PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842429

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842429
Rail Freight Transport - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Rail Freight Transport Market size is estimated at USD 326.09 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 405.76 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.47% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
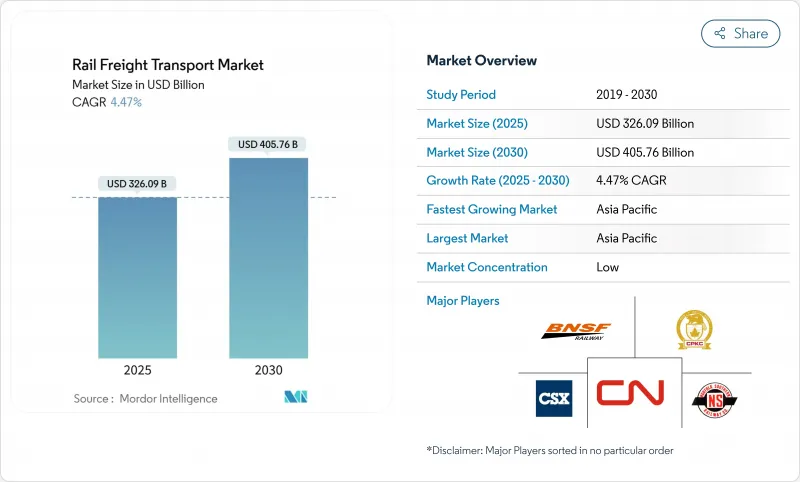
Sustained near-shoring in North America, higher automation along China-EU land bridges, and steady demand for bulk commodities position rail as a cost-efficient, lower-carbon alternative to long-haul trucking and ocean carriage. Asia remains the fastest-growing region thanks to China's network expansions, while government mandates in the EU and the United States accelerate adoption of electric and hydrogen traction. Intermodal container flows are rising as retailers integrate rail into time-sensitive logistics, and Class I operators continue double-tracking, siding extensions, and inland terminal upgrades that ease capacity constraints. Persistent network congestion in the U.S. Midwest, divergent wagon-coupling standards in Eurasia, and axle-load limits on narrow-gauge African lines temper the market's full growth potential.
Global Rail Freight Transport Market Trends and Insights
Decarbonisation mandates accelerate modal shift on long-haul corridors
Tighter emissions laws in the EU and the United States are nudging long-distance freight off roads and onto rails, a pattern reinforced by the U.S. Rail Energy and Emissions Innovation Action Plan, which charts a path to net-zero greenhouse-gas emissions in rail by 2050. Class I operators have started to respond: CSX rolled out its first hydrogen fuel-cell locomotive in April 2024, and CPKC ordered 20 additional fuel-cell engines that will operate on high-density lanes connecting Western Canada and the U.S. Midwest. The regulatory carrot of lower emissions fees pairs with the operational stick of city-center truck restrictions, creating a clear advantage for zero-tailpipe locomotives. With charging and fueling infrastructure now bundled into national clean-transport budgets, the cumulative effect lifts the competitive profile of the rail freight transport market on every lane exceeding 500 miles.
Nearshoring boosts North American cross-border volumes
Manufacturers relocating production from Asia to Mexico are redrawing freight flows between Monterrey, Laredo, and central U.S. hubs. Mexico overtook China as the largest U.S. trade partner in 2024, and rail carriers have responded: CPKC finalized a USD 100 million expansion that doubled capacity on the Laredo-Nuevo Laredo bridge, the busiest rail gateway on the continent. Schneider National followed by launching a through-train intermodal service linking Mexican origins with the U.S. Southeast, cutting transit times by two days and slashing border dwell times. The resulting surge in auto-parts, electronics, and white-goods traffic positions cross-border services as the fastest-growing slice of the rail freight transport market through 2030.
Class I congestion constrains U.S. grain corridors
Grain carloads on U.S. Class I railroads reached 1.07 million in 2024, up 84,000 from the prior year. Seasonal peaks stretched crew and siding capacity, elongating cycle times for unit trains that feed Gulf Coast export elevators. Chicago, the busiest interchange node, has responded; CN's siding extension added 17% capacity and boosted area speed by 30%, but recurring backlogs still cause shippers to divert volumes to barge and truck options. The Surface Transportation Board's proposed reciprocal-switching rule seeks to bring competitive pressure, yet implementation risks prolonging uncertainty in the rail freight transport market's largest agricultural lane.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Energy-transition minerals reshape bulk-rail corridors
- China-EU land-bridge programs diversify Asia-Europe trade
- Divergent coupling standards slow Eurasian integration
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Dry bulk generated the largest slice of 2024 revenue, accounting for 41% of the rail freight transport market share as high-tonnage coal, ore, and grain sustained baseline volumes across Australia, Brazil, and the U.S. Midwest. The rail freight transport market size for dry bulk is projected to grow modestly in line with commodity demand yet will continue to anchor network utilization levels. Containerized and intermodal traffic, however, is advancing at a 6.9% CAGR, reshaping asset allocation and hub design. Port congestion in Asia and investment in inland dry-ports have elevated rail's role in the global box cycle.
Dry bulk growth stands on long-term supply agreements with power utilities and steel mills, giving railroads steady cash-flow to modernize motive power fleets. Record e-commerce flows and stricter highway emissions limits trigger Intermodal's faster expansion. BNSF's USD 3.8 billion 2025 program, which funds a Phoenix green-field terminal and Chicago capacity upgrades, is a blueprint for doubling-stack corridors with 13.3% year-over-year lifts in international containers. Over the forecast horizon, intermodal's share of the rail freight transport market is likely to close the gap on bulk, propelling rolling-stock orders for low-emission, high-horsepower locomotives.
Core line-haul transportation controlled 84% of 2024 turnover, reflecting rail's comparative advantage in energy-efficient, long-haul moves. Tight timetables and economies of scale protect that revenue stream, yet allied services-maintenance, switching, storage, and last-mile drayage-will rise at an 7.6% CAGR as operators widen their profit pools. The rail freight transport market size for allied services is expanding because shippers increasingly outsource wagon upkeep and terminal handling to the same provider that hauls their cargo.
Tailored life-cycle support for hydrogen and battery electric locomotives requires new depots, fueling pads, and digital twins, creating revenue lines previously outside the traditional rail model. France's decision to carve Fret SNCF into Hexafret and Technis aims to lift service quality and unlock EUR 700 million (approximately USD 797 million) in 2025 revenue, underscoring how specialized maintenance has become a strategic pillar. In North America, several Class I carriers have integrated track-side analytics into subscription packages that guarantee uptime, deepening customer ties and reinforcing stickiness inside the broader rail freight transport market.
The Market is Segmented by Cargo Type (Containerized / Intermodal, Dry Bulk (Coal, Ores, Grains) and More), by Service Type (Transportation, Services Allied To Transportation), by End-User Industry (Mining & Minerals, Oil, Gas & Chemicals and More), by Traction Type (Diesel and More), by Destination (Domestic and International), by Geography (North America and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America's rail freight transport market benefits from deep Class I capital budgets and near-shoring that channels production to Mexico. The region is forecast to grow at 4.5% CAGR from 2025 to 2030. Union Pacific posted USD 1.8 billion Q4 2024 net income, underpinning track upgrades and locomotive overhauls that support grain, automotive, and energy. CN's purchase of Iowa Northern Railway adds 175 route-miles to its 20,000-mile matrix, strengthening fertilizer flows. Mexico's network expansion, including double-tracking at Laredo, secures faster clearance for USD 475 billion in northbound exports and enlarges the rail freight transport market.
Asia Pacific leads global growth with a 6.2% CAGR. By end-2024, 30% of China-Europe unit-trains traversed Manzhouli, aided by five-minute automated customs. India's dedicated freight corridors near completion, while Japan trials hydrogen locomotives on rural lines. Australia's Pilbara miners continue investing in heavy-haul railways that move iron ore at 40 tonnes-axle-load to coastal shipping points. Across ASEAN, Vietnam SuperPort's rail-linked hub in Hanoi exemplifies growing port-rail integration.
Europe's rail freight transport market is advancing at 4.1% CAGR as liberalization unlocks entry for private operators. Germany channels federal grants into Deutsche Bahn's H2goesRail program that pairs Siemens family multiple units with on-site hydrogen production deutschebahn.com. France's Hexafret targets 1,100 long-distance trains per week in 2025, while Spain widens gauge-change facilities on the Mediterranean Corridor. Nordic governments coordinate cross-border electrified links that reinforce the region's low-carbon freight ambitions.
South America shows 4.1% CAGR potential driven by mineral exports. Chile received a 1 MW hydrogen locomotive for FCAB's desert routes, designed for high altitude and temperature extremes. Brazil's concession model attracts private capital to soybean and iron-ore spurs, and Argentina's rolling-stock upgrades improve crop export lead times. The rail freight transport market size for bulk minerals is poised to rise as critical-metal projects advance.
Middle East and Africa carry the highest forward CAGRs-3.8% and 4.8%, respectively-from smaller bases. The USD 3 billion UAE-Oman rail link will slash Sohar-to-Abu Dhabi transit to 100 minutes, supporting port free-zone integration. South Africa's Transnet Freight Rail secured USD 1 billion to restore locomotive availability and rebuild export corridors to Richards Bay. Nigeria and Tanzania prioritize standard-gauge networks that connect mineral belts to seaports, expanding the rail freight transport market.
- Union Pacific Railroad
- BNSF Railway
- Canadian National Railway
- Canadian Pacific Kansas City
- CSX Transportation
- Norfolk Southern Railway
- DB Cargo (Deutsche Bahn)
- SNCF-Fret
- Swiss Federal Railways (SBB Cargo)
- Russian Railways (RZD)
- PKP Cargo
- Genesee & Wyoming
- Pacific National
- Qube Holdings
- Japan Freight Railway (JR Freight)
- Indian Railways (Dedicated Freight Corridors Corp.)
- Kansas City Southern de Mexico (now CPKC)
- Etihad Rail
- Qatar Rail
- South Africa Transnet Freight Rail*
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Decarbonization Mandates Driving Modal Shift on Long-haul (more than 800 km) North-South Corridors (EU & NA)
- 4.2.2 Near-shoring of Heavy Manufacturing to Mexico & CEE Boosting Cross-border Rail Volumes
- 4.2.3 Energy-transition Commodities (Lithium, Copper) Requiring Bulk Rail Capacity in Andean & Australian Basins
- 4.2.4 China-EU Land-Bridge Resilience Programs (Post-BRI Optimisation)
- 4.2.5 Tier-1 Port Congestion in Asia Spurs Inland Rail-based Intermodal to Dry-Ports
- 4.2.6 Government Stimulus for Hydrogen-ready Freight Locomotives in Germany & Japan
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Class-I Network Congestion on U.S. Midwest Grain Routes
- 4.3.2 Draft-imposed Axle-Load Limitations on Sub-Saharan Narrow-Gauge Lines
- 4.3.3 Divergent Wagon-Coupling Standards Hindering China-Central Asia Through-Traffic
- 4.3.4 Long-haul Trucking Cost Deflation (2023-24) Narrowing Rail Price Advantage in NAFTA
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Cost Structure & Pricing Analysis
- 4.9 Transport Corridors Analysis (Silk Road, NAFTA, TEN-T, GCC)
- 4.10 Impact of Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- 4.11 Key Trade Agreements Affecting Rail Freight
- 4.12 Impact of GEO-Political Events in the Market
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Cargo Type
- 5.1.1 Containerised / Intermodal
- 5.1.2 Dry Bulk (Coal, Ores, Grains)
- 5.1.3 Liquid Bulk (Crude, Chemicals)
- 5.1.4 Break-bulk & Project Cargo
- 5.2 By Service Type
- 5.2.1 Transportation
- 5.2.2 Services Allied to Transportation (Maintenance of Railcars and Rail Tracks, Switching of Cargo, and Storage)
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Mining & Minerals
- 5.3.2 Oil, Gas & Chemicals
- 5.3.3 Agriculture & Food
- 5.3.4 Manufacturing & Automotive
- 5.3.5 Retail & FMCG
- 5.3.6 Construction Materials & Forestry
- 5.4 By Traction Type
- 5.4.1 Diesel
- 5.4.2 Electric
- 5.4.3 Hybrid / Hydrogen & LNG
- 5.5 By Destination
- 5.5.1 Domestic
- 5.5.2 International / Cross-border
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Peru
- 5.6.2.3 Chile
- 5.6.2.4 Argentina
- 5.6.2.5 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 India
- 5.6.3.2 China
- 5.6.3.3 Japan
- 5.6.3.4 Australia
- 5.6.3.5 South Korea
- 5.6.3.6 South East Asia (Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Philippines)
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Europe
- 5.6.4.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.4.2 Germany
- 5.6.4.3 France
- 5.6.4.4 Spain
- 5.6.4.5 Italy
- 5.6.4.6 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.6.4.7 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden)
- 5.6.4.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.5 Middle East And Africa
- 5.6.5.1 United Arab of Emirates
- 5.6.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.3 South Africa
- 5.6.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.5 Rest of Middle East And Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Union Pacific Railroad
- 6.4.2 BNSF Railway
- 6.4.3 Canadian National Railway
- 6.4.4 Canadian Pacific Kansas City
- 6.4.5 CSX Transportation
- 6.4.6 Norfolk Southern Railway
- 6.4.7 DB Cargo (Deutsche Bahn)
- 6.4.8 SNCF-Fret
- 6.4.9 Swiss Federal Railways (SBB Cargo)
- 6.4.10 Russian Railways (RZD)
- 6.4.11 PKP Cargo
- 6.4.12 Genesee & Wyoming
- 6.4.13 Pacific National
- 6.4.14 Qube Holdings
- 6.4.15 Japan Freight Railway (JR Freight)
- 6.4.16 Indian Railways (Dedicated Freight Corridors Corp.)
- 6.4.17 Kansas City Southern de Mexico (now CPKC)
- 6.4.18 Etihad Rail
- 6.4.19 Qatar Rail
- 6.4.20 South Africa Transnet Freight Rail*
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook




