PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940729

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940729
Zero-emission Aircraft - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
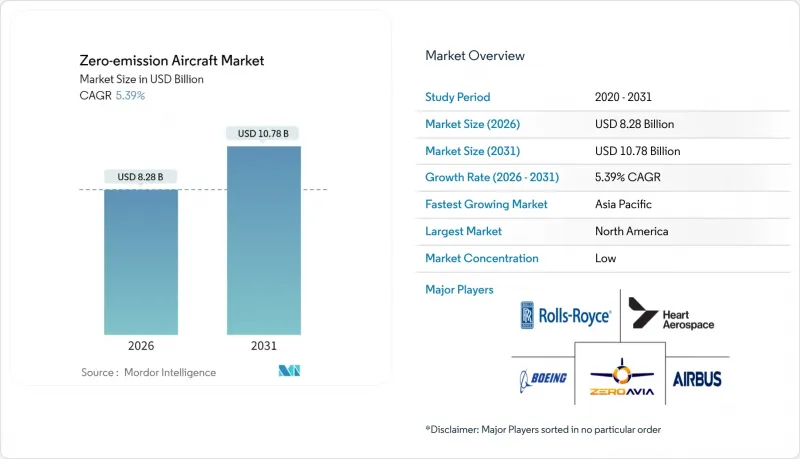
The zero-emission aircraft market was valued at USD 7.86 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 8.28 billion in 2026 to reach USD 10.78 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.39% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Robust policy support, record venture funding, and breakthroughs in hydrogen fuel cells and high-energy-density batteries accelerate technology readiness across commercial, general, and military platforms. Commercial operators remain the largest adopters on the strength of fleet replacement cycles, while general aviation is advancing fastest because of simpler certification pathways. Hybrid electric propulsion dominates, but hydrogen systems are gaining momentum as cryogenic storage hurdles ease. Battery advances are pushing viable range limits beyond the short-haul niche, and unmanned aerial systems (UAS) are proving out architectures more quickly than crewed programs thanks to lighter regulatory requirements.
Global Zero-emission Aircraft Market Trends and Insights
Advancements in Hydrogen Fuel Cell Power Systems for Aviation
Liquid-hydrogen demonstrations have validated cryogenic storage for medium-range missions following H2FLY's 2024 piloted flights. ZeroAvia has secured additional intellectual-property protection with 45 new patents, underscoring rapid design iteration. Airbus and Toshiba are collaborating on superconducting motors that use liquid hydrogen as fuel and cooling agents, a pairing expected to raise overall propulsion efficiency. Fuel-cell stacks now achieve higher specific power than early prototypes, cutting system weight and opening cabin space for revenue seats. Operators also gain lower acoustic signatures and maintenance savings than turbine engines, supporting community-noise regulations.
Global Policy Momentum Behind Green Hydrogen Aviation Infrastructure
The European Union's ReFuelEU Aviation regulation, Japan's National Green Hydrogen Mission, and multiple US state-level incentives align energy and aviation agencies around shared technical standards. Airport-centric projects such as Hamburg's hydrogen hub are shortening fuel logistics and reducing airline risk at early deployment sites. Carbon-pricing schemes and direct infrastructure grants create dual economic drivers that improve project bankability. The zero-emission aircraft market gains clearer pathways to scale as policymakers couple hydrogen production targets with aviation-sector carve-outs.
Lengthy Certification Timelines for Novel Electric and Hydrogen Propulsion Systems
Regulators are writing special conditions for technologies without commercial precedent, extending approval cycles by 24-36 months compared with conventional modifications. EASA is developing parallel guidance on cryogenic safety, but international harmonization remains incomplete. Capital efficiency suffers when manufacturers fund duplicative test programs for different jurisdictions. ZeroAvia's FAA G-1 basis offers a blueprint, yet the documentation volume highlights challenges for smaller entrants. The resulting schedule uncertainty weighs on investor confidence and may slow order conversions.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Breakthroughs in Next-Generation High-Energy-Density Aviation Batteries
- Sustainable Aviation Fuel Mandates Accelerating Zero-Emission Aircraft Development
- Limited Availability of Certified Aerospace-Grade Liquid Hydrogen Cryotanks
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Commercial operators accounted for 58.12% revenue in 2025, reflecting established fleet renewal cycles and long-term decarbonization road maps. Airlines like American have placed early power-plant reservations that translate into predictable line-fit demand once certification clears. General aviation, however, is scaling faster at 6.28% CAGR owing to lighter regulatory obligations and point-to-point operational flexibility. Charter operators and regional feeder airlines can integrate smaller zero-emission types without network-wide infrastructure overhauls. These dynamics ensure that the zero-emission aircraft market derives volumes from commercial fleets while technology proof points accumulate in general aviation first.
Beyond passenger movement, military stakeholders see tactical value in quieter, thermally discreet propulsion. Although defense orders remain nascent, long procurement cycles could lock in sizeable volumes as hydrogen systems mature. The combined effect of early general-aviation uptake and later large-scale airline replacements establishes a staggered adoption curve across sub-sectors, supporting long-run stability for the zero-emission aircraft market.
Hybrid electric systems delivered 45.62% of 2025 revenues as retrofit programs offered airlines lower entry friction. Yet hydrogen fuel-cell architectures are projected to expand at 8.98% CAGR to 2031, buoyed by superior gravimetric energy density and scalable refueling infrastructure initiatives. When liquid hydrogen flight tests with KLM validated three-hour endurance windows, stakeholder confidence in medium-range feasibility rose sharply. As cryotank mass declines, hydrogen aircraft are expected to close the payload gap with traditional turbine fleets, positioning them for core network routes where hybrid battery-assisted propulsion cannot economically compete.
Battery-only designs remain crucial for urban and short-regional missions where simplicity and lower infrastructure complexity provide immediate cost advantages. Continuous cell chemistry and thermal management improvements extend viable stage lengths, but industry consensus still sees hydrogen as the primary pathway for single-aisle category displacement. The technology mix, therefore, evolves from hybrid dominance today toward a dual-track future in which hydrogen captures middle-distance traffic and batteries serve dense short-haul corridors.
The Zero-Emission Aircraft Market Report is Segmented by Application (Commercial Aviation, General Aviation, and Military Aviation), Propulsion Technology (Hydrogen, Hybrid Electric, and Fully Electric), Range (Short-Range, Medium-Range, and Long-Range), Aircraft Type (Fixed-Wing, Rotorcraft, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America held 31.12% of 2025 sales, supported by FAA leadership in special-condition rule-making for electric and hydrogen propulsion. Canada's seaplane retrofits and the United States' airport-hydrogen task forces showcase operational breadth across passenger and cargo segments. Airline commitments secure installation demand, while manufacturers benefit from established aerospace labor pools and capital markets. Growth to 2031 hinges on timely infrastructure deployment at hub airports.
Asia-Pacific is advancing fastest at 6.55% CAGR, driven by sovereign investment vehicles and vertically integrated supply chains. Japan's USD 33 billion hydrogen aircraft program aligns aerospace primes with fuel producers, building an end-to-end ecosystem. China's battery-cell leadership and prototype hydrogen-drone milestones position local OEMs for export competitiveness once global certification reciprocity is achieved. India's carrier orders for hydrogen-electric powertrains indicate that secondary markets are also coming online quickly.
Europe remains influential through binding emissions targets and research funding instruments such as the Clean Aviation Joint Undertaking. Airbus's ZEROe demonstrators and Rolls-Royce propulsion investments underscore the region's advanced-technology credentials. Harmonized charging and refueling standards under ReFuelEU lower deployment friction across member states. Meanwhile, selected Middle East and African nations explore technology transfer partnerships tied to renewable-hydrogen mega-projects, though current volumes remain marginal.
- Airbus SE
- The Boeing Company
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- ZeroAvia, Inc.
- Heart Aerospace AB
- Bye Aerospace, Inc.
- Ampaire Inc.
- Pipistrel d.o.o. (Textron Inc.)
- Wright Electric Inc.
- BETA Technologies, Inc.
- Embraer S.A.
- GKN plc (Melrose Industries PLC)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Advancements in hydrogen fuel cell power systems for aviation
- 4.2.2 Global policy momentum behind green hydrogen aviation infrastructure
- 4.2.3 Breakthroughs in next-generation high-energy-density aviation batteries
- 4.2.4 Sustainable aviation fuel mandates accelerating zero-emission aircraft development
- 4.2.5 Rising public-private investments in airport-based hydrogen production facilities
- 4.2.6 Regulatory and economic incentives favoring low-noise electric propulsion technologies
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Limited availability of certified aerospace-grade liquid hydrogen cryotanks
- 4.3.2 High volatility in raw material prices for advanced battery chemistries
- 4.3.3 Lengthy certification timelines for novel electric and hydrogen propulsion systems
- 4.3.4 Widespread use of drop-in sustainable aviation fuels delaying zero-emission investments
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Application
- 5.1.1 Commercial Aviation
- 5.1.2 General Aviation
- 5.1.3 Military Aviation
- 5.2 By Propulsion Technology
- 5.2.1 Hydrogen
- 5.2.2 Hybrid Electric
- 5.2.3 Fully Electric
- 5.3 By Range
- 5.3.1 Short-Range
- 5.3.2 Medium-Range
- 5.3.3 Long-Range
- 5.4 By Aircraft Type
- 5.4.1 Fixed-Wing
- 5.4.2 Rotorcraft
- 5.4.3 Unmanned Aerial Systems
- 5.4.4 Regional Turboprop/Turbofan
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 Germany
- 5.5.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.3 Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- 6.4.4 ZeroAvia, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Heart Aerospace AB
- 6.4.6 Bye Aerospace, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Ampaire Inc.
- 6.4.8 Pipistrel d.o.o. (Textron Inc.)
- 6.4.9 Wright Electric Inc.
- 6.4.10 BETA Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.11 Embraer S.A.
- 6.4.12 GKN plc (Melrose Industries PLC)
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




