PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939749

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1939749
Cyber Warfare - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The cyber warfare market was valued at USD 38.2 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 40.29 billion in 2026 to reach USD 52.57 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.47% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
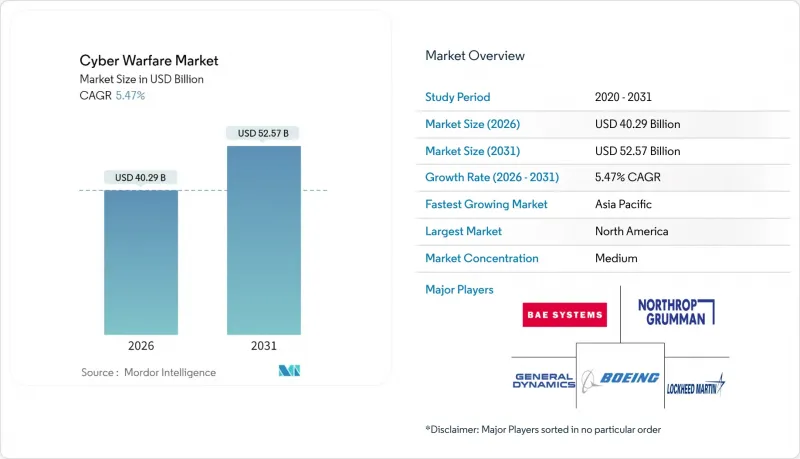
Escalating nation-state offensives, the rapid digitalization of military C4ISR networks, and the diffusion of autonomous tools continue to raise the strategic value of cyberspace, prompting defense ministries to protect and project power in this domain. North America retains technological primacy, yet faces intensified attacks on critical infrastructure, while the Asia-Pacific becomes the fastest-growing arena as regional tensions accelerate procurement cycles. Healthcare, once peripheral, now attracts high-grade ransomware that compels hospital groups to adopt military-grade defenses. Meanwhile, acquisition-driven consolidation among defense primes and cybersecurity specialists signals a shift toward integrated offensive-defensive suites that fuse artificial intelligence with autonomous response engines
Global Cyber Warfare Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Nation-State Sponsored Cyber-Espionage Programs
Cyber operations have shifted from episodic espionage to continuous "persistent engagement," forcing militaries to invest in offensive hunt teams and resilient defensive postures. The U.S. Cyber Command's 2024 forward-hunt missions clarified that deterrence now hinges on pre-positioning inside adversary networks. China's Strategic Support Force mirrors this approach, prompting regional counter-moves that expand budget lines for malware engineering, zero-day stockpiles, and deception tooling. Attribution ambiguity enables deniable aggression, heightens the risk of escalation, and sustains demand across the cyber warfare market. Vendors that package threat intelligence with automated response gain favor because governments are under pressure to shorten decision cycles without compromising secrecy.
Rapid Digitalization of Military C4ISR Networks
Allied forces are migrating to joint all-domain command frameworks that interlink sensors, shooters, and decision nodes. While digitization delivers operational agility, it also enlarges the attack surface that adversaries probe for zero-day access. AI-assisted planning tools now reside within mission-critical networks, creating new vulnerabilities alongside analytics advantages. Consequently, acquisition programs bundle endpoint detection, zero-trust architecture, and cross-domain gateways to secure data flows. Continued funding for hardened communications promises long-tail growth for cyber warfare market vendors that can certify interoperability across multinational task forces.
Acute Shortage of Cleared Cyber-Warfare Personnel
Vacancies for top-secret cleared operators surged in 2024, and vetting wait times stretched to 18 months. Commanders allocate program budgets to talent retention, squeezing procurement for new tools. Cyber ranges and AI-based tutoring partially offset the skills gap by accelerating on-the-job learning, but clearance backlogs slow the force-generation pipeline. This restraint caps how fast agencies can operationalize new offensive platforms, tempering the cyber warfare market's longer-term growth.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in Critical Infrastructure Attacks Prompting Defense Budgets
- NATO "Cyber as Domain" Doctrine and Allied Procurement Cycles
- Attribution Complexity Limiting Proportional Response
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Defense and aerospace contributed 32.08% of the cyber warfare market share in 2025, driven by classified budgets that combine offensive exploits with layered defenses. Healthcare, though smaller in absolute spend, records the fastest 6.83% CAGR as ransomware syndicates exploit medical urgency to force payments.The cyber warfare market size captured by BFSI remains steady because regulators compel multilayered safeguards, while corporate sectors move toward military-grade solutions as nation-state threat actors pivot to supply-chain infiltration. Utilities and energy operators tie procurement to industrial safety mandates, blending IT and OT security in ways that favor integrated platforms. Government civilian agencies outside defense pursue threat-hunting contracts to secure voter data and public-service portals. Transportation firms now rank in procurement queues after headline-grabbing port shutdowns, driving demand for endpoint isolation and encrypted telemetry. Cross-industry convergence prompts vendors to modularize their offerings, enabling tools to extend seamlessly from enterprise IT to mission-critical systems without requiring codebase forks. This versatility helps expand the cyber warfare market within customer segments that historically purchased consumer-grade cybersecurity tools.
Growth dynamics are influenced by sector-specific regulations and insurance clauses that increasingly reference military cyber doctrines. Defense primes leverage long-standing relationships to upsell analytics extensions into civilian industries, thereby compounding revenue streams. Healthcare consortia form information-sharing alliances that funnel threat intelligence back to defense labs, accelerating patch cycles. Banks valorize situational awareness by subscribing to defense-derived telemetry feeds that flag nation-state strategies. Such a crossover reinforces the cyber warfare industry's ecosystem, where data from one vertical enriches security outcomes in another, creating positive network effects that sustain multi-segment expansion.
The Cyber Warfare Market Report is Segmented by End-User Industry (Defense and Aerospace, BFSI, Corporate, Power and Utilities, Government, Healthcare, and More), Deployment Mode (On-Premises, Cloud-Based, and More), Solution Type (Offensive Platforms and Exploits, Defensive Platforms, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America controlled 31.18% of the cyber warfare market in 2025, led by the United States' defense outlays that fund both offensive penetration units and large-scale cyber ranges. The Five Eyes intelligence network amplifies platform demand because Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand procure interoperable solutions that share telemetry in real time. U.S. forward-hunt doctrines entrench spending on endpoint telemetry, deception grids, and mission-specific exploit chains that feed continuous engagement cycles. Canada increases procurement to safeguard critical mineral supply chains, while Mexico invests selectively to shield cross-border trade corridors.
Asia-Pacific is projected to grow at a 6.98% CAGR through 2031, reflecting strategic rivalry in the South China Sea and escalating cyber probes surrounding Taiwan. China's Strategic Support Force catalyzes regional investments; Japan doubles the headcount of its cyber unit, South Korea funds AI-enabled defensive lattices, and Australia coordinates joint red-team exercises with the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command. India's indigenous platforms gain traction under "Digital Bharat Shakti," reducing import dependency and fostering regional vendor ecosystems. Southeast Asian states, including Singapore and Vietnam, prioritize SOC modernization as digital trade expands their threat landscape.
Europe shows steady expansion as NATO doctrine synchronizes procurement, and the EU Cyber Solidarity Act streamlines funding for joint defensive projects.Germany and France allocate new funds for autonomous hunt platforms, while Nordic utilities procure winter-resilient defenses against grid sabotage. Eastern European states, wary of Russian hybrid tactics, are integrating mobile incident-response units into their border defense plans. Middle Eastern countries channel energy revenues into cyber arsenals that deliver asymmetric leverage in regional conflicts. African and South American militaries are beginning pilot projects to guard undersea cables and satellite nodes, creating nascent opportunities that will expand the global cyber warfare market size.
- BAE Systems plc
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- General Dynamics Corporation
- The Boeing Company
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Airbus Defence and Space SAS
- Thales Group
- Booz Allen Hamilton Holding Corporation
- Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC)
- Palantir Technologies Inc.
- CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Darktrace plc
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
- Kaspersky Lab JSC
- Trend Micro Incorporated
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Parsons Corporation
- FireEye Government Solutions LLC
- NCC Group plc
- CyberArk Software Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating nation-state sponsored cyber-espionage programs
- 4.2.2 Rapid digitalization of military C4ISR* networks
- 4.2.3 Surge in critical infrastructure attacks prompting defense budgets
- 4.2.4 NATO "Cyber as Domain" doctrine and allied procurement cycles
- 4.2.5 Proliferation of AI-enabled autonomous offensive tools
- 4.2.6 Commercial satellite internet creating new attack surface
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Acute shortage of cleared cyber-warfare personnel
- 4.3.2 Attribution complexity limiting proportional response
- 4.3.3 Fragmented international law on offensive cyber operations
- 4.3.4 Supply-chain trust gaps in open-source and COTS components
- 4.4 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
- 4.5 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.7 Technological Outlook
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By End-user Industry
- 5.1.1 Defense and Aerospace
- 5.1.2 BFSI
- 5.1.3 Corporate
- 5.1.4 Power and Utilities
- 5.1.5 Government
- 5.1.6 Healthcare
- 5.1.7 Transportation and Logistics
- 5.1.8 Other End-user Indutries
- 5.2 By Deployment Mode
- 5.2.1 On-premises
- 5.2.2 Cloud-based
- 5.2.3 Hybrid
- 5.3 By Solution Type
- 5.3.1 Offensive Platforms and Exploits
- 5.3.2 Defensive Platforms (SOC, SIEM, EDR)
- 5.3.3 Training, Simulation and Cyber Ranges
- 5.3.4 Advisory, Audit and Red-Team Services
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 South-East Asia
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.4.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.2 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.3 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.4 General Dynamics Corporation
- 6.4.5 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.6 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Leonardo S.p.A.
- 6.4.8 Airbus Defence and Space SAS
- 6.4.9 Thales Group
- 6.4.10 Booz Allen Hamilton Holding Corporation
- 6.4.11 Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC)
- 6.4.12 Palantir Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.13 CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Darktrace plc
- 6.4.16 Elbit Systems Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Kaspersky Lab JSC
- 6.4.18 Trend Micro Incorporated
- 6.4.19 Fortinet, Inc.
- 6.4.20 Parsons Corporation
- 6.4.21 FireEye Government Solutions LLC
- 6.4.22 NCC Group plc
- 6.4.23 CyberArk Software Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




