PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937293

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937293
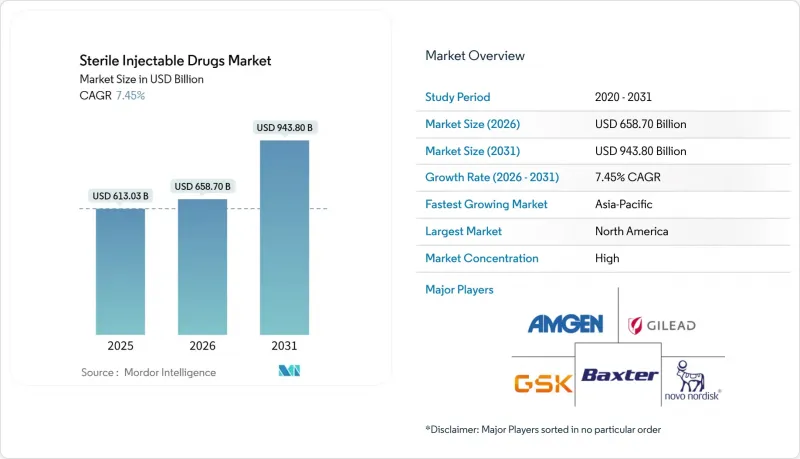
Sterile Injectable Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Sterile Injectable Drugs Market size is projected to expand from USD 613.03 billion in 2025 and USD 658.70 billion in 2026 to USD 943.80 billion by 2031, registering a CAGR of 7.45% between 2026 to 2031.
The competitive focus tilts toward biologics, where large-molecule formats have scaled quickly on the back of oncology, autoimmune, and rare disease pipelines. At the same time, small molecules regain momentum through complex injectables and acute-care use cases. Monoclonal antibodies extend their lead due to new indications and biosimilar entry, which broaden access and accelerate adoption in community settings. Packaging and delivery are shifting toward ready-to-administer and home-use formats as hospitals prioritize error reduction and, when clinically appropriate, payers move therapies out of high-cost infusion sites. Regionally, North America has the most significant revenue base, while Asia-Pacific is advancing through capacity expansion and export-ready manufacturing that support regulated markets.
Global Sterile Injectable Drugs Market Trends and Insights
Rising R&D Focus on Biotechnology-Engineered Anti-Cancer Drugs
Pipeline investment in oncology biologics continues to reshape the injectable drugs market, with immuno-oncology and targeted modalities requiring parenteral delivery to reach therapeutic exposure. FDA approvals of novel cancer agents remained active in 2025, reflecting ongoing advances in antibody-drug conjugates and bispecifics that align with sterile fill-finish and high-containment operations.
Pfizer's acquisition of Seagen for USD 43 billion underscored the premium for ADC platforms and strengthened its larger oncology franchise, anchored in targeted parenteral therapies. Manufacturing strategies increasingly favor smaller batch sizes and higher potency, which drives demand for closed isolators and single-use systems to mitigate cross-contamination risks without lengthening validation timelines. The trend expands the addressable base for specialized CDMOs that combine conjugation chemistry and sterile packaging at commercial scale for sponsors navigating complex analytical comparability. FDA approvals of additional conjugate constructs through late 2024 signaled continued maturation of linker and payload innovation, pointing to sustained commercial launches over the next several years.
Rapid Growth In Pre-Filled Syringes for Biologics
Prefilled platforms continue to displace vials as hospital systems and ambulatory providers reduce reconstitution steps and dosing errors while seeking to standardize administration at the bedside and in the home. Safety-engineered needles, connectivity features, and integrated autoinjector formats are improving usability and adherence for chronic biologic therapies. Regulators in the European Union and Japan emphasize extractables-and leachables controls for prefilled components, which extend development lead times but reinforce quality in real-world use. Device-data capture is creating feedback loops that support value-based reimbursement, as dose timing and persistence become measurable in routine care. In parallel, high-viscosity formulations with smaller volumes are expanding the scope of self-administration, making prefilled systems central to therapy delivery in the injectable drugs market.
High Expenses in Sterile-Inventory Management
Sterile inventory management elevates costs across warehousing, validated transport, and temperature monitoring, all of which must meet stringent compliance requirements. Just-in-time practices help reduce carrying costs but increase the risk of stockouts for small-volume orphan and oncology products subject to variable demand. Cold-chain investments are extending into last-mile delivery and home-based care, which increases the complexity of serialization and chain-of-custody controls for high-value biologics. Digital track-and-trace solutions offer better visibility but require data standards and interoperability that are still evolving across networks. Overall, these factors weigh on margins and complicate fulfillment strategies in the injectable drugs market, where sterility and temperature control are non-negotiable.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Increased Outsourcing Across the Injectable Value-Chain
- Growing Chronic-Disease Burden Demanding Parenteral Therapies
- Availability of Alternative Drug-Delivery Routes
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Large-molecule biologics held 74.30% of the injectable drugs market share in 2025, while small molecules are projected to grow faster at an 8.30% CAGR through 2031 as complex injectables see broader use. Small molecules benefit from shorter development cycles and lower capital intensity for sterile filtration and filling compared to mammalian cell culture and downstream purification. Biologics continue to command premium pricing due to clinical differentiation, but biosimilar entry is broadening access and accelerating formulary shifts. Many hospital-driven indications still rely on small-molecule injectables for rapid onset and predictable pharmacokinetics in critical care. Pipeline diversity across both categories ensures a two-speed market in which high-value biologics coexist with high-volume generics in hospital and retail channels.
Monoclonal antibodies accounted for 38.00% of the injectable drugs market share in 2025 and are set to grow at an 8.00% CAGR through 2031, driven by expanded adoption in oncology and immunology. Gene therapies have begun to displace routine prophylaxis in select hematology indications, including hemophilia A, where a one-time treatment has been approved. Peptide hormones maintain use in specialty endocrinology and fertility, while GLP-1 and dual-incretin agents reshape diabetes care pathways toward weight and cardiometabolic outcomes. Insulin use patterns are evolving as incretins take on a larger role in type 2 diabetes, with device and formulation innovation advancing on both fronts. Originators and biosimilar developers face an environment that rewards differentiated delivery, improved persistence, and a clear value proposition in outcomes.
The Sterile Injectable Drugs Market is Segmented by Molecule Type (Small Molecule, Large Molecule), Drug Class (Blood Factors, Cytokines, and More), Application (Oncology, Neurology, Cardiovascular Diseases, Autoimmune Diseases, Infectious Diseases, Pain, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America captured 38.40% of the regional share in 2025, driven by higher per-capita spending, strong specialty uptake, and a favorable reimbursement environment for innovative injectables. United States utilization patterns and coverage for physician-administered products support the growth of originator and biosimilar products across oncology and immunology. Canada applies more restrictive health-technology assessments that lengthen time-to-access for new therapies, while still enabling meaningful biosimilar uptake province by province. Mexico's hospital investments and expanded coverage continue to broaden access to sterile injectables across essential therapeutic categories.
Europe maintains the second-largest share with coordinated pathways that enable biosimilar entry, competitive tendering, and broad patient access over time. EMA's experience with biosimilars has helped normalize switching and price competition in oncology and immunology classes. Asia-Pacific is forecast to grow at an 8.03% CAGR through 2031, driven by capacity build-outs and export-oriented manufacturing that feed regulated markets. India and China expand fermentation and fill-finish capabilities to support CDMO contracts and local access to oncology and chronic therapies.
Japan's aging demographic sustains high biologics use, although conservative prescribing and longer review timelines slow adoption of novel classes. The Middle East and Africa, including GCC countries, invest in local manufacturing and hospital capacity to reduce import dependency and improve supply resilience. South America sees concentration in Brazil and Argentina, with public procurement emphasizing vaccines and essential antimicrobials and evolving pathways for specialty biologics. Across regions, policy and procurement structures shape price and access, yet the global pipeline and manufacturing investments continue to support steady adoption in the injectable drugs market.
- Abbvie
- Amgen
- AstraZeneca
- Baxter
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Fresenius
- Gilead Sciences
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals Public Limited Company
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck
- Novartis
- Novo Nordisk
- Pfizer
- Roche
- Sanofi
- Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising R&D Focus on Biotechnology-Engineered Anti-Cancer Drugs
- 4.2.2 Rapid Growth In Pre-Filled Syringes for Biologics
- 4.2.3 Increased Outsourcing Across the Injectable Value-Chain
- 4.2.4 Growing Chronic-Disease Burden Demanding Parenteral Therapies
- 4.2.5 Closed-System Robotics Cutting Contamination & Batch Failures
- 4.2.6 Lyophilized Nano-Suspensions Enabling Room-Temperature Shipping
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Expenses in Sterile-Inventory Management
- 4.3.2 Availability of Alternative Drug-Delivery Routes
- 4.3.3 Global Shortage of Pharma-Grade Vials & Stoppers
- 4.3.4 Tariff-Driven Volatility in Sterile API Import Costs
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Molecule Type
- 5.1.1 Small Molecule
- 5.1.2 Large Molecule (Biologics)
- 5.2 By Drug Class
- 5.2.1 Blood Factors
- 5.2.2 Cytokines
- 5.2.3 Peptide Hormones
- 5.2.4 Immunoglobulins
- 5.2.5 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
- 5.2.6 Insulin
- 5.2.7 Other Classes
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Oncology
- 5.3.2 Neurology
- 5.3.3 Cardiovascular Diseases
- 5.3.4 Autoimmune Diseases
- 5.3.5 Infectious Diseases
- 5.3.6 Pain Management
- 5.3.7 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Packaging Type
- 5.4.1 Vials (RTU/Bulk)
- 5.4.2 Prefilled Syringes
- 5.4.3 Cartridges & Ampoules
- 5.4.4 Ready-to-Use Blow-Fill-Seal Containers
- 5.5 By Route of Administration
- 5.5.1 Intravenous (IV)
- 5.5.2 Subcutaneous (SC)
- 5.5.3 Intramuscular (IM)
- 5.5.4 Intravitreal / Other Specialty Routes
- 5.6 By Distribution Channel
- 5.6.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.6.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.6.3 Online & Specialty Pharmacies
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 By Geography
- 5.7.1.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.1.3 Mexico
- 5.7.1.2 Europe
- 5.7.1.2.1 Germany
- 5.7.1.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.1.2.3 France
- 5.7.1.2.4 Italy
- 5.7.1.2.5 Spain
- 5.7.1.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.1.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.1.3.1 China
- 5.7.1.3.2 India
- 5.7.1.3.3 Japan
- 5.7.1.3.4 South Korea
- 5.7.1.3.5 Australia
- 5.7.1.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.1.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.1.4.1 GCC
- 5.7.1.4.2 South Africa
- 5.7.1.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.1.5 South America
- 5.7.1.5.1 Brazil
- 5.7.1.5.2 Argentina
- 5.7.1.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.1.1 North America
- 5.7.1 By Geography
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AbbVie
- 6.3.2 Amgen Inc.
- 6.3.3 AstraZeneca Plc
- 6.3.4 Baxter International Inc.
- 6.3.5 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- 6.3.6 Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc.
- 6.3.7 Eli Lilly & Company
- 6.3.8 Fresenius Kabi AG
- 6.3.9 Gilead Sciences Inc.
- 6.3.10 GSK plc
- 6.3.11 Hikma Pharmaceuticals Public Limited Company
- 6.3.12 Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- 6.3.13 Merck & Co., Inc.
- 6.3.14 Novartis AG
- 6.3.15 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 6.3.16 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.17 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.3.18 Sanofi SA
- 6.3.19 Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Limited
- 6.3.20 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




