 and China's subsidy program, which rebates up to 30% of farmers' purchases. Investment in decentralized production hubs mitigates cold-chain gaps, making biologicals viable in tropical smallholder systems. Regional market growth also benefits from mounting consumer backlash against chemical overuse and soil contamination. South America sustains robust volume growth anchored in Brazil's soybean dominance. Local fermentation capacity and Brazil's IN 36 fast-track process reduce approval costs, catalyzing a surge in domestic and multinational launches tailored to Cerrado soils. Argentina and Chile accelerate adoption to preserve export competitiveness as European importers enforce tougher residue ceilings.
- Corteva Agriscience
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG
- UPL Limited
- Novonesis A/S
- Koppert Biological Systems B.V.
- Biofirst Group NV
- Valent BioSciences LLC
- FMC Corporation
- Rovensa S.A.
- Certis USA LLC
- ProFarm Group Inc.
- Andermatt Biocontrol AG
- Yara International ASA
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
- 1.3 Research Methodology
2 Executive Summary and Key Findings
3 Report Offers
4 Key Industry Trends
- 4.1 Area Under Organic Cultivation
- 4.2 Per Capita Spending On Organic Products
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Argentina
- 4.3.2 Australia
- 4.3.3 Brazil
- 4.3.4 Canada
- 4.3.5 China
- 4.3.6 Egypt
- 4.3.7 France
- 4.3.8 Germany
- 4.3.9 India
- 4.3.10 Indonesia
- 4.3.11 Italy
- 4.3.12 Japan
- 4.3.13 Mexico
- 4.3.14 Netherlands
- 4.3.15 Nigeria
- 4.3.16 Philippines
- 4.3.17 Russia
- 4.3.18 South Africa
- 4.3.19 Spain
- 4.3.20 Thailand
- 4.3.21 Turkey
- 4.3.22 United Kingdom
- 4.3.23 United States
- 4.3.24 Vietnam
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Annalysis
- 4.5 Market Drivers
- 4.5.1 Rising demand for organic, residue-free produce
- 4.5.2 Stringent global curbs on synthetic agro-chemicals
- 4.5.3 Integration of biologicals into corporate IPM programs
- 4.5.4 Carbon-credit revenue from regenerative farming practices
- 4.5.5 AI-enabled microbial-strain discovery accelerates R&D cycles
- 4.5.6 On-farm fermentation and local bio-input manufacturing models
- 4.6 Market Restraints
- 4.6.1 Short shelf-life and cold-chain dependence of many formulations
- 4.6.2 Complex, non-harmonized registration pathways
- 4.6.3 Proliferation of counterfeit and sub-standard biologicals
- 4.6.4 Volatile supply of critical feedstocks such as seaweed
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Crop Nutrition
- 5.1.1.1 Organic Fertilizers
- 5.1.1.2 Biofertilizers
- 5.1.1.3 Biostimulants
- 5.1.2 Crop Protection
- 5.1.2.1 Biopesticides
- 5.1.2.2 Biocontrol Agents
- 5.1.1 Crop Nutrition
- 5.2 By Crop Type
- 5.2.1 Row Crops
- 5.2.2 Horticultural Crops
- 5.2.3 Cash Crops
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 South America
- 5.3.2.1 Brazil
- 5.3.2.2 Argentina
- 5.3.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Spain
- 5.3.3.5 Italy
- 5.3.3.6 Netherlands
- 5.3.3.7 Russia
- 5.3.3.8 Turkey
- 5.3.3.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4.1 China
- 5.3.4.2 India
- 5.3.4.3 Japan
- 5.3.4.4 Australia
- 5.3.4.5 Vietnam
- 5.3.4.6 Thailand
- 5.3.4.7 Indonesia
- 5.3.4.8 Philippines
- 5.3.4.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.5 Middle East
- 5.3.5.1 Iran
- 5.3.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.3.6 Africa
- 5.3.6.1 South Africa
- 5.3.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.3.6.3 Egypt
- 5.3.6.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Overview, Market Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 Bayer AG
- 6.4.4 Syngenta AG
- 6.4.5 UPL Limited
- 6.4.6 Novonesis A/S
- 6.4.7 Koppert Biological Systems B.V.
- 6.4.8 Biofirst Group NV
- 6.4.9 Valent BioSciences LLC
- 6.4.10 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.11 Rovensa S.A.
- 6.4.12 Certis USA LLC
- 6.4.13 ProFarm Group Inc.
- 6.4.14 Andermatt Biocontrol AG
- 6.4.15 Yara International ASA
7 Key Strategic Questions for Agricultural Biological CEOs




