PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940602

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940602
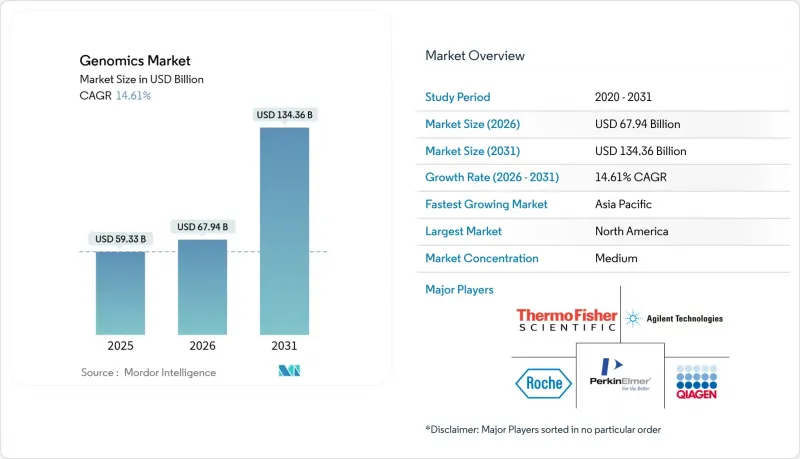
Genomics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The genomics market was valued at USD 59.28 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 67.94 billion in 2026 to reach USD 134.36 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 14.62% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Declining sequencing costs, population-scale initiatives, and rapid adoption of artificial intelligence position the genomics market for multi-year growth. Sovereign sequencing programs lower per-genome costs toward the USD 200-500 range, while national investments in domestic platforms insulate supply chains and support data sovereignty. Hospitals, pharmaceutical companies, and governments now view genomics as critical healthcare infrastructure rather than an experimental tool, catalyzing spending on instruments, consumables, and cloud analytics. Competitive dynamics continue to tilt toward firms offering integrated hardware-software stacks that reduce turnaround time and support regulatory compliance. Finally, moderated consolidation, anchored by partnerships rather than complete acquisitions, preserves room for innovative entrants that focus on long-read chemistry, AI interpretation, and cloud bioinformatics.
Global Genomics Market Trends and Insights
Population-Scale Newborn Genome Sequencing Programs
National health systems are adopting universal newborn genome sequencing to shift pediatric care from reactive to predictive. The UK NHS is scaling whole-genome screening, while Singapore's program targets familial hypercholesterolemia. Such initiatives lock in long-term reagent demand for high-throughput sequencers and generate datasets that pharmaceutical companies license for orphan-drug discovery. Analysts project a 10-to-1 economic return from avoided late-stage treatments, reinforcing sustained public funding. Implementation challenges, such as genetic-counselor shortages and secure data storage, drive hospitals toward cloud bioinformatics platforms.
Integration Of Genomic Data With AI-Driven Predictive Health Platforms
Artificial intelligence turns genomic outputs into longitudinal risk scores and treatment recommendations. Illumina's collaboration with NVIDIA demonstrates how GPU-accelerated algorithms cut secondary-analysis time and improve variant calling precision. US health systems report 30% fewer adverse drug reactions after adding AI-guided pharmacogenomics, while drug makers use multiomic AI to stratify trial populations.Firms fluent in both FDA device regulations and emerging AI governance are winning hospital contracts. Heightened privacy expectations are pushing vendors to adopt homomorphic encryption and federated learning.
Data-Sovereignty Rules Limiting Cross-Border Sample/Data Flows
The European Health Data Space and China's biosecurity legislation place strict controls on genomic transfers, forcing multinational providers to establish regional data centers and compliant workflows. These parallel infrastructures raise operating costs, slow collaboration, and favor domestically integrated competitors. Smaller firms lack regulatory bandwidth risk exit or acquisition, reinforcing consolidation among globally diversified players.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Long-Read Sequencing Unlocks Epigenomic & Structural Variant Insights
- Growing Government Funding & National Genomics Initiatives
- Consumer-Genomics Backlash Eroding Public Trust & Sample Supply
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Consumables delivered 43.05% of 2025 revenue, underscoring their essential role in daily sequencing workflows. Growth is supported by kit standardization that minimizes batch variability and by automation that speeds library preparation. The services category, supported by sequencing-as-a-service and bioinformatics outsourcing, is expanding at a 17.94% CAGR as laboratories convert capital outlays into operating budgets. Instrument demand remains steady because mid-life upgrades and long-read adoption offset hospital capital constraints. Software & informatics, once an accessory, now attracts premium spend as data interpretation becomes the primary bottleneck. Vendors bundle reagent subscriptions with AI-powered analytics and support contracts, securing predictable revenue and higher customer retention.
Consumable purchasing is no longer limited to core reagents. Labs order specialized extraction kits for challenging samples, CRISPR gene-editing consumables for functional assays, and barcoded microplates for high-throughput studies. Service providers add value with CLIA-certified testing, insurance billing, and cloud portals that deliver physician-ready reports. Hospitals gravitate toward these models to accelerate turnaround time without expanding in-house bioinformatics staff. The genomics market benefits because every incremental test pulls through consumables, software, and data-storage needs.
PCR still accounts for 34.78% of 2025 revenue because it delivers speed and low cost in targeted diagnostics and pathogen detection. Yet, sequencing platforms are expanding at 17.22% CAGR as comprehensive genomic profiling becomes feasible in routine care. Long-read and single-molecule systems detect structural variants and methylation states in one pass, closing clinical gaps left by short-read methods. Meanwhile, microarrays continue to lose ground but remain useful for high-volume genotyping.
Sequencing vendors are diversifying chemistries. Oxford Nanopore offers adaptive sampling that selects regions of interest on the fly. Roche is preparing nanopore-based SBX systems that promise higher speed and accuracy by 2026. As long-read accuracy rises and reagent costs fall, laboratories can consolidate multiple assays into a single workflow, reducing hands-on time and overall spending. PCR retains value in decentralized and point-of-care applications where instruments must be rugged, cheap, and fast.
The Genomics Market is Segmented by Product & Services (Consumables {Reagents, Kits, and More}, Instruments & Systems {NGS Platforms, and More} and More), Technology (PCR, Sequencing, and More), Application (Diagnostics, Drug Discovery and More), End User (Hospitals & Clinics, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and More). The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America held 42.05% of global revenue in 2025, supported by advanced reimbursement, large biopharma pipelines, and mature clinical genomics programs. The United States drives most spending through national cohort projects and aggressive hospital rollouts. Canada supports genomics with federal precision health grants, while Mexico collaborates cross-border to modernize diagnostic capacity. Regional headwinds include complex LDT regulations and shortages of bioinformaticians, which slow laboratory expansion.
Europe retains a strong installed base thanks to government-funded population programs and harmonized regulatory pathways. The European Health Data Space eases cross-border research once data-protection criteria are met, encouraging academic-industry partnerships. The United Kingdom's GBP 650 million commitment and universal newborn genome screening cement long-term demand. Germany and France scale clinical genomics through national insurance coverage, while Southern European countries leverage EU grants to catch up.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region at a 17.36% CAGR to 2031, propelled by China's self-reliance strategy, Japan's precision medicine reimbursement codes, and South Korea's AI-genomics clusters. BGI Genomics expands tuberculosis sequencing and oncology panels that meet domestic data-localization rules. India commercializes low-cost sequencing services for its expanding middle class, and Australia translates research strength into clinical adoption. Government mandates that keep data inside national borders incentivize local manufacturing and create regional winners.
Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa contribute smaller but rising shares. Brazil's USD 3.4 billion in healthcare M&A and genomic studies on African-Brazilian populations underline interest in diverse cohort research. Gulf states are investing in national precision health initiatives, often partnering with Western technology vendors to fast-track clinical readiness. African nations participate in consortium projects that build sequencing hubs and bioinformatics training, ensuring the genomics market eventually becomes more inclusive.
- 23andMe
- Agilent Technologies
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Eurofins
- Roche
- GE Healthcare
- Illumina
- Luminex
- Myriad Genetics
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- Pacific Bioscience
- PerkinElmer
- QIAGEN
- Quest Diagnostics
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- BGI
- 10x Genomics
- Guardant Health
- Fabric Genomics
- CD Genomics
- Color Health
- SOPHiA GENETICS
- Neogen
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Population-Scale Newborn Genome Sequencing Programs
- 4.2.2 Integration Of Genomic Data With AI-Driven Predictive Health Platforms
- 4.2.3 Long-Read Sequencing Unlocks Epigenomic & Structural Variant Insights
- 4.2.4 Growing Government Funding & National Genomics Initiatives
- 4.2.5 Rapid Cost Decline Of NGS & Ancillary Technologies
- 4.2.6 Expanding Clinical & Research Applications Across Precision Medicine
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Data-Sovereignty Rules Limiting Cross-Border Sample/Data Flows
- 4.3.2 Consumer-Genomics Backlash Eroding Public Trust & Sample Supply
- 4.3.3 Persistent High Capital Cost Of Advanced Sequencers & Reagents
- 4.3.4 Shortage Of Skilled Bioinformaticians/Genomic Counselors
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product & Services
- 5.1.1 Consumables
- 5.1.1.1 Reagents
- 5.1.1.2 Kits
- 5.1.1.3 Microplates
- 5.1.2 Instruments & Systems
- 5.1.2.1 NGS Platforms
- 5.1.2.2 PCR Machines
- 5.1.2.3 Microarray Scanners
- 5.1.3 Software & Informatics
- 5.1.3.1 Analysis Suites
- 5.1.3.2 LIMS
- 5.1.3.3 AI Decision Support
- 5.1.4 Services
- 5.1.4.1 Sequencing-As-A-Service
- 5.1.4.2 Data Analysis
- 5.1.4.3 Consulting
- 5.1.1 Consumables
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- 5.2.2 Sequencing
- 5.2.3 Long-Read/Single-Molecule Sequencing
- 5.2.4 Microarray
- 5.2.5 Nucleic Acid Extraction & Purification
- 5.2.6 Other Techniques
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Diagnostics
- 5.3.2 Drug Discovery & Development
- 5.3.3 Precision/Personalized Medicine
- 5.3.4 Agriculture & Animal Genomics
- 5.3.5 Forensics & Ancestry
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.4.2 Diagnostic & Reference Laboratories
- 5.4.3 Research Institutes & Centers
- 5.4.4 Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- 5.4.5 Other End Users
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 23andMe Inc.
- 6.3.2 Agilent Technologies
- 6.3.3 Bio-Rad Laboratories
- 6.3.4 Eurofins Scientific
- 6.3.5 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.3.6 GE HealthCare
- 6.3.7 Illumina Inc.
- 6.3.8 Luminex Corporation
- 6.3.9 Myriad Genetics Inc.
- 6.3.10 Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- 6.3.11 Pacific Biosciences of California Inc.
- 6.3.12 PerkinElmer Inc.
- 6.3.13 QIAGEN N.V.
- 6.3.14 Quest Diagnostics
- 6.3.15 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.3.16 BGI Group
- 6.3.17 10x Genomics
- 6.3.18 Guardant Health
- 6.3.19 Fabric Genomics
- 6.3.20 CD Genomics
- 6.3.21 Color Health
- 6.3.22 SOPHiA GENETICS
- 6.3.23 Neogen Corporation
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook




