PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836514

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836514
RF Test Equipment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The RF test equipment market size was valued at USD 4.02 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 5.51 billion by 2030, registering a 6.52% CAGR over 2025-2030.
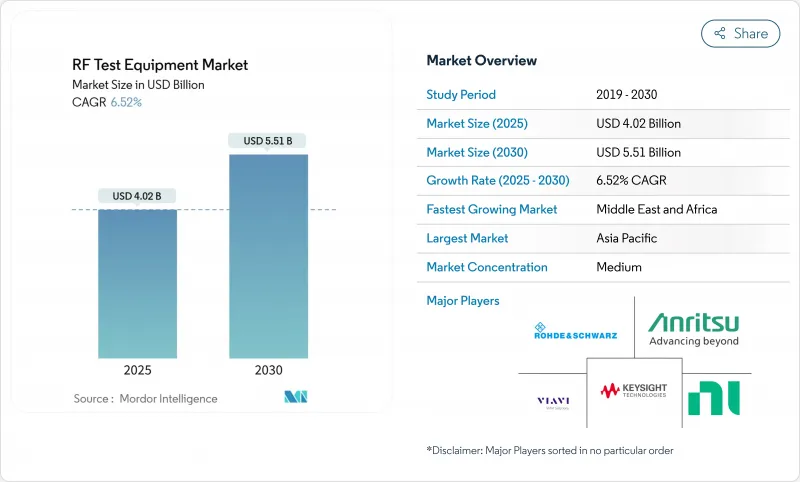
Uptake of 5G millimeter-wave links, the migration toward software-defined laboratories, and escalating radar and satellite programs all supported steady demand through 2024. Integration of GaN-on-Si power devices raised performance ceilings for amplifiers, while modular platforms compressed set-up times and operating costs. Asia-Pacific suppliers continued to scale output for domestic networks and export contracts, whereas North American laboratories prioritized cloud-connected automation to counter rising engineering labor shortages. Intensifying consolidation-highlighted by two separate bids for Spirent Communications-signalled an industry pivot toward turnkey hardware-software ecosystems that can evolve with 3GPP releases.
Global RF Test Equipment Market Trends and Insights
Surge in mmWave 5G Roll-outs Requiring >24 GHz Validation
Commercial roll-outs of 5G at 24-39 GHz demanded over-the-air chambers, phased-array beam verification, and wideband channel emulation. Keysight reported that integrated platforms combining generation, analysis, and fading cut test cycles by up to 40% and trimmed calibration overhead in research and development centers. Network operators in the United States, South Korea, and Germany placed bulk orders for 32- and 64-channel analyzers to validate beam-steering algorithms before dense-urban deployment. As mmWave small-cell density climbed, service labs shifted from single-box spectrum scans to automated, cloud-linked workflows that can sequence hundreds of parametric checks overnight. The trend pushed the RF test equipment market toward modular, FPGA-rich transceivers capable of 2 GHz instantaneous bandwidth per channel.
Proliferation of Massive-MIMO Base Stations in East Asia
China's and Japan's race to blanket metro areas with 64T64R radios created immediate needs for instruments that test dozens of RF chains concurrently. A 2024 RF Globalnet briefing cited 9.4 million new or upgraded sites worldwide, many of which employed massive-MIMO arrays. Multi-port vector signal analyzers with synchronized phase noise tracking enabled over-the-air characterization in a single pass, halving tower-side service times. East Asian OEMs further drove demand for PXIe blade sets that engineers can repurpose through software as 3GPP releases evolve. The swing toward flexible capacity underpinned the sustained growth of the RF test equipment market across production lines and field-service providers.
Rapidly Evolving ETSI and 3GPP Standards Creating Obsolescence
Release 18 of 3GPP entered freeze in June 2024, with Release 19 scheduled for late 2025. Each cycle introduced new air-interface features that legacy test sets could not easily emulate, forcing premature replacement or costly FPGA upgrades. Laboratories facing multi-standard certification workloads had to keep parallel benches for NR, LTE, and Wi-Fi, inflating operational budgets. While modular designs mitigated some risk, firmware licensing fees and retraining still curbed spending momentum within the RF test equipment market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Automotive RADAR/ADAS Test Demand Across Germany and Japan
- Satellite LEO Constellation Build-outs Driving Ka-Band Tests
- Form-factor Heat-Dissipation Challenges >40 GHz
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Modular GP instruments captured 35% of 2024 revenue as organizations sought configurable systems that evolve with 3GPP releases, accounting for the largest slice of the RF test equipment market size at this layer. Their 8.5% CAGR outlook outpaced traditional rack-mount analyzers, which ceded ground to PXIe and AXIe blades housing scripted FPGAs. National Instruments' PXIe-5842 vector signal transceiver delivered continuous coverage to 54 GHz with 2 GHz bandwidth, enabling unified generation and analysis in one slot. Rental GP models also grew where capital budgets were tight, especially in Latin America, offering subscription access to advanced capability without depreciating assets. Semiconductor ATE stayed essential for high-volume RF device makers, though its share narrowed modestly as discrete-channel counts rose on modular benches.
Conventional general-purpose instruments remained vital for precision metrology and government labs requiring absolute accuracy. Yet as software updates unlocked new modulation formats, enterprises gravitated toward card-based architectures that avoided forklift refreshes. Vendor roadmaps hinted at containerized microservices that would let engineers download test personalities on demand, further reinforcing the shift. This momentum suggests modularity will stay central to maintaining competitiveness across the broader RF test equipment market.
Benchtop units retained a 45% share in 2024, underpinned by unmatched dynamic range and low phase noise-qualities indispensable for research and development and calibration. Nevertheless, modular chassis logged the fastest 9.2% CAGR as service teams embraced scalable channel counts and smaller footprints, contributing measurably to overall RF test equipment market growth. Keysight's 2025 release of compact 54 GHz signal generators and synthesizers illustrated the push to shrink conventional boxes while preserving performance.
Handheld analyzers advanced through the integration of high-efficiency GaN PA stages and improved thermal paths to support installation and maintenance on rooftops, oil platforms, and defense ranges. Although thermal concerns above 40 GHz moderated adoption, field crews valued battery-operated spectrum capture and cloud-sync logs that accelerated troubleshooting. As networks densified and satellite gateways proliferated, the RF test equipment market increasingly balanced precision with mobility, driving converged product strategies among the top suppliers.
The RF Test Equipment Market is Segmented by Product Type (Modular GP Instrumentation, and More), by Form Factor (Benchtop, Portable, and More), by Frequency Range (< 1 GHz, 1 - 6 GHz, and More), by Component (RF Analyzers, RF Oscillators, and More), by End-User Industries (Telecommunication, Aerospace and Defense, and More), and by Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific commanded 39% of global revenue in 2024, underscoring its pre-eminence within the RF test equipment market. China's self-reliance agenda fuelled domestic tool chains, while Japan and South Korea pioneered radar and semiconductor test methodologies. Qualcomm, China Mobile, and Xiaomi demonstrated an 8.5 Gbps 5G Advanced mmWave testbed using the Snapdragon X75, spotlighting regional leadership in extended-reality validation. Heavy investment in 300 mm fabs expanded pull-through for high-frequency production testers across Taiwan and mainland foundries.
North America ranked second by value. U.S. labs rapidly adopted cloud-connected benches to mitigate a tightening pool of RF specialists, and defense allocations of USD 1.3 billion for counter-UAS projects spurred demand for wideband analyzers capable of real-time threat identification. Canada's satellite gateway build-outs further lifted Ka-band test bookings. Europe followed closely, anchored by Germany's automotive radar expertise and the Nordic region's acute talent shortages, which encouraged the outsourcing of complex conformance tasks to third-party labs.
The Middle East and Africa segment, while smaller, posted the fastest 8.7% CAGR. Saudi Arabia's plan to develop a USD 35 billion space economy by 2030 created demand for Ka-band payload and ground-segment validation. The UAE's missions to Mars and the asteroid belts accelerated the procurement of channel emulators. South America exhibited distinct rental preferences as Brazilian carriers opted for short-term leases during 700 MHz refarming projects, shaping adaptive go-to-market models for suppliers within the RF test equipment market.
- Keysight Technologies Inc.
- Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co. KG
- Anritsu Corporation
- Viavi Solutions Inc.
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Tektronix Inc.
- Teledyne Technologies Inc.
- National Instruments Corporation
- Fortive Corp. (Fluke)
- Teradyne Inc.
- Chroma ATE Inc.
- EXFO Inc.
- Cobham Ltd.
- TESSCO Technologies Inc.
- Advantest Corporation
- LitePoint Corporation
- Spirent Communications plc
- RIGOL Technologies Inc.
- Aim-TTi (Thurlby Thandar Instruments)
- Boonton Electronics
- SIGLENT Technologies
- GW Instek
- PMK Messtechnik
- Picotest Corp.
- B&K Precision Corporation
- TestEquity LLC
- Copper Mountain Technologies
- Giga-tronics Inc.
- Empirix Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in mmWave 5G Roll-outs Requiring >24 GHz Validation
- 4.2.2 Proliferation of Massive-MIMO Base-Stations in East Asia
- 4.2.3 Automotive RADAR/ADAS Test Demand Across Germany and Japan
- 4.2.4 Satellite LEO Constellation Build-outs Driving Ka-Band Tests
- 4.2.5 Miniaturised IoT Chipsets Boosting Hand-held RF Analyzers
- 4.2.6 Migration to Software-Defined, Cloud-Connected Labs in US
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Rapidly Evolving ETSI and 3GPP Standards Creating Obsolescence
- 4.3.2 Form-factor Heat-Dissipation Challenges >40 GHz
- 4.3.3 Skilled RF Test Engineering Talent Shortage in Nordics
- 4.3.4 High Cap-Ex vs. Rental Preference in Latin America
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory or Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Investment Analysis
- 4.8 Impact of Macroeconomic factors
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Modular GP Instrumentation
- 5.1.2 Traditional GP Instrumentation
- 5.1.3 Semiconductor ATE
- 5.1.4 Rental GP
- 5.1.5 Other Types
- 5.2 By Form Factor
- 5.2.1 Benchtop
- 5.2.2 Portable
- 5.2.3 Modular
- 5.3 By Frequency Range
- 5.3.1 < 1 GHz
- 5.3.2 1 - 6 GHz
- 5.3.3 > 6 GHz
- 5.4 By Component
- 5.4.1 RF Analyzers
- 5.4.2 RF Oscillators
- 5.4.3 RF Synthesizers
- 5.4.4 RF Amplifiers
- 5.4.5 RF Detectors
- 5.4.6 Other Components
- 5.5 By End-user Industry
- 5.5.1 Telecommunication
- 5.5.2 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.5.3 Consumer Electronics
- 5.5.4 Automotive
- 5.5.5 Semiconductor Manufacturing
- 5.5.6 Healthcare
- 5.5.7 Industrial and IoT
- 5.5.8 Other End-user Industries
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Sweden
- 5.6.3.6 Norway
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.4.1 Middle East
- 5.6.4.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.4.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.4.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.4.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.4.2 Africa
- 5.6.4.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.4.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.4.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.5 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5.1 China
- 5.6.5.2 Japan
- 5.6.5.3 India
- 5.6.5.4 South Korea
- 5.6.5.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Keysight Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.2 Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.3 Anritsu Corporation
- 6.4.4 Viavi Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.5 Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- 6.4.6 Tektronix Inc.
- 6.4.7 Teledyne Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.8 National Instruments Corporation
- 6.4.9 Fortive Corp. (Fluke)
- 6.4.10 Teradyne Inc.
- 6.4.11 Chroma ATE Inc.
- 6.4.12 EXFO Inc.
- 6.4.13 Cobham Ltd.
- 6.4.14 TESSCO Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.15 Advantest Corporation
- 6.4.16 LitePoint Corporation
- 6.4.17 Spirent Communications plc
- 6.4.18 RIGOL Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.19 Aim-TTi (Thurlby Thandar Instruments)
- 6.4.20 Boonton Electronics
- 6.4.21 SIGLENT Technologies
- 6.4.22 GW Instek
- 6.4.23 PMK Messtechnik
- 6.4.24 Picotest Corp.
- 6.4.25 B&K Precision Corporation
- 6.4.26 TestEquity LLC
- 6.4.27 Copper Mountain Technologies
- 6.4.28 Giga-tronics Inc.
- 6.4.29 Empirix Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




