PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842504

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842504
Aircraft Landing Gear Systems - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
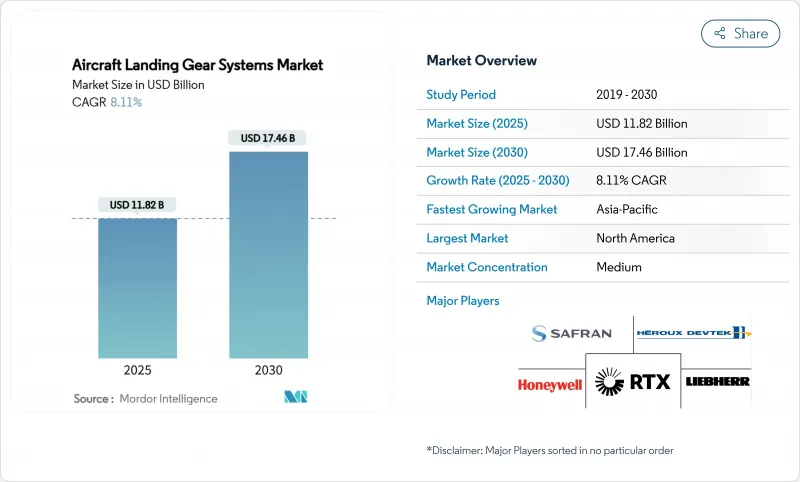
The aircraft landing gear systems market size stands at USD 11.82 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 17.46 billion by 2030, advancing at an 8.11% CAGR.
Fleet renewal programs, the return of long-range travel, and the rise of electric-actuation technologies are fuelling demand. Commercial airframers are accelerating production to work through record backlogs, while defense ministries are modernizing tactical fleets. Airlines are shifting to managed maintenance agreements that guarantee gear availability and lower capital exposure, and urban-air-mobility prototypes are opening new low-weight, high-cycle niches. At the same time, supply-chain pressures around titanium, carbon fiber, and high-precision castings are forcing OEMs to dual-source critical forgings and invest in local capacity.
Global Aircraft Landing Gear Systems Market Trends and Insights
Lightweight-materials demand surge
Airframers are deploying titanium alloys and carbon-fiber composites to trim landing-gear weight by up to 30%, translating directly into lower fuel burn and longer range. A titanium-aluminum super-elastic alloy developed by Tohoku University maintains strength from -269°C to 127°C, widening its applicability across extreme operating environments. Boeing and Airbus wide-bodies already feature airframes with more than 50% CFRP content, and regional supply chains across China and India are scaling carbon-fiber output to keep pace with demand. The 2024 investigation into counterfeit titanium underscored the importance of full material traceability. Military programs favour ultra-high-strength steels such as AerMet 310 for superior fracture toughness, further diversifying material choices.
OEM push for electric/hydraulic-free eBrake systems
Leading suppliers are replacing central hydraulic circuits with distributed electro-hydrostatic actuators to reduce pipeline complexity, slash maintenance hours, and lower system weight. Collins Aerospace invested USD 200 million to add 70,000 sq ft at its Spokane carbon-brake plant, boosting capacity by 50% to meet eBrake demand. The Clean Aviation Electrical Nose Landing Gear System demonstrator validates full electric steering and retraction modules, moving towards zero-hydraulic architectures. Certification teams must now evaluate new fault modes, but electric solutions promise modular upgrades and smoother scalability for future aircraft.
Titanium and composite supply-chain bottlenecks
Accelerating aerospace demand has lengthened forging lead times past 12 months, especially for large 300M and Ti-6-4 billets. China produces only about 7,000 MT of aerospace-grade carbon fiber against global use of 22,000 MT, leaving a gap that drives prices higher and slows composite spar production. OEMs fund dual-sourcing and in-house forging lines to mitigate exposure, yet skilled-labor shortages and certification audits restrict rapid scale-up.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Commercial aircraft production ramp-ups post-2025
- MRO outsourcing and exchange-service adoption
- Regulatory certification delays for novel architectures
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The aircraft landing gear systems market size for commercial platforms remained the largest in 2024, driven by narrowbody jets that captured 43.55% market share as carriers renewed ageing fleets and chased fuel-burn savings. Airbus's backlog covers 40% of projected single-aisle deliveries, implying sustained volume through 2030. Widebody programs resumed steady output as intercontinental routes reopened, and freight conversions kept twin-aisle lines busy. Military demand is rising faster, posting an 8.85% CAGR as governments recapitalise fighter and tanker fleets and extend lifecycles on legacy aircraft. The US Department of Defense allocated USD 57.2 billion to tactical-aircraft operations between 2018 and 2023. Across Asia, Japan, India, and South Korea are inducting indigenous fighters that specify local content in landing-gear assemblies, diversifying the supplier map. Business-jet and rotorcraft segments remain niche yet important incubators for electro-mechanical actuation and additive manufacturing practices that migrate to higher-volume airliners.
Commercial operators will continue to dominate procurement volumes, but military programs will account for a larger share of R&D spending, particularly in corrosion-resistant alloys and automatic retraction diagnostics. As blended-wing-body demonstrators proceed, gear-position loads shift, encouraging spring-strut innovations that military prototypes often adopt first. The spillover accelerates technology maturity, shortening the time to commercial adoption and supporting the broader aircraft landing gear systems market.
Main undercarriage units sustained 63.45% of the aircraft landing gear systems market share in 2024, reflecting their structural heft, complex truck assemblies, and high-value brake packs. Twin-aisle designs can impose landing weights above 560 tons, demanding robust heat-treated steels, redundant shock absorbers, and multi-wheel bogies. Digital brake-by-wire upgrades and carbon/carbon discs keep repair shops busy, sustaining aftermarket revenues at every A-check cycle.
Nose gear volumes are lower, yet growth is stronger, tracking a 9.55% CAGR to 2030. Electric steering actuators spearhead weight cuts, and modular electro-mechanical jackscrew assemblies slash line-replaceable-unit counts. Clean Aviation's nose-gear demonstrator validates electro-hydrostatic retraction methods that can shave several kilograms per shipset. Business-jet makers are early adopters; Liebherr's high-reliability nose-gear prototype, unveiled at NBAA-BACE 2024, positions the company to capture both eVTOL and regional-jet awards.
The Aircraft Landing Gear Systems Market Report is Segmented by Aircraft Type (Commercial Aviation, Military Aviation, and General Aviation), Gear Position (Nose Landing Gear and Main Landing Gear), Material (High-Strength Steel Alloys, Titanium Alloys, Composites, and More), End-User (OEM and Aftermarket (MRO)) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America remained the largest regional contributor with 37.89% of 2024 revenue. Boeing's Renton and Everett lines, Collins's Spokane brake factory, and Pratt & Whitney landing-gear machining centers anchor a dense supplier footprint that feeds civil and defense orders. US defense budgets guarantee high-tempo overhauls, and the emerging air-mobility ecosystem centred in California and Texas will soon require thousands of lightweight shipsets. Regulatory scrutiny, including a 2024 FAA probe into counterfeit titanium, has tightened oversight, nudging primes to in-source more metallurgical testing.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-expanding arena, rising at an 8.32% CAGR on the back of burgeoning traffic in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Airbus forecasts that the region will absorb 45% of global jet deliveries over two decades, and COMAC's C919 certification accelerates indigenous supply chains. China's carbon-fiber output remains skewed to industrial grades, encouraging joint ventures with international prepreg specialists. Japan and South Korea, with long aerospace pedigrees, are scaling super-plastic-forming operations that support regional jet and fighter programs.
Europe retains a strong technology edge, housing Safran Landing Systems, Liebherr-Aerospace, and major Airbus plants. EU sustainability mandates incentivise electrification roadmaps and life-cycle impact disclosures for landing-gear hardware. Eastern European clusters in Poland and the Czech Republic attract investment for precision-machined sub-assemblies. Middle-East, Latin American, and African operators form smaller but strategic nodes, leveraging geographic positioning to serve long-haul hub-and-spoke networks and charter segments that require flexible MRO availability.
- Safran SA
- Collins Aerospace (RTX Corporation)
- Liebherr Group
- Heroux-Devtek
- Triumph Group, Inc.
- GKN Aerospace
- Honeywell International, Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Magellan Aerospace Corporation
- Whippany Actuation Systems LLC
- CIRCOR International, Inc.
- Parker-Hannifin Corporation
- SPP Canada Aircraft, Inc.
- Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Lightweight-materials demand surge
- 4.2.2 OEM push for electric/hydraulic-free eBrake systems
- 4.2.3 Commercial aircraft production ramp-ups post-2025
- 4.2.4 MRO outsourcing and exchange-service adoption
- 4.2.5 Urban-air-mobility (eVTOL/air-taxi) landing-gear volumes
- 4.2.6 Digital twin-enabled predictive maintenance
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Titanium and composite supply-chain bottlenecks
- 4.3.2 Regulatory certification delays for novel architectures
- 4.3.3 High capex and eight-to-ten-year overhaul costs
- 4.3.4 OEM-airline power-by-the-hour dominance squeezing independents
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Aircraft Type
- 5.1.1 Commercial Aviation
- 5.1.1.1 Narrowbody Aircraft
- 5.1.1.2 Widebody Aircraft
- 5.1.1.3 Regional Aircraft
- 5.1.2 Military Aviation
- 5.1.2.1 Combat Aircraft
- 5.1.2.2 Non-Combat Aircraft
- 5.1.2.3 Helicopters
- 5.1.3 General Aviation
- 5.1.3.1 Business Jets
- 5.1.3.2 Turboprop Aircraft
- 5.1.3.3 Piston Aircraft
- 5.1.3.4 Helicopters
- 5.1.1 Commercial Aviation
- 5.2 By Gear Position
- 5.2.1 Nose Landing Gear
- 5.2.2 Main/Undercarriage Landing Gear
- 5.3 By Material
- 5.3.1 High-Strength Steel Alloys
- 5.3.2 Titanium Alloys
- 5.3.3 Composites (CFRP/GFRP)
- 5.3.4 Aluminum Alloys
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 OEM
- 5.4.2 Aftermarket (MRO)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 Germany
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Egypt
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Safran SA
- 6.4.2 Collins Aerospace (RTX Corporation)
- 6.4.3 Liebherr Group
- 6.4.4 Heroux-Devtek
- 6.4.5 Triumph Group, Inc.
- 6.4.6 GKN Aerospace
- 6.4.7 Honeywell International, Inc.
- 6.4.8 Eaton Corporation plc
- 6.4.9 Magellan Aerospace Corporation
- 6.4.10 Whippany Actuation Systems LLC
- 6.4.11 CIRCOR International, Inc.
- 6.4.12 Parker-Hannifin Corporation
- 6.4.13 SPP Canada Aircraft, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




