PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940905

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1940905
US Insecticide - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
The US insecticide market was valued at USD 7.98 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 8.35 billion in 2026 to reach USD 10.45 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.60% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
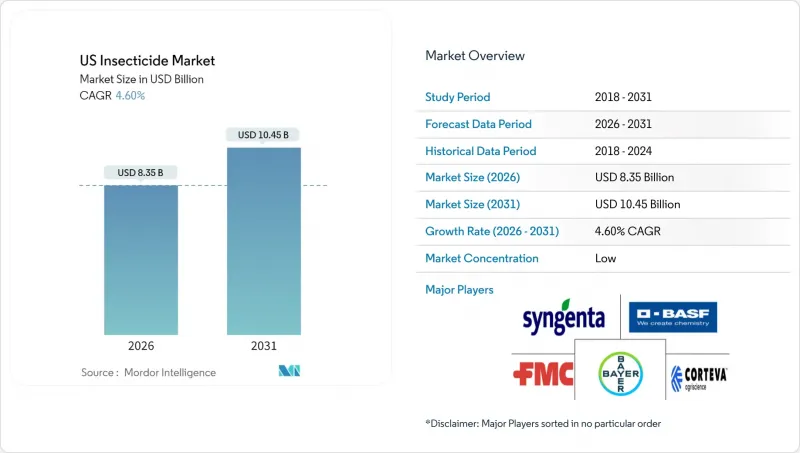
Rising specialty-crop acreage, wider precision-agriculture deployment, and persistent resistance issues are sustaining demand even as regulatory scrutiny tightens. Growth also reflects the drive for earlier-stage protection through seed treatment, the premium assigned to low-rate active ingredients that lighten environmental loading, and escalating labor costs that favor automated or one-pass application tactics. While foliar sprays still dominate, the US insecticide market is steadily tilting toward technology-enabled approaches that reduce operator exposure and improve return on investment. Competitive strategies now center on portfolio breadth, regulatory adaptability, and integration with data platforms that support variable-rate decisions.
US Insecticide Market Trends and Insights
Specialty-Crop Acreage Expansion
Revenue potential per acre for almonds, citrus, and wine grapes grew markedly between 2020 and 2024, encouraging heavier investment in premium chemistry that meets export residue rules. In California, almond plantings rose 12% over the period, while Florida citrus recovery efforts enlarged insecticide programs aimed at Asian citrus psyllid suppression. Specialty crops often deliver three-to-five-fold higher gross returns relative to grains, so growers willingly adopt high-priced, reduced-risk formulations that protect both yield and quality. Climate shifts are simultaneously opening new production zones in the Pacific Northwest, widening the addressable acreage. As a result, the US insecticide market gains reliable volume from premium categories that absorb price increases without material demand destruction.
Resistance management needs
Regulatory mandates now codify rotation of modes of action for pests such as corn rootworm and cotton bollworm. University extension data show 67% of corn growers implemented formal resistance programs in 2024 versus 23% in 2020, a shift that creates predictable peaks for newer actives while hastening obsolescence of aging compounds. Portfolio depth, therefore, becomes a revenue hedge, with suppliers able to fill entire seasonal plans, enjoying greater share security. Structured rotation also stimulates development of formulations that blend multiple actives, bundling insecticidal and fungicidal protection in single passes to ensure compliance and labor savings.
EPA-Driven Withdrawals
Regulatory withdrawals of established insecticide active ingredients are creating market disruptions that force rapid adoption of alternative chemistries, often at higher per-acre costs that strain grower economics while benefiting companies with robust replacement product portfolios. The EPA's 2024 decision to restrict neonicotinoid applications on pollinator-attractive crops eliminated approximately USD 340 million in annual market value, creating immediate demand for alternative chemistries that command premium pricing due to limited supply. These regulatory actions are accelerating industry consolidation as smaller companies struggle to maintain viable product portfolios amid shrinking chemistry options.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growth in seed-treatment adoption
- Approvals of low-rate AIs (Active Ingredients)
- Pollinator-Health Pressures
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Foliar sprays led with 55.87% of the US insecticide market share in 2025, whereas seed treatment posted the fastest growth at a 4.78% CAGR through 2031, anchored by their versatility across crop systems. The US insecticide market size for seed treatment is poised to eclipse by 2031 if current penetration continues. Adoption is supported by evidence that a single coating delivers four-to-six-week protection at up to 40% lower total cost than comparable foliar-only programs. Labor savings are significant because treated seed enters the soil in one operation, eliminating additional passes. Regulatory pressure also favors closed-system seed coaters that reduce applicator exposure.
Demand for chemigation and drip injection rises where irrigation infrastructure permits, especially in water-limited regions aiming for simultaneous pest and moisture management. Fumigation retains a niche in strawberry beds and nursery stock but exhibits minimal growth. Soil treatments remain important in perennial orchards where root-zone protection is critical. Product development now focuses on encapsulated microgranules and biological inoculants that complement systemic actives, offering sustained release throughout root flushes. Together, these trends illustrate the diversified pathway through which the US insecticide market accommodates evolving agronomic and labor realities.
The US Insecticide Market Report is Segmented by Application Mode (Chemigation, Foliar, Fumigation, Seed Treatment, and More), and Crop Type (Commercial Crops, Fruits and Vegetables, Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Metric Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- FMC Corporation
- Nufarm Ltd
- Syngenta Group
- UPL Limited
- PI Industries
- Sumitomo Chemical Co.
- American Vanguard Corporation
- Envu US LLC (Cinven)
- Helena Agri-Enterprises (Marubeni Corporation)
- Nutrien Ltd
- Gowan Company
- Atticus LLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
- 1.3 Research Methodology
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Consumption Of Pesticide Per Hectare
- 4.2 Pricing Analysis For Active Ingredients
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 United States
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.5 Market Drivers
- 4.5.1 Specialty-crop acreage expansion
- 4.5.2 Resistance management needs
- 4.5.3 Growth in seed-treatment adoption
- 4.5.4 Approvals of low-rate AIs (Active Ingredients)
- 4.5.5 Protected agriculture demand
- 4.5.6 Drone-based precision spraying
- 4.6 Market Restraints
- 4.6.1 EPA-driven withdrawals
- 4.6.2 Pollinator-health pressures
- 4.6.3 GM insect-resistant traits
- 4.6.4 Applicator labor shortage
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECAST (VALUE AND VOLUME)
- 5.1 Application Mode
- 5.1.1 Chemigation
- 5.1.2 Foliar
- 5.1.3 Fumigation
- 5.1.4 Seed Treatment
- 5.1.5 Soil Treatment
- 5.2 Crop Type
- 5.2.1 Commercial Crops
- 5.2.2 Fruits & Vegetables
- 5.2.3 Grains & Cereals
- 5.2.4 Pulses & Oilseeds
- 5.2.5 Turf & Ornamental
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BASF SE
- 6.4.2 Bayer AG
- 6.4.3 Corteva Agriscience
- 6.4.4 FMC Corporation
- 6.4.5 Nufarm Ltd
- 6.4.6 Syngenta Group
- 6.4.7 UPL Limited
- 6.4.8 PI Industries
- 6.4.9 Sumitomo Chemical Co.
- 6.4.10 American Vanguard Corporation
- 6.4.11 Envu US LLC (Cinven)
- 6.4.12 Helena Agri-Enterprises (Marubeni Corporation)
- 6.4.13 Nutrien Ltd
- 6.4.14 Gowan Company
- 6.4.15 Atticus LLC
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CROP PROTECTION CHEMICALS CEOS




