PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842537

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842537
Global Particle Therapy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The particle therapy market stands at USD 1.76 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2.49 billion by 2030, reflecting a healthy 7.15% CAGR.
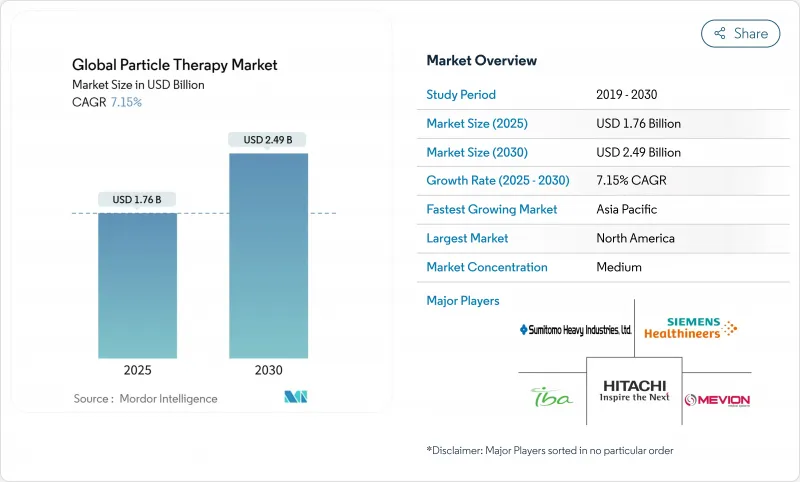
The current growth comes from sustained investments in precision oncology equipment, a steady rise in global cancer incidence, and continuous reimbursement improvements that are widening patient eligibility. Vendors are capturing demand through compact single-room systems that trim civil-works budgets by up to 60%, allowing mid-sized hospitals to enter the field without building multi-room bunkers. Clinical momentum behind FLASH-dose delivery is further enlarging the total addressable patient pool, because ultra-high dose rates finish treatment in milliseconds and reduce normal-tissue toxicity, an advantage that resonates with both pediatric and adult cohorts. A supportive policy environment-most notably Medicare's 2024 local-coverage determinations and Japan's national insurance listing of carbon-ion therapy-provides near-term revenue certainty, while artificial-intelligence planning tools are easing workflow bottlenecks created by workforce shortages. Collectively, these factors sustain the particle therapy market's positive outlook and signal that capital formation will stay robust well into the forecast window.
Global Particle Therapy Market Trends and Insights
Advances in FLASH-dose Delivery
FLASH radiotherapy delivers dose rates above 40 Gy/s, condensing an entire curative course into a single sub-second exposure that spares surrounding tissue . Pre-clinical and early-phase human studies at Stanford and the University of Pennsylvania report comparable tumor control yet markedly lower fibrosis and dermatitis, supporting broader protocol enrollment. Existing cyclotron lines can integrate FLASH with minimal hardware upgrade, making it a cost-effective differentiator for incumbent hospitals. Regulatory discussions now focus on consensus dose-verification techniques rather than foundational safety, signaling that multi-center trials will soon evolve into guideline-shaping phase III studies. As payers recognize lower toxicity-related complications, value-based reimbursement frameworks are expected to accelerate, reinforcing the driver's growth contribution.
Rising Global Cancer Incidence
WHO recorded 20 million new cases in 2022 and forecasts 35 million by 2050, a trajectory that intensifies demand for modality portfolios capable of minimizing late-stage side effects. Emerging economies are witnessing faster incidence growth than their healthcare infrastructure can match, magnifying the relevance of portable or retrofittable particle centers. In aging societies like Japan and South Korea, oncologists seek treatments that limit secondary malignancies because survivors often live another two decades. The rise in pediatric cancers, though modest at 0.8% annually in developed regions, carries disproportionately high quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gains, cementing particle therapy's value proposition. This epidemiological tide underpins steady patient volume expansion that feeds directly into particle therapy market revenue streams.
High CAPEX & OPEX of Beamline Infrastructure
Even after cost reductions, turnkey projects often exceed USD 50 million, dwarfing conventional linac replacement budgets. Shielding, cryogenics, and power-conditioning systems escalate operating costs, with annual service contracts reaching USD 3 million. Hospitals with thin oncology margins struggle to justify these figures unless local payers reimburse at rates that cover both depreciation and service overhead. Because capital grants are finite, a single large particle project can crowd out other equipment purchases, causing institutional inertia. Until vendors unlock sub-USD 20 million systems at scale, capital intensity will remain the most significant drag on the particle therapy market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Improved Reimbursement Frameworks (US & JP)
- Technological Shift to Compact Single-Room Systems
- AI-based Adaptive Treatment Planning
- Shortage of Particle-Physics Trained Staff
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Proton therapy accounted for an 82.72% particle therapy market share in 2024, buoyed by a robust base of phase III evidence, payer familiarity and a pipeline of single-room installations. Heavy-ion therapy is the fastest mover, growing at 8.17% CAGR to 2030 on the back of superior relative biological effectiveness against hypoxic or radioresistant tumors. Early adopters such as Yonsei Cancer Center reported five-year overall survival of 97.5% in localized prostate protocols, results that transcend proton benchmarks. North American acceptance could accelerate once Mayo Clinic's forthcoming carbon-ion unit enters service, creating spill-over demand for heavy-ion expertise within the particle therapy market. As compact carbon-ion platforms mature, the economic barrier narrows, signaling a more balanced modality mix beyond 2030.
Proton vendors have not remained static. Systems incorporating FLASH capability, intensity-modulated scanning and AI-enabled daily replanning continue to widen the clinical ceiling. Meanwhile, carbon-ion innovators are integrating superconducting gantries to cut magnet mass and facility span. Technology cross-pollination is expected, with proton platforms adopting heavy-ion beam-steering algorithms and heavy-ion systems leveraging proton-era QA automation. The competitive interplay keeps the particle therapy market dynamic and favors suppliers who maintain a multi-modality portfolio.
Multi-room centers held 63.17% share of the particle therapy market size in 2024 because legacy hubs treat 1,000+ patients yearly and benefit from economies of scale. However, single-room footprints are climbing 7.92% CAGR as CFOs prioritize modular expansion over mega-projects. Facilities like Atlantic Health's retrofit of an existing linac vault-notably completed 40% faster than a greenfield build-prove the model's economic appeal. The newest compact units operate with independent cyclotrons per room, so downtime in one suite no longer halts the entire complex, a historical disadvantage of beam-switching designs.
On the engineering front, magnet miniaturization and improved energy selection systems allow single-room solutions to match the clinical reach of their larger cousins, eliminating trade-off concerns. Vendors market phased build-outs that start with one vault and scale to three or four as case volume rises, giving administrators capital-spend optionality. As leasing and public-private partnerships mature, single-room growth is expected to outstrip multi-room additions, reinforcing the decentralizing trend within the particle therapy market.
The Report Covers Particle Therapy Market Forecast and It is Segmented by Type (Proton Therapy and Heavy Ion Therapy), System (Multi-Room Systems, and Single-Room Systems), Cancer Type (Pediatric Cancer, Prostate Cancer, and More), Application (Therapeutic and Clinical Research), and Geography. The Market Values are Provided (in USD Million) for the Above Segments.
Geography Analysis
North America controlled 44.61% of the particle therapy market in 2024. Medicare's broadened coverage stabilized cash flows, and an established pipeline of more than 40 operational centers continues to undertake multi-room expansions. Penn Medicine's USD 224 million Roberts Proton Therapy Center extension illustrates the region's willingness to invest in next-generation vaults that include independent cyclotrons for redundancy. Academic ecosystems funnel steady referral streams, while philanthropic campaigns absorb portions of capital costs, mitigating budget risk. The United States also houses most commercial OEM headquarters and third-party service firms, reinforcing supply-chain security. Canada remains an outlier with no domestic center, but provincial task forces in Ontario and Quebec have advanced site-selection studies, a sign that regional demand will soon convert into procurement tenders.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region at 9.25% CAGR, fueled by public-sector spending and demographic shifts toward older populations. China hosts an expanding mix of flagship institutions and cost-disruptive entrants. P-Cure's ultra-compact system in Shandong, priced below USD 30 million, exemplifies a local strategy to bring particle therapy into secondary cities . South Korea commissioned the Yonsei heavy-ion facility in 2024, and preliminary data already support broader case enrollment beyond prostate cancer. Australia's Bragg Centre, though facing vendor realignment after delays, retains bipartisan commitment, indicating that regulatory approvals are temporary rather than structural obstacles. Regional governments often pair accelerator procurement with domestic-manufacturing mandates, stimulating supply-chain localization that lowers long-term operating expenditures.
Europe presents a dual narrative of technological sophistication and incremental capacity growth. Germany's carbon-ion centers deliver both routine care and multi-site trial leadership, positioning the region as a global hub for heavy-ion expertise. Public-private joint ventures in France and Italy are expanding proton reach, while MRI-guided proton prototypes in Dresden edge toward clinical readiness. Cross-border referral agreements allow smaller nations to send complex cases to neighboring centers, optimizing utilization. Meanwhile, the Middle East, Africa and South America hold early-stage potential. Argentina's 230-tonne cyclotron installation signals Latin America's first foray into the particle therapy market, and preliminary feasibility studies are underway in Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Collectively, geographic diversification spreads supplier risk and creates multi-tier demand profiles that sustain long-run growth.
- Abbvie
- Amneal Pharmaceuticals
- Viatris
- Boehringer Ingelheim Intl. GmbH
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Pfizer
- Novartis
- Roche
- ABL bio
- KISSEI PHARMACEUTICAL
- AstraZeneca
- Prevail Therapeutics
- Newron Pharmaceuticals S.p.A.
- Kyowa Kirin
- ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- UCB
- Sunovion Pharmaceuticals
- Neurocrine Biosciences
- Lundbeck A/S
- Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
- Supernus Pharmaceuticals
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Geriatric Population & Rising Disease Burden
- 4.2.2 Growing Awareness & Early Diagnosis Initiatives
- 4.2.3 Expanding Reimbursement & Insurance Coverage
- 4.2.4 Increasing R&D Investment & Continuous Drug Approvals
- 4.2.5 Adoption Of Long-Acting Continuous Infusion Formulations
- 4.2.6 Ai-Driven Drug-Repurposing Pipelines Targeting A-Synuclein
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Adverse Events Associated With Current Therapeutics
- 4.3.2 High Treatment & R&D Costs
- 4.3.3 Supply-Chain Constraints For Levodopa Apis
- 4.3.4 Regulatory Uncertainty Around Disease-Modifying Claims
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD million)
- 5.1 By Mechanism of Action
- 5.1.1 Dopamine Agonists
- 5.1.2 Anticholinergics
- 5.1.3 MAO-B Inhibitors
- 5.1.4 Amantadine
- 5.1.5 Carbidopa-levodopa
- 5.1.6 Adenosine A2A Antagonists
- 5.1.7 Other Mechanisms of Action
- 5.2 By Route of Administration
- 5.2.1 Oral
- 5.2.2 Transdermal
- 5.2.3 Subcutaneous
- 5.2.4 Infusion
- 5.2.5 Intranasal
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.3.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.3.3 Online Pharmacies
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 Japan
- 5.4.3.3 India
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.4.4.1 GCC
- 5.4.4.2 South Africa
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.4.5 South America
- 5.4.5.1 Brazil
- 5.4.5.2 Argentina
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.2 Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
- 6.3.3 Viatris
- 6.3.4 Boehringer Ingelheim Intl. GmbH
- 6.3.5 GSK plc
- 6.3.6 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
- 6.3.7 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.8 Novartis AG
- 6.3.9 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.3.10 ABL bio
- 6.3.11 Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.12 AstraZeneca
- 6.3.13 Prevail Therapeutics
- 6.3.14 Newron Pharmaceuticals S.p.A.
- 6.3.15 Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.16 ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.17 UCB S.A.
- 6.3.18 Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.19 Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc.
- 6.3.20 Lundbeck A/S
- 6.3.21 Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
- 6.3.22 Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




