PUBLISHER: Roots Analysis | PRODUCT CODE: 1932846

PUBLISHER: Roots Analysis | PRODUCT CODE: 1932846
Japan In vitro Diagnostics Market: Distribution by Test Type, Type of Offering, Type of Technology, Therapeutic Area, End Users and Geographical Regions - Industry Trends and Forecast 2026-2035
Japan In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Overview
As per Roots Analysis, the Japan in vitro diagnostics market is estimated to grow from USD 3.30 billion in the current year to USD 5.28 billion by 2035 at a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period, 2026-2035.
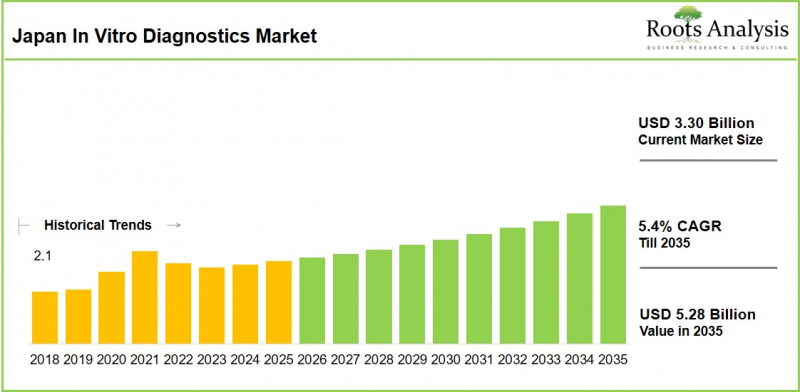
Japan In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Growth and Trends
In vitro diagnostic tests (IVD) refer to tests performed on human samples, such as blood or tissue, outside the body to facilitate precise disease diagnosis. These tests can help identify illnesses, track treatment advancements, and predict healthcare results.
IVD products, despite being non-invasive, are still subject to the same regulatory standards as medical devices because of their critical function in healthcare. These diagnostic solutions vary from self-administered glucose monitoring systems to advanced in-laboratory diagnostic techniques. In vitro diagnostic solutions encompass a variety of tests, like blood typing, cancer detection, and kidney profiling, utilized for different purposes, including disease identification and monitoring.
The World Health Organization reports that more than 40,000 in vitro diagnostic products are currently on the market. This extensive selection of products emphasizes the vital importance of diagnostics in healthcare. Additionally, it should be noted that more than 70% of healthcare choices are based on laboratory test outcomes, highlighting the significance of these diagnostic instruments in patient treatment. This is due to the capacity of these solutions to deliver accurate diagnoses and facilitate timely intervention to prevent disease advancement.
The in vitro diagnostics (IVD) sector in Japan shows significant potential for growth, fueled by a quickly aging population that increases the need for tests aimed at managing chronic illnesses such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, advancements in technology, including AI, automation, precision medicine, genetic testing, and point-of-care devices, are facilitating growth by enhancing both accuracy and efficiency. Given the benefits of diagnostic assays in providing rapid diagnostic results and improving patient care, the IVD market in Japan is expected to grow significantly throughout the forecast period.
Growth Drivers: Strategic Enablers of Market Expansion
Japan's in vitro diagnostics (IVD) market benefits from strong growth drivers owing to its aging population and technological innovations, including AI integration, molecular diagnostics, point-of-care testing, and automation, enhance efficiency, accuracy, and adoption of personalized medicine. Further, supportive government policies, increased healthcare spending, preventive care initiatives, and R&D investments further propel expansion of the Japan in vitro diagnostics market growth.
Market Challenges: Critical Barriers Impeding Progress
Despite these growth drivers, the market faces significant challenges from stringent regulatory frameworks enforced by the PMDA, which prolong approval timelines, raise compliance costs, and complicate entry for other players. High costs for R&D, advanced equipment, and clinical trials strain budgets, while inadequate reimbursement systems and hospital finance distress limit accessibility. Additional hurdles include supply chain vulnerabilities, shortages of skilled personnel, price pressures and resistance to new technologies amid economic constraints.
Laboratory Tests: Leading Market Segment
Currently, laboratories segment captures nearly 85% of the overall market share. This dominance is primarily due to their capacity for high-volume, complex testing and specialized infrastructure. However, the point-of-care testing segment is likely to grow at a higher CAGR of 4% during the forecast period.
Reagents: Dominating Market Segment
In terms of type of offering, the Japan in vitro diagnostics market is segmented across reagents, instruments and services. Currently, majority (~75%) of the market share is held by reagents. This is due to their consumable-centric business model, generating recurring revenue through high-volume, routine testing in clinical chemistry, immunoassay, and hematology. Further, the instruments segment is likely to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period.
In vitro Diagnostics Market: Key Segments
Test Type
- Laboratory Testing
- Point-of-Care / POC Testing
Type of Offering
- Reagents
- Instruments
- Services
Type of Technology
- Clinical Chemistry
- Hematology
- Immunoassay
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Others
Therapeutic Area
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Cardiovascular Disorders
- Diabetes
- Infectious Diseases
- Renal Disorders
- Oncological Disorders
- Others
End Users
- Hospitals
- Laboratories
- Others
Example Players in the Japan In vitro Diagnostics Market
- Abbott Laboratories
- Arkray
- Danaher
- Fujirebio Holdings
- H.U. Group Holdings (formerly Hitachi)
- Roche Diagnostics
- Sysmex
- Tosoh
Key Questions Answered in this Report
- How many Japan in vitro diagnostic service providers are currently engaged in this market?
- Which are the leading companies in this market?
- Which country dominates the Japan in vitro diagnostics market?
- What are the key trends observed in the Japan in vitro diagnostics market?
- What factors are likely to influence the evolution of this market?
- What are the primary challenges faced by in vitro diagnostic service providers in Japan?
- What is the current and future Japan in vitro diagnostics market size?
- What is the CAGR of Japan in vitro diagnostics market?
- How is the current and future market opportunity likely to be distributed across key market segments?
Reasons to Buy this Report
- The report provides a comprehensive market analysis, offering detailed revenue projections of the overall market and its specific sub-segments. This information is valuable to both established market leaders and emerging entrants.
- The report offers stakeholders a comprehensive overview of the market, including key drivers, barriers, opportunities, and challenges. This information empowers stakeholders to stay abreast of market trends and make data-driven decisions to capitalize on growth prospects.
- The report can aid businesses in identifying future opportunities in any sector. It also helps in understanding if those opportunities are worth pursuing.
- The report helps in identifying customer demand by understanding the needs, preferences, and behavior of the target audience in order to tailor products or services effectively.
- The report equips new entrants with requisite information regarding a particular market to help them build successful business strategies.
- The report allows for more effective communication with the audience and in building strong business relations.
Complementary Benefits
- Complimentary Excel Data Packs for all Analytical Modules in the Report
- 15% Free Content Customization
- Detailed Report Walkthrough Session with Research Team
- Free Updated report if the report is 6-12 months old or older
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PREFACE
- 1.1. Introduction
- 1.2. Market Share Insights
- 1.3. Key Market Insights
- 1.4. Report Coverage
- 1.5. Key Questions Answered
- 1.6. Chapter Outlines
2. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1. Chapter Overview
- 2.2. Research Assumptions
- 2.2.1. Market Landscape and Market Trends
- 2.2.2. Market Forecast and Opportunity Analysis
- 2.2.3. Comparative Analysis
- 2.3. Database Building
- 2.3.1. Data Collection
- 2.3.2. Data Validation
- 2.3.3. Data Analysis
- 2.4. Project Methodology
- 2.4.1. Secondary Research
- 2.4.1.1. Annual Reports
- 2.4.1.2. Academic Research Papers
- 2.4.1.3. Company Websites
- 2.4.1.4. Investor Presentations
- 2.4.1.5. Regulatory Filings
- 2.4.1.6. White Papers
- 2.4.1.7. Industry Publications
- 2.4.1.8. Conferences and Seminars
- 2.4.1.9. Government Portals
- 2.4.1.10. Media and Press Releases
- 2.4.1.11. Newsletters
- 2.4.1.12. Industry Databases
- 2.4.1.13. Roots Proprietary Databases
- 2.4.1.14. Paid Databases and Sources
- 2.4.1.15. Social Media Portals
- 2.4.1.16. Other Secondary Sources
- 2.4.2. Primary Research
- 2.4.2.1. Types of Primary Research
- 2.4.2.1.1. Qualitative Research
- 2.4.2.1.2. Quantitative Research
- 2.4.2.1.3. Hybrid Approach
- 2.4.2.2. Advantages of Primary Research
- 2.4.2.3. Techniques for Primary Research
- 2.4.2.3.1. Interviews
- 2.4.2.3.2. Surveys
- 2.4.2.3.3. Focus Groups
- 2.4.2.3.4. Observational Research
- 2.4.2.3.5. Social Media Interactions
- 2.4.2.4. Key Opinion Leaders Considered in Primary Research
- 2.4.2.4.1. Company Executives (CXOs)
- 2.4.2.4.2. Board of Directors
- 2.4.2.4.3. Company Presidents and Vice Presidents
- 2.4.2.4.4. Research and Development Heads
- 2.4.2.4.5. Technical Experts
- 2.4.2.4.6. Subject Matter Experts
- 2.4.2.4.7. Scientists
- 2.4.2.4.8. Doctors and Other Healthcare Providers
- 2.4.2.5. Ethics and Integrity
- 2.4.2.5.1. Research Ethics
- 2.4.2.5.2. Data Integrity
- 2.4.2.1. Types of Primary Research
- 2.4.3. Analytical Tools and Databases
- 2.4.1. Secondary Research
- 2.5. Robust Quality Control
3. MARKET DYNAMICS
- 3.1. Chapter Overview
- 3.2. Forecast Methodology
- 3.2.1. Top-down Approach
- 3.2.2. Bottom-up Approach
- 3.2.3. Hybrid Approach
- 3.3. Market Assessment Framework
- 3.3.1. Total Addressable Market (TAM)
- 3.3.2. Serviceable Addressable Market (SAM)
- 3.3.3. Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM)
- 3.3.4. Currently Acquired Market (CAM)
- 3.4. Forecasting Tools and Techniques
- 3.4.1. Qualitative Forecasting
- 3.4.2. Correlation
- 3.4.3. Regression
- 3.4.4. Extrapolation
- 3.4.5. Convergence
- 3.4.6. Sensitivity Analysis
- 3.4.7. Scenario Planning
- 3.4.8. Data Visualization
- 3.4.9. Time Series Analysis
- 3.4.10. Forecast Error Analysis
- 3.5. Key Considerations
- 3.5.1. Demographics
- 3.5.2. Government Regulations
- 3.5.3. Reimbursement Scenarios
- 3.5.4. Market Access
- 3.5.5. Supply Chain
- 3.5.6. Industry Consolidation
- 3.5.7. Pandemic / Unforeseen Disruptions Impact
- 3.6. Limitations
4. MACRO-ECONOMIC INDICATORS
- 4.1. Chapter Overview
- 4.2. Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1. Time Period
- 4.2.1.1. Historical Trends
- 4.2.1.2. Current and Forecasted Estimates
- 4.2.2. Currency Coverage
- 4.2.2.1. Major Currencies Affecting the Market
- 4.2.2.2. Factors Affecting Currency Fluctuations on the Industry
- 4.2.2.3. Impact of Currency Fluctuations on the Industry
- 4.2.3. Foreign Currency Exchange Rate
- 4.2.3.1. Impact of Foreign Exchange Rate Volatility on the Market
- 4.2.3.2. Strategies for Mitigating Foreign Exchange Risk
- 4.2.4. Recession
- 4.2.4.1. Assessment of Current Economic Conditions and Potential Impact on the Market
- 4.2.4.2. Historical Analysis of Past Recessions and Lessons Learnt
- 4.2.5. Inflation
- 4.2.5.1. Measurement and Analysis of Inflationary Pressures in the Economy
- 4.2.5.2. Potential Impact of Inflation on the Market Evolution
- 4.2.6. Interest Rates
- 4.2.6.1. Interest Rates and Their Impact on the Market
- 4.2.6.2. Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk
- 4.2.7. Commodity Flow Analysis
- 4.2.7.1. Type of Commodity
- 4.2.7.2. Origins and Destinations
- 4.2.7.3. Value and Weights
- 4.2.7.4. Modes of Transportation
- 4.2.8. Global Trade Dynamics
- 4.2.8.1. Import Scenario
- 4.2.8.2. Export Scenario
- 4.2.8.3. Trade Policies
- 4.2.8.4. Strategies for Mitigating the Risks Associated with Trade Barriers
- 4.2.8.5. Impact of Trade Barriers on the Market
- 4.2.9. War Impact Analysis
- 4.2.9.1. Russian-Ukraine War
- 4.2.9.2. Israel-Hamas War
- 4.2.10. COVID Impact / Related Factors
- 4.2.10.1. Global Economic Impact
- 4.2.10.2. Industry-specific Impact
- 4.2.10.3. Government Response and Stimulus Measures
- 4.2.10.4. Future Outlook and Adaptation Strategies
- 4.2.11. Other Indicators
- 4.2.11.1. Fiscal Policy
- 4.2.11.2. Consumer Spending
- 4.2.11.3. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- 4.2.11.4. Employment
- 4.2.11.5. Taxes
- 4.2.11.6. Stock Market Performance
- 4.2.11.7. Cross-Border Dynamics
- 4.2.1. Time Period
- 4.3. Conclusion
5. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
6. INTRODUCTION
- 6.1. Chapter Overview
- 6.2. Overview of In Vitro Diagnostics
- 6.3. Classification of In Vitro Diagnostic Products
- 6.4. Types of In Vitro Diagnostic Tests
- 6.5. Therapeutic Areas Targeted by In Vitro Diagnostic Solutions
- 6.6. Challenges in the In Vitro Diagnostics Domain
- 6.7. Recent Developments in the In Vitro Diagnostics Domain
7. MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 7.1. Chapter Overview
- 7.2. Japan In vitro Diagnostics Market: Overall Market Landscape
- 7.2.1. Analysis by Year of Establishment
- 7.2.2. Analysis by Company Size
- 7.2.3. Analysis by Location of Headquarters
- 7.2.4. Analysis by Annual Revenues
- 7.2.5. Analysis by Type of Technology
- 7.2.6. Analysis by Diagnostic Applications
- 7.2.6.1. Analysis by Type of Technology and Diagnostic Applications
8. COMPANY COMPETITIVENESS ANALYSIS
- 8.1. Chapter Overview
- 8.2. Assumptions and Key Parameters
- 8.3. Methodology
- 8.4. In vitro Diagnostic Solution Providers in Japan: Company Competitiveness Analysis
- 8.4.1. Small In vitro Diagnostics Solution Providers (Peer Group I)
- 8.4.2. Mid-sized In vitro Diagnostics Solution Providers (Peer Group II)
- 8.4.3. Large In vitro Diagnostics Solution Providers (Peer Group III)
- 8.5. Capability Benchmarking of top Japan In vitro Diagnostics Solution Providers
9. COMPANY PROFILES: JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET
- 9.1. Chapter Overview
- 9.2. Abbott Laboratories
- 9.2.1. Company Overview
- 9.2.2. Product Portfolio
- 9.2.3. Financial Information
- 9.2.4. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
- 9.3. Danaher
- 9.4. Fujirebio Holdings
- 9.5. H.U. Group Holdings
- 9.6. Roche Diagnostics
- 9.7. Sysmex
- 9.8. Tosoh
10. PARTNERSHIPS AND COLLABORATIONS
- 10.1. Chapter Overview
- 10.2. Partnership Models
- 10.3. Japan In vitro Diagnostic Solution Providers: Partnerships and Collaborations
- 10.3.1. Analysis by Year of Partnership
- 10.3.2. Analysis by Type of Partnership
- 10.3.3. Most Active Players: Analysis by Number of Partnerships
- 10.3.4. Analysis by Geography
- 10.3.4.1. Intercontinental and Intracontinental Agreements
- 10.3.4.2. Local and International Agreements
11. MARKET IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 11.1. Chapter Overview
- 11.2. Market Drivers
- 11.3. Market Restraints
- 11.4. Market Opportunities
- 11.5. Market Challenges
- 11.6. Conclusion
12. JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET
- 12.1. Chapter Overview
- 12.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 12.3. Japan In vitro Diagnostics Market: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 12.4. Roots Analysis Perspective on Market Growth
- 12.5 Scenario Analysis
- 12.5.1. Conservative Scenario
- 12.5.2. Optimistic Scenario
- 12.6. Key Market Segmentations
13. JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET, BY TEST TYPE
- 13.1. Chapter Overview
- 13.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 13.3. In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Distribution by Test Type
- 13.3.1. Laboratory Testing, Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted (Till 2035)
- 13.3.2. Point-of-Care Testing, Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.4. Data Triangulation and Validation
14. JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET, BY TYPE OF TECHNOLOGY
- 14.1. Chapter Overview
- 14.2. Assumptions and Methodology
- 14.3. In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Distribution by Type of Technology
- 14.3.1. Immunoassay: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1.1. Chemiluminescence Immunoassays: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1.2. ELISA: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1.3. ELISPOT: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1.4. Immunofluorescence Assays: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1.5. Rapid Tests: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1.6. Other Immunoassays: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2. Clinical Chemistry: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2.1. Electrolyte Panels: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2.2. Lipid Profiles: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2.3. Liver Panels: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2.4. Metabolic Panels: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2.5. Renal Profiles: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.2.6. Other Clinical Chemistry Tests: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3. Molecular Diagnostics: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.1. PCR: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.2. In situ Hybridization: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.3. Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.4. Next Generation Sequencing: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.5. Microarrays: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.6. Mass Spectrometry: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.3.7. Other Molecular Diagnostic Tests: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.4. Hematology: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.5. Other Technologies: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.3.1. Immunoassay: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.4. Data Triangulation and Validation
15. JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET, BY TYPE OF OFFERING
- 15.1. Chapter Overview
- 15.2. Assumptions and Methodology
- 15.3. In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Distribution by Type of Offering
- 15.3.1. Reagents: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.3.2. Instruments: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.3.2.1. In-house Instruments: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.3.2.2. Outsourced Instruments: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.3.3. Services: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.4. Data Triangulation and Validation
16. JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET, BY THERAPEUTIC AREA
- 16.1. Chapter Overview
- 16.2. Assumptions and Methodology
- 16.3. In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Distribution by Therapeutic Area, 2018, 2024 and 2035
- 16.3.1. Infectious Diseases: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.1. COVID-19: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.2. Healthcare-associated Infections: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.3. Hepatitis: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.4. HIV: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.5. Respiratory Infections (Excluding COVID-19): Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.6. STD: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1.7. Other Infectious Diseases: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.2. Cardiovascular Diseases: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.3. Oncological Disorders: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.4. Diabetes: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.5. Autoimmune Diseases: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.6. Renal Disorders: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.7. Other Therapeutic Areas: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.3.1. Infectious Diseases: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.4. Data Triangulation and Validation
17. JAPAN IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS MARKET, BY END USERS
- 17.1. Chapter Overview
- 17.2. Assumptions and Methodology
- 17.3. In Vitro Diagnostics Market: Distribution by End Users, 2018, 2024 and 2035
- 17.3.1. Hospitals: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.3.2. Laboratories: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.3.2.1. Large Laboratories: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.3.2.2. Small and Medium-sized Laboratories: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.3.3. Other End Users: Historical Trends (Since 2023) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.4. Data Triangulation and Validation
18. CONCLUDING REMARKS
19. APPENDIX I: TABULATED DATA
20. APPENDIX II: LIST OF COMPANIES AND ORGANIZATIONS




