PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939577

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939577
Satellite Manufacturing And Launch Vehicle - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The satellite manufacturing and launch vehicle market was valued at USD 41.50 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 45.24 billion in 2026 to reach USD 69.68 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 9.02% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
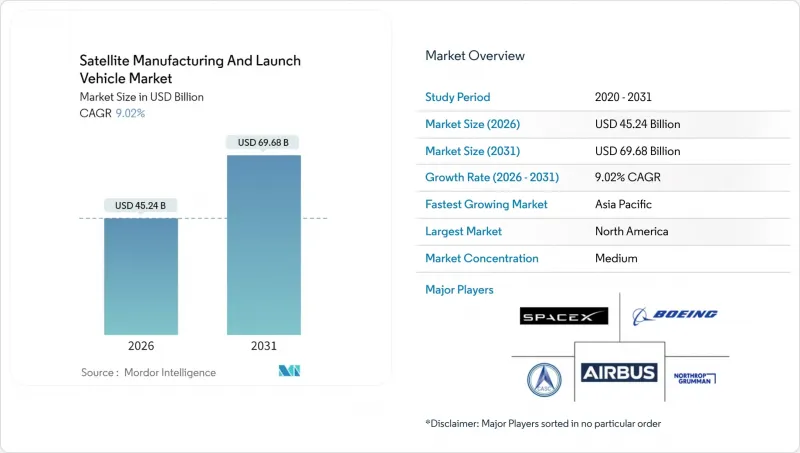
The expansion stems from a production shift toward assembly-line methods, which enable hundreds of identical spacecraft to be produced per month, a capability essential for proliferated constellations that blend low Earth orbit networks with traditional geostationary assets. The broader adoption of commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) electronics, electric propulsion, and software-defined payloads reduces unit costs to below USD 500,000 for standardized satellites, while preserving upgrade flexibility. These innovations unlock broadband coverage for rural populations, create real-time Earth observation services, and support national security architectures that demand resilient, multi-orbit connectivity. From a supply-side perspective, vertical integration of launch and spacecraft production compresses schedules, while streamlined licensing regimes in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific accelerate constellation deployment.
Global Satellite Manufacturing And Launch Vehicle Market Trends and Insights
Surge in Broadband-Internet Constellation Deployments
Volume production now defines the satellite manufacturing segment of the satellite manufacturing and launch vehicle market, with assembly lines producing up to eight identical spacecraft daily, as seen at SpaceX's Redmond facility. Standardized buses, modular payload bays, and automated test stations reduce build-to-launch cycles to under three months. Operators such as Project Kuiper and OneWeb follow similar blueprints, allowing break-even economics once subscriber numbers exceed 1 million users. Regulatory bodies have responded by shortening license review times, though spectrum coordination remains a hurdle for newcomers. Competitive pressure is driving component commonality across satellite generations, enabling software-defined payload swaps without altering mechanical interfaces.
Growing Demand for Real-Time Earth Intelligence
Commercial and government customers seek sub-hour revisit times, pushing demand for multi-sensor fleets that include compact synthetic-aperture radar and hyperspectral imagers. Rapid integration benches allow a new sensor to move from design freeze to space qualification in under nine months. AI-enabled onboard processing now condenses raw imagery into analytics summaries, lowering downlink requirements by 60% and enabling critical insights for disaster response and maritime monitoring. Data fusion across visible, radar, and thermal bands provides decision-quality intelligence, driving growth in dedicated tasking services and per-scene subscription models.
Launch-Site Capacity Bottlenecks at Cape Canaveral and Baikonur
Cape Canaveral handled 44 orbital missions in 2024, flirting with pad turnaround limits despite reusable boosters. Delays ripple back through production, forcing completed spacecraft into storage and straining cash flows. Manufacturers now design dispensers that can switch between Falcon 9, Electron, and emerging European microlaunchers with minimal re-qualification. New commercial spaceports in Scotland, Australia, and South Korea offer additional capacity but require updates to payload interfaces and revised environmental tests.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- National Security Focus on Resilient Multi-Orbit Architectures
- Commercial-Off-The-Shelf Component Cost Deflation
- Geopolitical Export-Control Tightening
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Communication satellites accounted for 78.35% of the satellite manufacturing segment in 2025, supplying broadband constellations that each demand several hundred identical units. Earth-observation satellites are forecast to post a 9.55% CAGR through 2031, with synthetic-aperture radar fleets driving sensor diversity. Navigation satellites benefit from Galileo, BeiDou, and NavIC extensions, while science missions sustain steady orders from international space agencies.
The satellite manufacturing market size for communication payloads reached USD 32.52 billion in 2025, reflecting economies of scale and vertically integrated launch options. Meanwhile, hybrid payload designs blend connectivity with optical imaging, creating incremental demand for reconfigurable buses. Revenue models are shifting toward capacity-as-a-service, prompting operators to specify plug-and-play payload slots that can be swapped in-orbit as new sensors mature.
Mid-class platforms with a weight range of 100-500 kg held a 63.05% share in 2025, representing the optimal balance between payload power and rideshare economics. In contrast, smallsats weighing 10-100 kg are expected to expand at a 15.20% CAGR to 2031, driven by the proliferation of imaging, IoT, and weather constellations.
The satellite manufacturing segment of the satellite manufacturing and launch vehicle market size for small satellites stood at USD 7.36 billion in 2025 and is set to more than double by 2031 as standardized CubeSat formats reach higher performance levels. For heavier classes exceeding 1,000 kg, demand remains tied to flagship GEO missions and science observatories, niches that still justify bespoke manufacturing but are expected to contribute less than 15% of the total build count by 2031.
Low Earth orbit fleets captured 71.40% of the satellite manufacturing segment of the satellite manufacturing and launch vehicle market in 2025 and are expected to continue adding units at an annual rate eight times that of GEO satellites. Medium Earth orbit is forecast to record the fastest 10.78% CAGR, powered by navigation modernization and new secure-backhaul services.
Manufacturing lines focus on radiation-tolerant yet low-cost designs for LEO's harsh cycling, while GEO units retain high-reliability components and deployable antennas. Regulatory pressure now mandates controlled deorbit within five years of mission end, prompting bus suppliers to package drag sails or electric-propulsion disposal kits as standard options.
The Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Vehicle Market Report is Segmented by Application (Communication, and More), Satellite Mass (Below 10 Kg, and More), Orbit Class (LEO, MEO, GEO), Launch Vehicle MTOW (Light, and More), End User (Commercial, and More), Satellite Subsystem (Propulsion Hardware and Propellant, and More), Propulsion Technology (Electric, and More), and Geography (North America, and More).
Geography Analysis
North America accounted for 67.10% of 2025 revenue, driven by integrated manufacturing-to-launch ecosystems exemplified by companies such as SpaceX, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin. Automated lines in Washington and California feed both commercial and defense constellations, while venture capital ensures a steady pipeline of subsystem startups. Regulatory support includes streamlined Federal Aviation Administration payload approvals and tax incentives for the export of space hardware. Canada complements US leadership with high-rate antenna, payload processor, and ground segment products, securing niche export wins across Asia-Pacific and Europe.
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing region, with a 10.95% CAGR through 2031, driven by Chinese mass-production hubs that shipped over 200 satellites in 2024. India's liberalized policies encourage domestic firms to build and launch commercial spacecraft without state sponsorship. Japanese suppliers leverage their long-standing reputations for reliability to partner with the US companies on next-generation smallsat buses. At the same time, South Korea's Hanwha Aerospace invests in turnkey factories aimed at regional operators.
Europe retains a solid share through Airbus and Thales Alenia Space but faces slower growth due to programmatic fragmentation and strict export frameworks. The European Space Agency's sovereignty initiatives support indigenous component lines for secure processors, solar cells, and electric thrusters. South America and the Middle East & Africa show rising demand for satellite bandwidth for connectivity and intelligence services, but remain reliant on imports, opening opportunities for joint ventures that pair local integration facilities with foreign-built bus modules.
- Airbus SE
- The Boeing Company
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- ISRO
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Lanteris Space LLC (Maxar Technologies)
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Sierra Nevada Company, LLC
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- Thales Alenia Space (Thales Group and Leonardo S.p.A)
- United Launch Alliance, LLC
- Eutelsat Communications SA
- Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- Rocket Lab Corporation
- Relativity Space, Inc.
- Arianespace SA
- Astroscale Holdings Inc.
- OHB SE
- Spire Global, Inc.
- Planet Labs PBC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in broadband-internet constellation deployments
- 4.2.2 Growing demand for real-time Earth intelligence (EO/ISR)
- 4.2.3 National security focus on resilient multi-orbit architectures
- 4.2.4 Commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) component cost deflation
- 4.2.5 Emergence of in-orbit servicing and assembly ecosystems
- 4.2.6 Lunar and cis-lunar exploration programs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Launch-site capacity bottlenecks at Cape Canaveral and Baikonur
- 4.3.2 Persistent spectrum-allocation congestion at ITU
- 4.3.3 Geopolitical export-control tightening
- 4.3.4 Space-debris mitigation cost compliance
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 By Satellite Mass
- 5.2.1 Below 10 kg
- 5.2.2 10 - 100 kg
- 5.2.3 100 - 500 kg
- 5.2.4 500 - 1,000 kg
- 5.2.5 Above 1,000 kg
- 5.3 By Orbit Class
- 5.3.1 LEO
- 5.3.2 MEO
- 5.3.3 GEO
- 5.4 By Launch-Vehicle MTOW
- 5.4.1 Light
- 5.4.2 Medium
- 5.4.3 Heavy
- 5.5 By End-user
- 5.5.1 Commercial
- 5.5.2 Military and Government
- 5.5.3 Other
- 5.6 By Satellite Subsystem
- 5.6.1 Propulsion Hardware and Propellant
- 5.6.2 Satellite Bus and Sub-systems
- 5.6.3 Solar Array and Power Hardware
- 5.6.4 Structures, Harness and Mechanisms
- 5.7 By Propulsion Technology
- 5.7.1 Electric
- 5.7.2 Liquid Fuel
- 5.7.3 Gas-based/Hybrid
- 5.8 By Geography
- 5.8.1 North America
- 5.8.1.1 United States
- 5.8.1.2 Canada
- 5.8.2 South America
- 5.8.2.1 Brazil
- 5.8.2.2 Rest of South America
- 5.8.3 Europe
- 5.8.3.1 Germany
- 5.8.3.2 France
- 5.8.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.8.3.4 Russia
- 5.8.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.8.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.8.4.1 China
- 5.8.4.2 India
- 5.8.4.3 Japan
- 5.8.4.4 South Korea
- 5.8.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.8.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.8.5.1 Middle East
- 5.8.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.8.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.8.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.8.5.2 Africa
- 5.8.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.8.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.8.5.1 Middle East
- 5.8.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.3 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- 6.4.4 ISRO
- 6.4.5 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.6 Lanteris Space LLC (Maxar Technologies)
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.9 Sierra Nevada Company, LLC
- 6.4.10 Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.11 Thales Alenia Space (Thales Group and Leonardo S.p.A)
- 6.4.12 United Launch Alliance, LLC
- 6.4.13 Eutelsat Communications SA
- 6.4.14 Blue Origin Enterprises, L.P.
- 6.4.15 Rocket Lab Corporation
- 6.4.16 Relativity Space, Inc.
- 6.4.17 Arianespace SA
- 6.4.18 Astroscale Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.19 OHB SE
- 6.4.20 Spire Global, Inc.
- 6.4.21 Planet Labs PBC
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment
8 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS




