PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934901

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1934901
Commercial Vehicle Financing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
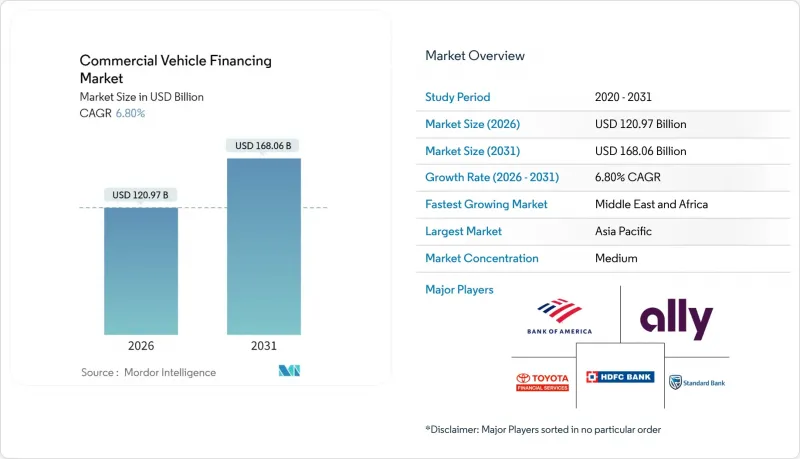
The commercial vehicle financing market is expected to grow from USD 113.27 billion in 2025 to USD 120.97 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 168.06 billion by 2031 at 6.8% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Rising electrification mandates, the spread of embedded finance inside OEM telematics, and the rapid build-out of last-mile delivery fleets are directing capital toward cleaner, more connected vehicles. Banks still originate the bulk of loans, yet non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) are expanding faster as they rely on digital underwriting, alternative credit data, and flexible repayment structures. Captive finance arms from manufacturers now embed credit offers directly into vehicle dashboards, cutting approval times and lowering acquisition costs. Regional growth patterns are bifurcated: Asia-Pacific retains leadership, while Middle East & Africa delivers the strongest CAGR as infrastructure spending and broader credit-bureau coverage unlock demand. The global funding environment remains supportive despite Basel IV capital headwinds because lenders are shifting portfolios to ESG-aligned vehicles in search of preferential terms.
Global Commercial Vehicle Financing Market Trends and Insights
Electrification Incentives for Medium-Duty Fleets
Federal and state programs are compressing payback periods for electric trucks, spurring sizeable loan origination volumes. The EPA's Clean Heavy-Duty Vehicles Program offers a considerable amount per truck, while Section 45W of the Inflation Reduction Act adds credits that grow exponentially, stacking with state-level rebates . California's Advanced Clean Fleets Rule compels large purchasers to reach 100% zero-emission buys by 2036, pushing fleets to secure funding earlier to lock in compliance. Massachusetts and Oregon mirror these incentives, giving lenders headroom to structure blended products that monetize credits up front. As a result, residual-value models now factor in incentive expiry dates and secondary-market demand for battery-electric vehicles. The mechanism widens the commercial vehicle financing market as borrowers capitalize on lower effective interest rates.
Growth of Last-Mile Delivery Start-Ups
Urban couriers experience high vehicle-turnover rates, driven by a surge in e-commerce, leading to a rising demand for lending. Amazon's Relay is linking preferred lenders with independent delivery providers, while Uber Freight has teamed up with AtoB, offering a blend of fuel cards and credit lines. Better Trucks, with significant funding, and Veho, raising substantial capital, are both scaling their regional networks, underscoring investor faith in fleet-centric fintech models. TruckSmarter has secured a major debt facility, aiming to introduce invoice factoring for gig-based owner-operators. These firms are gravitating towards flexible, usage-based products, fine-tuned to seasonal variations, thereby broadening the clientele for unconventional lenders. Yet, with saturation in key cities, growth in origination might face limitations post-2026.
Spike in Benchmark Rates Post-2025
As consumer auto rates ease, central-bank tightening is driving up costs for commercial vehicle loans. According to CNBC, average U.S. auto loans are expected to rise significantly in the near future. However, fleet borrowers often face higher costs compared to individual consumers. The Federal Reserve's cautious approach to rate cuts has resulted in sustained high coupon rates. This has led borrowers to opt for extended loan tenors, ultimately increasing their total interest expenses. Smaller operators, grappling with tight margins, find their eligibility diminished. As a result, many are turning to operating leases and revenue-share agreements, which transfer the residual-value risk to lessors. Additionally, funding pressures are driving consolidation among smaller lenders. Notably, several regional finance houses in the U.S. have pulled back from new-truck loans recently. Consequently, these shifts have led to a noticeable slowdown in originations across segments of the rate-sensitive commercial vehicle financing market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rise of Embedded Finance in OEM Telematics Platforms
- ESG-Linked Lending Mandates at Global Banks
- Stricter Basel IV Capital Rules for CV Portfolios
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Banks controlled 45.12% of the commercial vehicle financing market size in 2025 due to robust deposit funding and entrenched relationships with large fleets. However, NBFCs outpaced all rivals with a 6.86% CAGR and now underwrite growing slices of the gig-economy courier universe. The segment's ascent is linked to digital KYC, alternative credit scoring, and branch-light operations that cut overhead. CRISIL projects NBFC vehicle-finance disbursements will increase one-fifth annually through 2026 as lenders penetrate semi-urban freight corridors. Captive finance arms, once product-centric lenders, are extending into bundled service contracts that include telematics subscriptions and insurance, boosting retention and cross-sell revenue.
NBFCs' flexible structures allow interest-only grace periods, escalating payment schedules, and mileage-pegged amortization, terms that appeal to small operators facing cyclical income. Banks respond by accelerating portal rollouts and enhancing residual-value analytics, but compliance burdens limit speed. Mutuals and credit unions remain important in rural pockets, offering cooperative-based underwriting to agricultural haulers. Competition tightens, yet the commercial vehicle financing market widens as each provider finds distinct niches.
Loans still cover 67.05% of the commercial vehicle financing market share because many owners favor asset accumulation for collateral value. Operating leases, though smaller, expand at 6.83% CAGR as fleets prioritize flexibility amid rapid drivetrain innovation. With battery costs falling and regulations evolving, operators hesitate to lock capital into long-life diesel assets. Lessors absorb technology and residual-value risk, using sophisticated analytics, often powered by AI models, to price contracts competitively.
Finance leases serve middle-ground borrowers needing ownership benefits with balance-sheet optimization, while revolvers support seasonal capacity spikes such as harvest surges. Rising benchmark rates tilt the cost equation favor leases with lower upfront cash. As lenders push to diversify fee-based income, operating lease portfolios gain strategic relevance, accelerating commercial vehicle financing market growth.
The Commercial Vehicle Financing Market Report is Segmented by Provider Type (Banks, Captive (OEM) Finance Arms, and More), Financing Type (Loans, Finance Lease, and More), Vehicle Condition (New Commercial Vehicles and Used Commercial Vehicles), Vehicle Type (Light Commercial Vehicles, Medium and Heavy Duty Trucks, and More), Channel (Direct and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained 38.45% of the commercial vehicle financing market share in 2025, fueled by China's modernization and India's NBFC push. In China, macro indicators show freight-ton-kilometers stabilizing, yet electric-truck subsidies sustain credit demand as carriers pivot to battery models. Indian lenders expand reach into rural freight corridors, tapping government-backed loan-guarantee programs. ASEAN members integrate regional trade routes, spurring cross-border haulage and equipment purchases.
The Middle East & Africa exhibit the fastest CAGR at 6.89% as large infrastructure projects in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and East Africa widen logistics needs. Newly formed credit bureaus in Kenya and Nigeria lift approval rates for small fleet buyers. North America preserves high absolute volumes, although Basel-driven capital shifts and interest-rate pressures slow growth. Europe benefits from ESG-linked funding windows and strict emission targets that stimulate financing for electric vans and hydrogen trucks. Latin America experiences mixed outcomes: Brazil's freight reforms raise fleet-replacement intent, but elevated policy rates restrain borrowing. Chile and Colombia court green-bond proceeds to expand clean-truck lending. Each regional vector shapes the broader commercial vehicle financing market, underscoring the need for localized risk metrics.
- Bank of America Corporation
- Wells Fargo & Co.
- Ally Financial Inc.
- JPMorgan Chase Commercial Vehicle Finance
- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc.
- Banco Santander S.A.
- HDFC Bank Limited
- Mahindra & Mahindra Financial Services Ltd.
- Tata Motors Finance
- Toyota Financial Services
- Volkswagen Financial Services
- Daimler Truck Financial Services
- Volvo Financial Services
- CNH Industrial Capital
- PACCAR Financial
- Navistar Financial
- Bank of China
- ICBC Leasing
- Standard Bank Group Ltd.
- Credit Europe Group N.V.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Electrification Incentives for Medium-Duty Fleets
- 4.2.2 Growth of Last-Mile Delivery Start-Ups
- 4.2.3 Rise of Embedded Finance in OEM Telematics Platforms
- 4.2.4 ESG-Linked Lending Mandates at Global Banks
- 4.2.5 Expansion of Credit Bureaus Covering Informal Operators
- 4.2.6 AI-Driven Residual-Value Analytics Lowering Lender Risk
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Spike in Benchmark Rates Post-2025
- 4.3.2 Stricter Basel IV Capital Rules for CV Portfolios
- 4.3.3 Plateauing E-Commerce Freight Volumes in China
- 4.3.4 Volatility in Used-Truck Resale Prices
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD))
- 5.1 By Provider Type
- 5.1.1 Banks
- 5.1.2 Captive (OEM) Finance Arms
- 5.1.3 Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- 5.1.4 Credit Unions & Mutuals
- 5.2 By Financing Type
- 5.2.1 Loans
- 5.2.2 Finance Lease
- 5.2.3 Operating Lease
- 5.2.4 Line-of-Credit / Revolver
- 5.3 By Vehicle Condition
- 5.3.1 New Commercial Vehicles
- 5.3.2 Used Commercial Vehicles
- 5.4 By Vehicle Type
- 5.4.1 Light Commercial Vehicles
- 5.4.2 Medium and Heavy Duty Trucks
- 5.4.3 Buses and Coaches
- 5.4.4 Special-purpose Vehicles
- 5.5 By Channel
- 5.5.1 Direct
- 5.5.2 Online Aggregators & Digital Platforms
- 5.5.3 Broker-assisted
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 Egypt
- 5.6.5.5 South Africa
- 5.6.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Bank of America Corporation
- 6.4.2 Wells Fargo & Co.
- 6.4.3 Ally Financial Inc.
- 6.4.4 JPMorgan Chase Commercial Vehicle Finance
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc.
- 6.4.6 Banco Santander S.A.
- 6.4.7 HDFC Bank Limited
- 6.4.8 Mahindra & Mahindra Financial Services Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Tata Motors Finance
- 6.4.10 Toyota Financial Services
- 6.4.11 Volkswagen Financial Services
- 6.4.12 Daimler Truck Financial Services
- 6.4.13 Volvo Financial Services
- 6.4.14 CNH Industrial Capital
- 6.4.15 PACCAR Financial
- 6.4.16 Navistar Financial
- 6.4.17 Bank of China
- 6.4.18 ICBC Leasing
- 6.4.19 Standard Bank Group Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Credit Europe Group N.V.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




