PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939150

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939150
Carbon Black - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The Carbon Black market is expected to grow from USD 24.61 billion in 2025 to USD 25.95 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 33.82 billion by 2031 at 5.44% CAGR over 2026-2031.
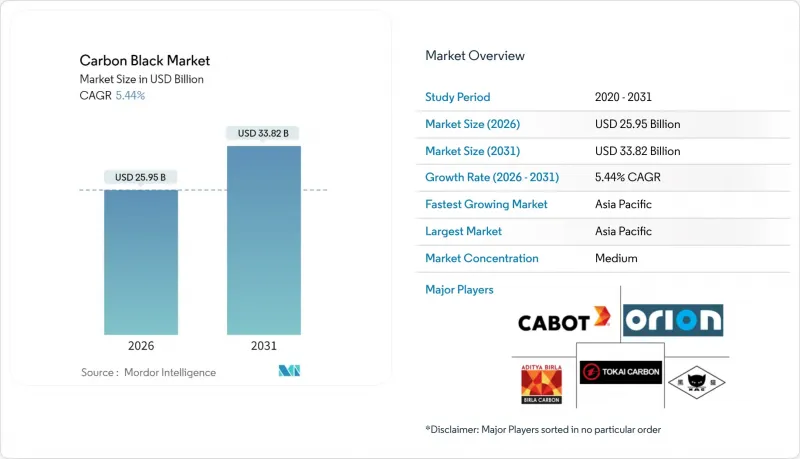
Strong demand from tire reinforcement, plastics compounding, battery electrodes, and high-performance coatings anchors steady volume growth while enabling a gradual mix shift toward premium specialty grades. Capacity additions across Asia-Pacific underpin output expansion, yet feedstock volatility and rising sustainability requirements force producers to adopt tighter cost control and process innovation. Heightened electrification accelerates conductive grade uptake, and process breakthroughs such as plasma methane pyrolysis reshape competitive positioning. The carbon black market continues to capture value as a critical material input for traditional mobility and emerging energy storage supply chains.
Global Carbon Black Market Trends and Insights
Surge in tire manufacturing capacity, especially in the Asia-Pacific region
New tire plants across China, India, and Southeast Asia continue to lock in multi-year carbon black off-take contracts that underpin predictable demand patterns. Yokohama's ongoing Chinese capacity additions exemplify how large tire complexes stimulate parallel investments in nearby carbon black units, lowering logistics costs and encouraging just-in-time delivery models. Regional clustering raises carbon black demand density and supports economies of scale that benefit furnace black producers. Suppliers with ISO 14001-certified operations secure preferred vendor status, consolidating share among environmentally compliant facilities. The structural link between tire output and carbon black consumption therefore provides a demand floor that smooths revenue cycles and aids long-range capital planning.
Rapid shift from standard to specialty blacks
OEM requirements for lower rolling resistance and higher conductivity push tire makers to adopt engineered grades that command 40-60% premiums over commodity furnace blacks. These specialty formulations enhance fuel economy and extend tread life, thereby generating measurable performance benefits that outweigh incremental cost. Producers investing in proprietary surface modification and ultra-clean furnace configurations gain sustainable advantages in a higher-margin niche. Technical differentiation and customer qualification protocols create switching costs that strengthen supplier lock-in, while the share of specialty shipments in the carbon black market rises steadily each year. Tight integration between research and development teams and tire designers accelerates the pivot toward advanced grades.
Volatile feedstock pricing
Carbon black production relies heavily on carbonaceous feedstocks such as coal tar and residual fuel oil that can represent up to 50% of total operating cost. The Producer Price Index for carbon and graphite products climbed sharply through late 2024, squeezing margins before contractual pass-through clauses could take effect. Import-dependent plants face added freight exposure that widens regional price differentials and influences trade flow arbitrage. Integrated producers with long-term supply agreements partially shield earnings, whereas spot buyers endure profit swings that influence maintenance turnarounds and capacity utilization. Effective hedging and procurement strategies, therefore, remain essential to stabilize cash flows across the carbon black market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Electrification-led demand for conductive/acetylene grades
- Low-carbon plasma-methane blacks gain OEM credits
- Regulatory caps on CO2/PAH emissions from furnaces
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Furnace black accounted for 76.30% of 2025 revenue, highlighting its versatility and competitive economics across core tire and rubber goods. Nonetheless, the carbon black market size in furnace applications confronts a gradual share drift as specialty processes gain traction. Lamp black, supported by a 7.35% forecast CAGR through 2031, benefits from an inherent high-surface-area morphology that delivers superior conductivity in electronics and energy storage coatings. Gas black maintains usage in fine-dispersion inks, whereas thermal black serves niche polymer blends requiring low structure. The disruptive entrance of plasma methane technology extends the process palette by offering a low-emission pathway that can align with OEM carbon accounting frameworks.
Competitive responses include modular reactor retrofits that enable production of semi-specialty grades within existing furnace lines. Cabot Corporation and Birla Carbon are piloting advanced feed-injection controls to tighten particle size distribution and boost structure indices without needing new processes. Successful adaptation preserves scale advantages while capturing value migration toward specialty products. As ASTM develops a unified classification for recovered carbon black, furnace producers may incorporate rCB blending strategies to meet circularity targets without jeopardizing compound performance. Overall, the coexistence of commodity and specialty processes drives a dual-track growth model within the carbon black market.
The Carbon Black Market Report is Segmented by Process Type (Furnace Black, Gas Black, Thermal Black, and Lamp Black), Application (Tire and Industrial Rubber Product, Plastic, Toner and Printing Ink, Coating, Textile Fiber, and Others), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held 61.85% of global revenue in 2025, supported by China's tire manufacturing concentration and India's specialty grade expansion, and is forecast to log a 5.85% CAGR to 2031. China integrates large tire plants with adjacent carbon black units, achieving feedstock and logistics efficiencies that bolster regional competitiveness. India's Himadri Speciality Chemical added 70,000 MTPA of premium capacity in 2024, signaling a shift from commodity supply toward higher-margin powders for performance tires and battery components. Japan and South Korea contribute technology leadership, while Southeast Asian economies supply cost-effective labor and growing domestic auto demand.
North America records mature yet stable consumption, driven by replacement tire demand, high-performance coatings, and early adoption of low-emission processes. Monolith Materials' Nebraska plasma facility introduces an alternative supply base aligned with green procurement objectives, while Cabot Corporation leverages its U.S. specialty plants to pass through inflationary costs without significant volume attrition. The Inflation Reduction Act's battery incentives indirectly support conductive grade growth, providing a structural tailwind for the carbon black market in the region.
Europe emphasizes sustainability and specialty applications, with the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism encouraging localized production or preferential sourcing from low-carbon suppliers. Caps on PAH and CO2 emissions accelerate modernization or closure of legacy furnaces. Producers with advanced after-treatment systems maintain market access and negotiate price premiums that offset compliance expenditures.
South America, the Middle East, and Africa collectively account for a smaller share but exhibit pockets of high growth linked to expanding automotive assembly and broader industrialization. Brazil's automotive recovery drives localized tire output that stimulates domestic carbon black production investment. Middle Eastern players leverage petrochemical raw material integration to propose new furnace units, though downstream demand still lags Asia-Pacific scale. South Africa's coatings and mining sectors require specialty dispersion blacks, yet currency volatility clouds capital planning. Combined, these regions offer expansion optionality as primary markets mature, allowing diversified producers to balance regional cycles within the global carbon black market.
- Asahi Carbon Co. Ltd
- Birla Carbon (Aditya Birla Group)
- BKT Carbon
- Black Bear Carbon B.V.
- Cabot Corporation
- Continental Carbon Company
- Denka Company Limited
- Epsilon Carbon Pvt Ltd
- Himadri Speciality Chemical Ltd
- Imerys S.A.
- Jiangxi Black Cat Carbon Black Co. Ltd
- Longxing Chemical Stock Co. Ltd
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- OCI Company Ltd
- Omsk Carbon Group
- Orion Engineered Carbons S.A.
- PCBL Limited
- Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in tire manufacturing capacity, especially in the Asia-Pacific region
- 4.2.2 Rapid shift from standard to specialty blacks
- 4.2.3 Electrification-led demand for conductive/acetylene grades
- 4.2.4 Low-carbon plasma-methane blacks gain OEM credits
- 4.2.5 Surging electric vehicle demand fuels carbon black market growth
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Volatile feedstock pricing
- 4.3.2 Regulatory caps on CO2/PAH emissions from furnaces
- 4.3.3 Quality variability of recovered carbon black (rCB)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Degree of Competition
- 4.7 Pricing Analysis
- 4.8 Production and Trade Analysis
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Process Type
- 5.1.1 Furnace Black
- 5.1.2 Gas Black
- 5.1.3 Thermal Black
- 5.1.4 Lamp Black
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Tire and Industrial Rubber Product
- 5.2.2 Plastic
- 5.2.3 Toner and Printing Ink
- 5.2.4 Coating
- 5.2.5 Textile Fiber
- 5.2.6 Others
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 Thailand
- 5.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.3 South Africa
- 5.3.5.4 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Asahi Carbon Co. Ltd
- 6.4.2 Birla Carbon (Aditya Birla Group)
- 6.4.3 BKT Carbon
- 6.4.4 Black Bear Carbon B.V.
- 6.4.5 Cabot Corporation
- 6.4.6 Continental Carbon Company
- 6.4.7 Denka Company Limited
- 6.4.8 Epsilon Carbon Pvt Ltd
- 6.4.9 Himadri Speciality Chemical Ltd
- 6.4.10 Imerys S.A.
- 6.4.11 Jiangxi Black Cat Carbon Black Co. Ltd
- 6.4.12 Longxing Chemical Stock Co. Ltd
- 6.4.13 Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- 6.4.14 OCI Company Ltd
- 6.4.15 Omsk Carbon Group
- 6.4.16 Orion Engineered Carbons S.A.
- 6.4.17 PCBL Limited
- 6.4.18 Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




