PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937368

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1937368
Wi-Fi - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Wi-Fi Market was valued at USD 18.48 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 21.06 billion in 2026 to reach USD 40.44 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 13.94% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
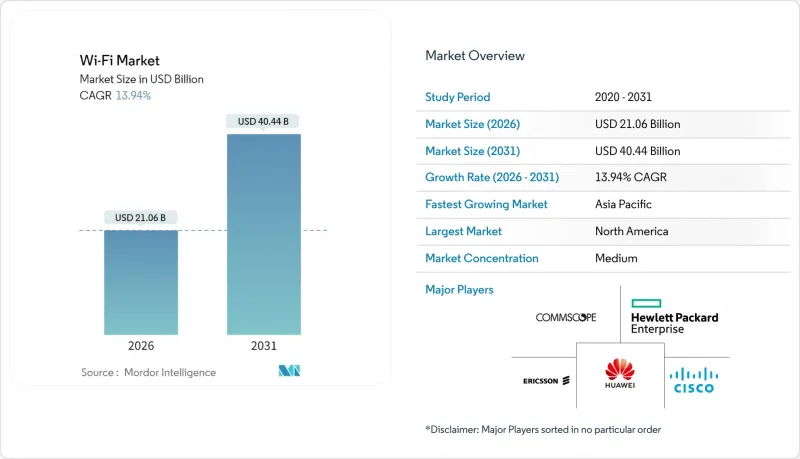
Growing enterprise preference for wireless-first architecture, the commercial debut of Wi-Fi 7, and the adoption of OpenRoaming standards are the primary forces propelling this acceleration . Enterprises view high-capacity WLAN as pivotal for hybrid work enablement, edge-hosted artificial intelligence, and real-time industrial automation, prompting refresh cycles that shorten from eight years to five. Rapid mesh penetration in residential and small-office environments further broadens the addressable base, while federal broadband programs in North America stimulate public-sector opportunities. Spectrum allocations in the 6 GHz band supply temporary congestion relief, yet also spark demand for tri-band access points that can assure deterministic latency for robotics, telemedicine, and immersive reality services. The competitive landscape remains open because interoperability requirements prevent lock-in, allowing new service-centric entrants to challenge incumbent hardware vendors.
Global Wi-Fi Market Trends and Insights
Proliferation of IoT and smart devices
Enterprises deploy dense sensor networks that often exceed 100 connected endpoints per access point, a profile economically serviced only by Wi-Fi 6E's OFDMA scheduling and multi-user MIMO capabilities. Smart-building operators integrate HVAC, lighting, and surveillance over Wi-Fi mesh to cut structured-cabling costs by 40% and enable predictive maintenance analytics. Demand for sub-10 ms response in edge inference workflows makes Wi-Fi 7's multi-link operation attractive because it sustains jitter-free traffic under load. Industrial automation pilots report 99.9% uptime on dedicated 6 GHz channels versus 97.8% on congested 5 GHz links, validating the migration to new spectrum for mission-critical robotics. These gains encourage organizations to absorb higher capital outlays in return for long-run productivity .
Smart-city initiatives and public Wi-Fi roll-outs
Municipal broadband programs increasingly favor Wi-Fi as the primary medium for digital inclusion because installation is quicker and less capital-intensive than fiber in sprawling rural territories. The Philippines commits USD 1.2 billion to deploy more than 100,000 public hotspots across 17,000 barangays by 2028, a template mirrored by several emerging economies. Europe's Digital Decade targets gigabit coverage by 2030 and positions Wi-Fi 7 mesh as an affordable last-mile alternative in mountainous and island regions. Cities monetize infrastructure by layering sensor backhaul for traffic, air-quality, and emergency-response schemes that self-fund through efficiency gains. Neutral-host deployments that blend Wi-Fi and 5G radios under OpenRoaming agreements generate fresh revenue as roaming fees while delivering seamless citizen connectivity.
Spectrum congestion and interference in unlicensed bands
Dense urban precincts such as Manhattan experience throughput drops near 60% during peak usage, even when Wi-Fi 6E hardware is present, because legacy devices crowd the 2.4 GHz spectrum. Microwave ovens, Bluetooth handsets, and older routers create overlapping noise that adaptive algorithms cannot fully evade. Enterprises increasingly hire spectrum consultants, a service costing USD 50,000-200,000 on expansive campuses, to engineer channel plans that meet service-level objectives. Regulators consider quasi-licensed regimes akin to CBRS so that critical IoT traffic can operate free of consumer interference. Although the 6 GHz allocation temporarily alleviates pressure, forecasts show saturation within five years as IoT endpoints grow exponentially.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid adoption of Wi-Fi 6/6E and upcoming Wi-Fi 7
- Hybrid/remote work models demanding high-capacity WLAN
- Heightened data-privacy and security compliance costs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2025, access points contributed 35.92% to the Wi-Fi market share, underlining hardware's continuing relevance even as revenue mix shifts. The services segment, however, is projected to compound at 15.98% through 2031, reflecting the pivot to Network-as-a-Service frameworks that convert upfront capital into recurring operating expense. Cost pressures commoditize standalone routers and range extenders, while cloud-native orchestration platforms take over the policy and analytics roles previously executed by on-premises controllers. Managed service providers leverage artificial intelligence to automate channel allocation, load balancing, and anomaly detection, ultimately delivering 75% fewer unplanned-outage minutes than customer-operated networks. By 2031, the Wi-Fi market size attributed to software and services is expected to eclipse hardware contribution in mature economies as organizations prioritize life-cycle flexibility over asset ownership.
The shift mirrors broader IT procurement trends that favor outcomes over ownership. Consumption-based pricing aligns WLAN costs with occupancy levels, flattening budget spikes and improving CFO visibility. Vendors bundle proactive maintenance, security compliance, and real-time experience scoring to differentiate beyond hardware. Edge gateways and ruggedized IoT bridges constitute a small but fast-rising category, supplying deterministic connectivity in harsh industrial zones where vibration, dust, and temperature extremes invalidate consumer-grade gear. As AI chips embed inside access points, even commodity hardware gains value when offered as a managed experience that abstracts complexity and accelerates time to productivity.
The Wi-Fi Market Report is Segmented by Component (Hardware, Solutions, Services), End-User Vertical (Consumer, Enterprise/Corporate Campuses, Education, Healthcare, Hospitality and Retail, Industrial and Logistics), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America accounts for 40.55% of the Wi-Fi market in 2025, owing to USD 65 billion in broadband incentives and rapid enterprise refresh cycles. Early access to 6 GHz spectrum allows institutions to pioneer tri-band deployments, creating a performance gap over regions still seeking regulatory clearance. Fortune 500 companies refresh their WLAN every five years, two years faster than the global average, to equip smart offices tailored for hybrid work. Healthcare and education pillars represent robust growth nodes as telehealth and distance learning require enterprise-grade reliability.
Asia Pacific records the fastest trajectory with a 15.12% CAGR through 2031, enabled by national digital strategies that treat wireless as primary rather than complementary infrastructure. China's factory-automation boom, amplified by policy to cultivate domestic chipset capability, translates to bulk orders for industrial-grade Wi-Fi 6E equipment. India's Digital India mission envisions connecting 600,000 villages via Wi-Fi mesh, making wireless the linchpin of rural inclusion. Southeast Asian economies integrate WLAN across tourism hubs and export-oriented manufacturing parks, while government subsidies shrink payback periods and accelerate deployments. Smart-city funding rounds across Jakarta, Bangkok, and Ho Chi Minh City further elevate regional demand.
Europe's growth remains orderly as Industry 4.0 uptake and Digital Decade mandates require gigabit household coverage by 2030. Wi-Fi serves as the cost-effective last-mile solution in rugged topographies like the Alps and the Greek islands. OpenRoaming agreements spearheaded by the EU Digital Single Market create frictionless cross-border connectivity, bolstering tourism and remote business travel. Germany leads industrial adoption, whereas Nordic nations focus on smart-grid and sustainability use cases that rely on energy-efficient TWT scheduling. The Middle East and Africa invest in Wi-Fi to diversify economies beyond hydrocarbons and to bridge digital divides in rural deserts and mountainous terrain.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (Aruba)
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.(Ruckus Networks)
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Extreme Networks, Inc.
- Ubiquiti Inc.
- Fortinet Inc.
- TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Netgear Inc.
- D-Link Corporation
- Zyxel Communications Corp.
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- Broadcom Inc.
- Intel Corporation
- MediaTek Inc.
- Cambium Networks Ltd.
- EnGenius Networks, Inc. (Elitegroup)
- Purple WiFi Ltd.
- Cloud4Wi Inc.
- MetTel Inc.
- Singtel Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Proliferation of IoT and smart devices
- 4.2.2 Smart-city initiatives and public WiFi roll-outs
- 4.2.3 Rapid adoption of WiFi 6/6E and upcoming WiFi 7
- 4.2.4 Hybrid/remote work models demanding high-capacity WLAN
- 4.2.5 Convergence of WiFi and 5G via OpenRoaming/Passpoint
- 4.2.6 Energy-efficient TWT features for battery-powered IoT nodes
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Spectrum congestion and interference in unlicensed bands
- 4.3.2 Heightened data-privacy/security compliance costs
- 4.3.3 Li-Fi and 60 GHz alternatives cannibalizing dense-WiFi use cases
- 4.3.4 Chipset supply constraints delaying WiFi 7 device launches
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 Access Points
- 5.1.1.2 Routers and Extenders
- 5.1.1.3 Wireless Controllers
- 5.1.1.4 Other Device Types
- 5.1.2 Solutions
- 5.1.3 Services
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.2 By End-user Vertical
- 5.2.1 Consumer
- 5.2.2 Enterprise/Corporate Campuses
- 5.2.3 Education
- 5.2.4 Healthcare
- 5.2.5 Hospitality and Retail
- 5.2.6 Industrial and Logistics
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.2 South America
- 5.3.2.1 Brazil
- 5.3.2.2 Argentina
- 5.3.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Spain
- 5.3.3.6 Russia
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.3.4.1 China
- 5.3.4.2 Japan
- 5.3.4.3 South Korea
- 5.3.4.4 India
- 5.3.4.5 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.3.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.3.5 Middle East
- 5.3.5.1 GCC
- 5.3.5.2 Turkey
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.3.6 Africa
- 5.3.6.1 South Africa
- 5.3.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.3.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Hewlett Packard Enterprise (Aruba)
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 CommScope Holding Company Inc.(Ruckus Networks)
- 6.4.5 Juniper Networks Inc.
- 6.4.6 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.7 Extreme Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.8 Ubiquiti Inc.
- 6.4.9 Fortinet Inc.
- 6.4.10 TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Netgear Inc.
- 6.4.12 D-Link Corporation
- 6.4.13 Zyxel Communications Corp.
- 6.4.14 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.15 Broadcom Inc.
- 6.4.16 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.17 MediaTek Inc.
- 6.4.18 Cambium Networks Ltd.
- 6.4.19 EnGenius Networks, Inc. (Elitegroup)
- 6.4.20 Purple WiFi Ltd.
- 6.4.21 Cloud4Wi Inc.
- 6.4.22 MetTel Inc.
- 6.4.23 Singtel Group
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




