PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940857

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940857
Stepper Motor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
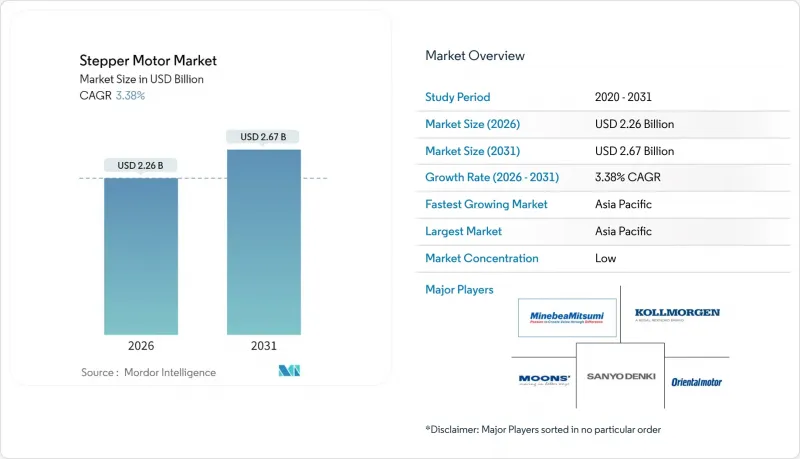
The stepper motor market is expected to grow from USD 2.19 billion in 2025 to USD 2.26 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 2.67 billion by 2031 at 3.38% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Demand holds steady as manufacturers in robotics, medical devices, and semiconductor equipment continue choosing stepper technology for precise open-loop positioning that avoids the higher system cost of servo platforms. Collaborative robots are gaining traction in assembly cells and are accelerating the adoption of compact NEMA-frame units that deliver predictable torque and simplified programming.Semiconductor capital spending, particularly in packaging and lithography lines, sustains orders for hybrid and linear variants that operate reliably in clean-room environments. Growth also stems from laboratory automation, desktop 3-D printers, and battery-manufacturing lines seeking low-maintenance actuators with tight repeatability. While the overall motion-control sector contracted in 2024 because of inventory corrections, renewed factory-automation investment in 2025 signals a return to steady purchasing cycles.
Global Stepper Motor Market Trends and Insights
Growing adoption of robotics and collaborative automation
Manufacturing plants deploying collaborative robots favor stepper drives because predictable step increments allow intrinsic torque limiting that enhances human-machine safety. U.S. reshoring programs and European productivity upgrades are standardizing on modular motion platforms that accept low-voltage, two-phase hybrids with microstepping controllers. Encoder-equipped closed-loop models are now achieving near-servo smoothness, broadening the feasible working envelope for pick-and-place systems. Ethernet-based protocols integrate the motors into plant networks, enabling condition monitoring that minimizes unplanned downtime. As small-lot production dominates contract manufacturing, easy changeover and fast programming keep stepper solutions attractive for integrators.
Rising demand for precision motion control in medical devices
Surgical robots, hematology analyzers, and drug-delivery pumps require sub-micron accuracy within compact footprints, a specification matched by modern hybrid steppers coupled to high-resolution encoders. Designers select the motors for repeatable holding torque that maintains instrument position even when power is cut, a critical patient-safety safeguard. Quiet operation is delivered by damping algorithms that shift resonance away from audible frequencies, meeting hospital noise norms. FDA and CE rules highlight traceability, favoring vendors with ISO 13485 certificates and validated design-history files. Long replacement cycles in healthcare extend revenue visibility for component suppliers.
Performance limits versus servo / BLDC motors
Despite incremental gains, torque in stepper stacks declines sharply above 1,000 RPM, capping suitability in high-speed pick-and-place or conveyor drives. Price erosion in entry-level servos reduces the historical cost gap that once favored steppers for medium-precision work. Integrated servo packages now include automatic tuning and fieldbus options, simplifying commissioning and reducing the total installed cost delta. Marketers, therefore, emphasize use cases where positional holding torque at standstill outweighs dynamic requirements, such as valve actuation or microplate indexing.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of 3-D printing and desktop manufacturing ecosystems
- Surge in semiconductor packaging-equipment investments
- Integrated smart-actuators cannibalizing discrete motors
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hybrid variants commanded 54.65% stepper motor market share in 2025 due to their balance of torque density and 1.8-degree step resolution, and they are forecast to expand at a 3.95% CAGR, outpacing permanent-magnet and variable-reluctance formats. This dominance translates into sustained research and development allocations for finer magnetic circuits that raise flux density without enlarging frame size. Vendors now deploy high-fill-factor windings that shave I2R losses and allow operation at reduced current, extending bearing life through lower heat generation.
Hybrid improvements also underpin energy-efficiency upgrades needed to comply with IEC 60034-30-1 classes. Neodymium-iron-boron magnet blanks are laser-machined to minimize post-assembly skew, improving microstep linearity essential for photonics test stages. Permanent-magnet units still serve cost-sensitive vending machines, while variable-reluctance designs retain niches in extreme-temperature pumps where magnet decay is a concern. Overall, the stepper motor market benefits from a technology roadmap centered on hybrid refinements that close the performance gap with inexpensive servos without surrendering the cost advantage.
The Stepper Motor Market Report is Segmented by Motor Type (Hybrid, Permanent Magnet, and Variable Reluctance), Drive Technique (Open-Loop, and Closed-Loop), Application (Industrial Equipment, Robotics and Cobots, Medical and Laboratory Devices, Computing / 3-D Printing, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific remained the 2025 revenue leader with a 35.74% share, anchored by Chinese component ecosystems that streamline magnet, shaft, and driver sourcing. Regional titans such as MOONS' Electric leverage scale economies above 1 million units per year, supporting aggressive pricing that feeds global export channels. Japan complements volume with technology, patented closed-loop firmware, and high-vacuum designs that power the region's semiconductor equipment exports. South Korea and Southeast Asia have emerged as contract-manufacturing hubs that integrate imported hybrids into finished printer and robot sub-assemblies, reinforcing intra-regional value chains.
North America, projected at a 3.76% CAGR, benefits from federal incentives that reimburse automation upgrades and onshore semiconductor fabs. U.S. integrators increasingly specify standardized NEMA frames over custom servos to shorten lead times during green-field EV battery-plant construction. Canadian facilities in life sciences and food packaging drive demand for wash-down IP65 variants, while Mexico supports automotive harness production lines using cost-optimized open-loop steppers.
Europe experiences steady gains under energy-efficiency directives such as Regulation 2019/1781 that push factories toward closed-loop retrofits. German OEMs exploit local precision-machining expertise to supply high-vacuum variants to the global wafer-tool sector. Meanwhile, emerging Middle-East and African economies begin specifying stepper drives in desalination, textile, and packaging projects, though volumes remain a fraction of mature regions. Altogether, geographic diversification shields the stepper motor market from isolated downturns and underscores a resilient multi-regional demand base.
- AMETEK, Inc.
- Anaheim Automation, Inc.
- Arcus Technology Inc.
- Changzhou Fulling Motor Co., Ltd.
- Changzhou Leili Intelligent Drive Systems Co., Ltd.
- ElectroCraft, Inc.
- Faulhaber Group
- JVL Industri Elektronik A/S
- Kollmorgen (Regal Rexnord Corp.)
- Lin Engineering, Inc.
- MinebeaMitsumi Inc.
- MOONS' Electric Co., Ltd.
- Nanotec Electronic GmbH & Co. KG
- Nidec Servo Corporation
- Nippon Pulse America, Inc.
- Oriental Motor Co., Ltd.
- Parker-Hannifin Corp.
- Performance Motion Devices, Inc.
- Phytron GmbH
- Schneider Electric SE
- Sanyo Denki Co., Ltd.
- Sonceboz SA
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Tamagawa Seiki Co., Ltd.
- Texas Instruments Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing adoption of robotics and collaborative automation
- 4.2.2 Rising demand for precision motion control in medical devices
- 4.2.3 Expansion of 3-D printing and desktop manufacturing ecosystems
- 4.2.4 Surge in semiconductor packaging-equipment investments
- 4.2.5 Shift to energy-efficient closed-loop stepper solutions
- 4.2.6 Government incentives for localised motion-component production
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Performance limits versus servo / BLDC motors
- 4.3.2 Price pressure from low-cost Asian manufacturers
- 4.3.3 Integrated smart-actuators cannibalising discrete motors
- 4.3.4 Thermal-management challenges in compact designs
- 4.4 Industry Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Motor Type
- 5.1.1 Hybrid
- 5.1.2 Permanent Magnet
- 5.1.3 Variable Reluctance
- 5.2 By Drive Technique
- 5.2.1 Open-Loop
- 5.2.2 Closed-Loop
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Industrial Equipment
- 5.3.2 Robotics and Cobots
- 5.3.3 Medical and Laboratory Devices
- 5.3.4 Computing / 3-D Printing
- 5.3.5 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 South-East Asia
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.5.2 Africa
- 5.4.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.4.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Middle East
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AMETEK, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Anaheim Automation, Inc.
- 6.4.3 Arcus Technology Inc.
- 6.4.4 Changzhou Fulling Motor Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Changzhou Leili Intelligent Drive Systems Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.6 ElectroCraft, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Faulhaber Group
- 6.4.8 JVL Industri Elektronik A/S
- 6.4.9 Kollmorgen (Regal Rexnord Corp.)
- 6.4.10 Lin Engineering, Inc.
- 6.4.11 MinebeaMitsumi Inc.
- 6.4.12 MOONS' Electric Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Nanotec Electronic GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.14 Nidec Servo Corporation
- 6.4.15 Nippon Pulse America, Inc.
- 6.4.16 Oriental Motor Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Parker-Hannifin Corp.
- 6.4.18 Performance Motion Devices, Inc.
- 6.4.19 Phytron GmbH
- 6.4.20 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.21 Sanyo Denki Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.22 Sonceboz SA
- 6.4.23 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.24 Tamagawa Seiki Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.25 Texas Instruments Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




