PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1403756

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1403756
India Agricultural Tractor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts 2024 - 2029
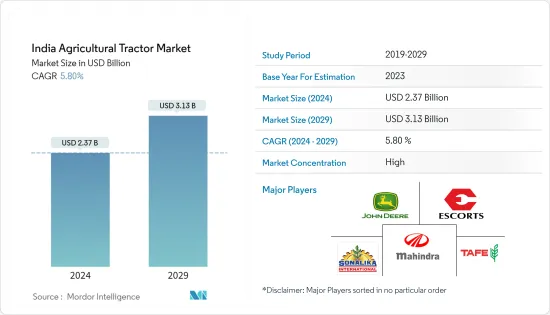
The India Agricultural Tractor Market size is estimated at USD 2.37 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 3.13 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.80% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The tractor industry in India remained largely unaffected due to the impact of COVID-19, and tractor sales in India decreased only in April 2020 due to lockdown restrictions. Throughout the remaining part of 2020 and moving into 2021, the demand for agricultural machinery, including tractors, increased due to higher Kharif sowing, good cash flows to farmers, a timely and normal monsoon in the country across June and July, continued higher rural spending by the government, and exemption from lockdown restrictions.
Government initiatives toward rural development, farm mechanization, and various factors, such as high rural wages and scarcity of farm labor, are likely to increase the tractor volume over the long term. In terms of units, India is one of the largest tractor markets globally, selling 600,000 to 700,000 tractors per annum on average between 2016-2021.
Two-wheel drive tractors are found to be more popular than four-wheel-drive tractors in the Indian market. The agriculture tractor market is dominated by aboriginal Indian OEMs, namely Mahindra & Mahindra Limited, TAFE, International Tractors Ltd (Sonalika), and Escorts Limited. Key international tractor manufacturers, such as Deere & Company, CNH penetrated the market and established a decent market presence.
India remains a highly lucrative tractor market because of the decreasing availability of farm labor and the rise of innovative business models, such as custom hiring solutions for tractors. In India, under the mechanization component of the macro-management scheme of agriculture by the Indian government, there is a provision of subsidy for promoting agricultural mechanization, including 25% of the cost limited to INR 30,000 for buying tractors of up to 35 PTO HP. Thus, with the rising government support for enhancing farm mechanizations and expansion in crop production, the sale of agriculture tractors is anticipated to rise in the upcoming years.
India Agricultural Tractor Machinery Market Trends
Increasing Trend of Mechanization in Agriculture Sector
In recent years, farm mechanization practices have come a long way. Issues concerning farm productivity are tackled mainly through the extensive use of tractors and other farm equipment. The employment of mechanized power in the field has been the pioneer for impressive changes in the country's agriculture sector. Providing the subsidy involves all stakeholders, including the Indian government, state governments, state agro-industries corporations, machinery manufacturers associations, Farm Machinery Testing and Training Institutes (FMTTIs), manufacturers, importers, dealers, and farmers. Under direct benefit transfer in agricultural mechanization, the subsidy in the market is shared by both center and state governments.
Easy credit availability to farmers is made possible through many financial institutions, and favorable government policies and subsidy programs lead these. Various loan schemes, easy breakdown of installments according to crop cycles, and low-interest rate plans generate funding for mechanization. As per India's National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) norms, any farmer with 8 acres of land can take a tractor loan to be paid over nine years, with 12.5% interest over the principal amount. Various concessions from the Indian government, like exemption of excise duty for tractors less than 1800 cc of capacity, have helped small farmers purchase the machine. In order to offer loans to a higher number of small and marginal farmers, the government has also reduced the minimum land holding from 10 acres to 4 acres over the years, and the credit period has been increased from 7 to 9 years.
In addition to the schemes mentioned above, under central sector extension programs, the government provides subsidies for purchasing tractors below 18 HP. This subsidy is being provided to farmers individually or in groups, with irrigated land between 2.4-3.2 ha. The farm power availability has increased to 2.76 kW/ha in 2021 and the government has set a target to achieve 4 kW/ha by 2030. This in turn is anticipated to boosted the sale of agricultural machinery in India.
Thus, with substantial support from the government, the adoption of tractors for agricultural practices is increasing over the years. Hence, the farm mechanization goals of the Indian government are acting as the prime driver and are expected to boost the growth of the market during the forecast period.
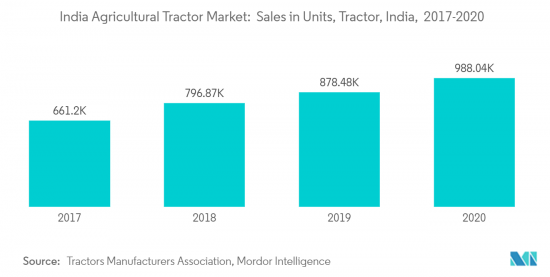
Two-wheel Drives Dominate the Drive Type Segment
Two-wheel tractors are prominently used in dry farming conditions where fields are not excessively muddy, sloped, or wet. These are suitable for sowing seeds, spraying fertilizers and pesticides, topping the pastures, etc. The two-wheel-drive tractors are cost-effective and affordable for small and marginal farmers, who are prominent in the Indian agriculture sector. Furthermore, these tractors are easy to handle and have improved maneuverability, resulting in them being operated comfortably.
Some of the players operating in this segment include Sonilka, Mahindra and Mahindra, John Deere, Swaraj, and Eicher. The players in the market are focusing on research and development and the launch of new products to increase their market share. For instance, in 2018, Swaraj Tractors launched Swaraj 963 FE with a two-wheel-drive mechanism to cater to the customers in the country. The tractor backhoe loader is used for digging, loading, backfilling, trenching, and provides the maximum power and performance in all outdoor activities. These are used in the construction and mining sectors. Players such as Gainwell CAT are offering tractor backhoe loaders with two-wheel drive mechanisms for construction sectors in the country. Factors such as the low fuel efficiency of two-wheel drive tractors due to unnecessary wear and tear and the low brand availability of two-wheel drive tractors compared to four-wheel drive tractors are expected to hinder the growth of the segment during the forecast period.
Furthermore, additional maintenance costs for this segment restrained their adoption during the study period. Thus, the introduction of advanced models by market players clubbed with the cost-effective nature of these tractors is expected to drive the growth of this segment during the forecast period.
India Agricultural Tractor Machinery Industry Overview
The agricultural tractor market in India is consolidated and dominated by large global and domestic manufacturers, and farmers prefer trusted brands for assurance of quality and better after-sales services. Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd is the leading player occupying the highest share in the Indian agricultural tractors market, followed by Tractor and Farm Equipment Ltd (TAFE), International Tractor Ltd, and Escorts Limited. These major players are investing in new products and improvisation of products, expansions, and acquisitions for business expansions. Another major area of investment is the focus on R&D to launch new products at lower prices.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Drivers
- 4.2 Market Restraints
- 4.3 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Engine Power
- 5.1.1 Less than 30 HP
- 5.1.2 31-50 HP
- 5.1.3 51-80 HP
- 5.1.4 Above 80 HP
- 5.2 Drive Type
- 5.2.1 Two-wheel Drive
- 5.2.2 Four-wheel Drive
- 5.3 Application
- 5.3.1 Row Crop Tractors
- 5.3.2 Orchard Tractors
- 5.3.3 Other Applications
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Mahindra & Mahindra Limited
- 6.3.2 John Deere India Private Limited
- 6.3.3 CNH Industrial (India) Pvt. Ltd
- 6.3.4 TAFE Ltd
- 6.3.5 International Tractors Limited (Sonalika)
- 6.3.6 Escorts Group
- 6.3.7 Kubota Corporation
- 6.3.8 Force Motors Limited
- 6.3.9 Preet Tractors (P) Limited
- 6.3.10 Standard Corporation India Limited
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
8 AN ASSESSMENT OF COVID-19 IMPACT ON THE MARKET




