PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934783

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934783
United States School Bus - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
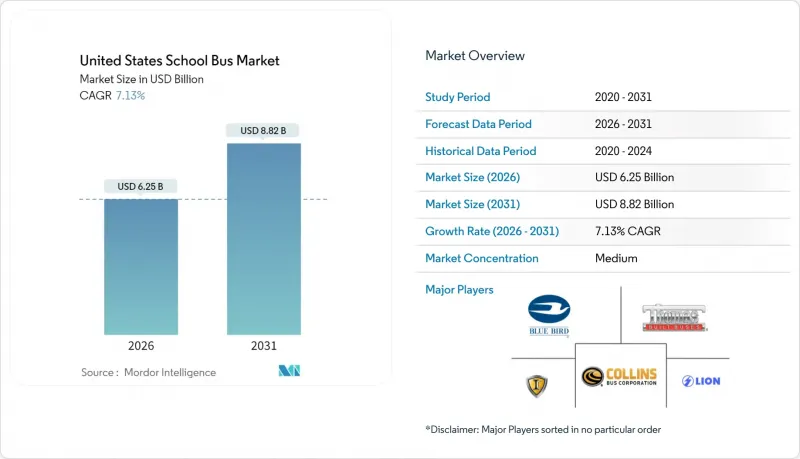
The United States school bus market was valued at USD 5.83 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 6.25 billion in 2026 to reach USD 8.82 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 7.13% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
With technological advancements, the emergence of electric school buses on roads underscores a dedication to environmental care and the future of younger generations. The swift transition towards battery-electric vehicles and innovative low-NOx solutions is poised to boost the adoption of electric school buses significantly. Simultaneously, stricter NHTSA safety mandates and state-level zero-emission purchase deadlines are advancing replacement decisions that might otherwise have been deferred. Industry participants are therefore balancing near-term chassis shortages, technician training gaps, and uneven charging infrastructure with longer-term opportunities such as vehicle-to-grid revenue streams and depot-based micro-grids that materially reduce total cost of ownership.
United States School Bus Market Trends and Insights
Federal Funding Surge via EPA Clean School Bus Program
The EPA Clean School Bus Program has altered procurement economics by offsetting up to 80% of incremental costs for battery-electric models, prompting districts to accelerate replacement schedules beyond normal depreciation cycles. Priority scoring directs 45% of funds to low-income and tribal communities, creating adoption clusters in markets that have historically faced limitations due to low tax bases. This wave of subsidized demand is expected to peak before the program sunsets in 2026, compressing procurement windows and intensifying competition for production slots. OEMs and battery suppliers are therefore expanding domestic capacity while forging utility partnerships to streamline charging deployments.
Aging National Fleet (Above 11 yrs) Pushing Replacement Demand
Average bus age now exceeds 11 years, well beyond the Federal Transit Administration's 12-year or 500,000-mile guidance, creating a backlog of sigiifcnat amount of buses units that must be cycled out within five years. Deferred maintenance costs are escalating, particularly in the Midwest, where harsh winters accelerate corrosion. Electric models cost roughly USD 0.40 per mile to maintain versus USD 0.70 for diesel, allowing life-cycle savings to offset higher purchase prices over 12 years . Rural systems with the oldest fleets are exploring propane or CNG bridges while evaluating grants for electrification infrastructure. OEMs are responding with modular electrified chassis that reuse existing Type C layouts, shortening the learning curve for district mechanics. This alignment of end-of-life timing and incentive availability underpins the robust growth outlook for the United States school bus market.
Sparse Rural Charging Infrastructure
Rural districts face a five-to-ten-fold deficit in public charging density compared with urban areas, complicating route planning for long daily runs. While Illinois' Williamsfield Schools overcame the hurdle via a campus microgrid that now meets 94% of energy needs, most rural systems lack the technical staff or utility partnerships to replicate the model. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act allocated USD 1.25 billion for rural EV infrastructure. However, project lead times exceed immediate replacement cycles, resulting in timing misalignments. Until Level 3 chargers become more widely available, diesel and propane will remain important fallback options, tempering overall electrification momentum in the United States school bus market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Stringent On-Board Safety Mandates Accelerating Fleet Renewal
- Low-NOx "Other Fuels" Demand in Non-Attainment Counties
- High Upfront Cost Of E-Buses Despite Incentives
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Type C (conventional) buses anchored the United States school bus market in 2025 with 78.05% share, and the segment is expected to deliver an 8.05% CAGR through 2031 as districts favor its blend of maneuverability and seating capacity. The United States school bus market size for this design is therefore poised to rise steadily as replacement cycles align with incentive windows that subsidize battery-electric retrofits. OEMs are fortifying Type C platforms with updated driver-assistance suites, while maintaining frame dimensions familiar to maintenance staff. Upgrade packages include electronic stability control and 360-degree camera systems that simplify driver training and reduce insurance premiums.
A parallel modernization wave is unfolding in Type D transit-style configurations, which cater to consolidated routes requiring 90-passenger capacity. Thomas Built's Saf-T-Liner EFX2 launch in March 2025 added rollover-enhanced body structures and lane-departure warnings, signaling an industry shift toward mass-transit safety norms. As districts consolidate depots and extend route lengths, Type D demand is projected to outpace historical averages, though limited production slots may constrain near-term deliveries. At the smaller end, Type A and B buses serve special-needs transport and tight urban corridors. While they remain niche in unit volume, a surge in individualized education programs is boosting growth prospects, especially for electric variants that can operate quietly during early-morning pickup windows.
Internal-combustion engines captured 88.40% of the United States School Bus Market size in 2025, yet the segment's share is forecast to shrink as battery-electric deployments accelerate under federal funding schemes. The United States school bus market size for electric models is set to climb rapidly, given their 37.09% CAGR through 2031. Diesel retains an edge in remote geographies where winter resilience and fuel availability remain paramount. Nevertheless, OEMs are integrating lower-NOx engines and idle-reduction systems to extend diesel relevance amid environmental scrutiny.
Electric momentum is particularly strong in states with zero-emission purchase mandates and utility demand-response incentives. Hybrid powertrains occupy a small but strategic niche, offering districts a transitional pathway that mitigates range anxiety while providing fuel savings of 20-30%. Propane and CNG models underpin compliance in ozone-non-attainment counties, their adoption bolstered by lower acquisition prices and familiar fueling infrastructure. Collectively, this diverse propulsion mix underlines why the United States school bus market remains simultaneously mature and transformative.
The United States School Bus Market Report is Segmented by Design Type (Type A (Cut-Away), Type B, and More), Powertrain Type (Internal Combustion Engine, Hybrid, and Electric), Ownership Model (District-Owned Fleets and Contractor-Owned Fleets), and Seating Capacity (Less Than 30 Seats, 30-60 Seats, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Blue Bird Corporation
- Daimler Truck North America LLC (Thomas Built)
- Navistar Inc. (IC Bus)
- Collins Bus Corporation
- Lion Electric Company
- GreenPower Motor Company Inc.
- Micro Bird Inc. (Girardin)
- BYD Motors USA
- Van-Con, Inc.
- Starcraft Bus
- Trans Tech Bus
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Federal Funding Surge via EPA Clean School Bus Program
- 4.2.2 Aging National Fleet (Above 11 yrs) Pushing Replacement Demand
- 4.2.3 Stringent On-board Safety Mandates Accelerating Fleet Renewal
- 4.2.4 Low-NOx "Other Fuels" Demand in Non-attainment Counties
- 4.2.5 Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) Revenue Potential for School Districts
- 4.2.6 Depot Micro-grid and Solar Pairing Lowers Electric TCO
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Sparse Rural Charging Infrastructure
- 4.3.2 High Upfront Cost Of E-Buses Despite Incentives
- 4.3.3 Scarcity Of High-Voltage Maintenance Technicians
- 4.3.4 Medium-Duty Chassis Supply Bottlenecks
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory & Funding Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD and Volume in Units)
- 5.1 By Design Type
- 5.1.1 Type A (Cut-away)
- 5.1.2 Type B
- 5.1.3 Type C (Conventional)
- 5.1.4 Type D (Transit-Style)
- 5.2 By Powertrain Type
- 5.2.1 Internal Combustion Engine (IC Engine)
- 5.2.2 Hybrid and Electric
- 5.3 By Ownership Model
- 5.3.1 District-Owned Fleets
- 5.3.2 Contractor-Owned Fleets
- 5.4 By Seating Capacity
- 5.4.1 Less than 30 Seats
- 5.4.2 30-60 Seats
- 5.4.3 Above 60 Seats
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves & Partnerships
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Blue Bird Corporation
- 6.4.2 Daimler Truck North America LLC (Thomas Built)
- 6.4.3 Navistar Inc. (IC Bus)
- 6.4.4 Collins Bus Corporation
- 6.4.5 Lion Electric Company
- 6.4.6 GreenPower Motor Company Inc.
- 6.4.7 Micro Bird Inc. (Girardin)
- 6.4.8 BYD Motors USA
- 6.4.9 Van-Con, Inc.
- 6.4.10 Starcraft Bus
- 6.4.11 Trans Tech Bus
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




