PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842606

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842606
Global Cell Line Development - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The cell line development market reached USD 4.97 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand to USD 8.23 billion by 2030, reflecting a 10.60% CAGR through the period.
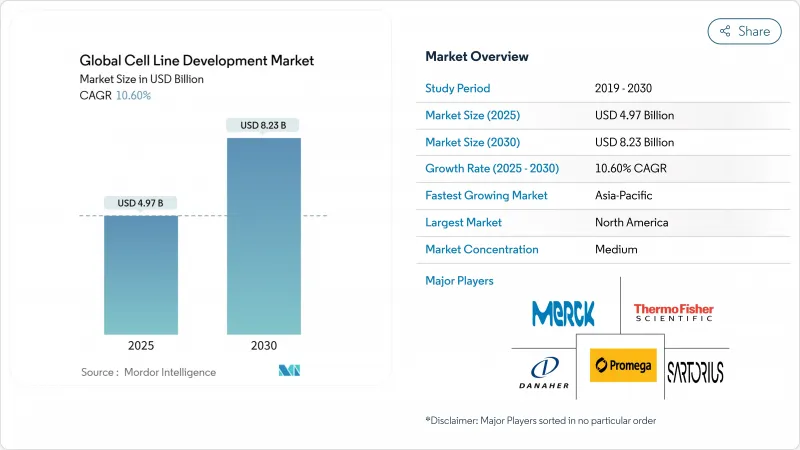
Expanding demand for biologics, which accounted for more than 40% of 2024 drug approvals, anchors this growth as complex proteins, monoclonal antibodies, and gene therapies all require highly engineered cell lines for commercial-scale production. Heightened capital expenditure on continuous bioprocessing, an accelerating shift toward outsourcing, and the advent of AI-guided optimization platforms have already shortened development cycles from 6-9 months to 3-4 months, giving first movers a tangible competitive edge. Regulatory reforms that favor risk-based viral safety evaluations create both compliance costs and quality incentives, while geopolitical tensions encourage regional manufacturing clusters that reduce exposure to single-country supply risks. Taken together, these structural forces reinforce the central role that the cell line development market will play in delivering the next wave of biologics.
Global Cell Line Development Market Trends and Insights
Growing Biopharmaceutical Demand
Monoclonal antibodies already dominate biologic pipelines, and their growth into autoimmune and rare disease indications sustains pressure on cell line productivity. Over 200 antibody therapeutics are approved, with nearly 1,400 candidates in active development, forcing sponsors to secure robust, high-yielding cell lines early in clinical programs. The cell line development market therefore functions as a strategic bottleneck that largely dictates overall project timelines and commercial viability. Rising volumes of bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates require engineered cell lines capable of balanced chain expression, driving premium pricing for specialized development services. Across every major geography, large molecules now receive preferential investment over small molecules, cementing long-term demand for sophisticated cell culture systems.
Expansion of Monoclonal Antibody Pipelines
Clinical approvals of bispecific antibodies since 2020 highlight the shift toward dual-target formats, which double the complexity of cell engineering workflows. Pharmaceutical majors continue to finance dedicated facilities, such as AstraZeneca's USD 1.5 billion Singapore site, to secure end-to-end antibody-drug conjugate production capacity. As each novel antibody format carries unique folding and glycosylation needs, sponsors increasingly favor proprietary cell platforms that can be locked into long-term supply agreements. Those dynamics intensify the competitive race within the cell line development market, particularly for service providers that offer turnkey engineering plus downstream analytics.
Stringent Regulatory Compliance
The FDA's updated Q5A(R2) guidance on viral safety requires extended characterization studies, adding up to one year of additional testing for new cell substrates. Companies lacking in-house regulatory expertise must absorb higher consulting fees and possible rework if submissions fall short of evolving standards. Divergent regional expectations complicate global launch sequencing, as Europe often requests supplementary adventitious-agent screens not demanded elsewhere. These pressures raise the fixed costs of operating in the cell line development market and may lead smaller firms to exit or consolidate, shifting bargaining power toward large, vertically integrated providers.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- CAPEX Race for Continuous Bioprocessing Infrastructure
- AI-Guided Cell-Line Optimisation Platforms
- Shortage of cGMP-Grade Raw-Material Supply Chains
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Reagents and media represented 44.12% of 2024 revenue, as every production lot consumes large volumes of culture medium, feed, and buffer. The segment's 10.94% forecast CAGR exceeds that of capital equipment because each new therapy approval scales recurring consumable orders, ensuring predictable demand within the broader cell line development market. Suppliers prioritize chemically defined and serum-free formulations that improve batch consistency while reducing contamination risks, and AI-enabled design tools optimize nutrient blends to lift peak titers. Equipment, which covers bioreactors and automated cell-handling systems, remains crucial because rising cell densities require precise process control to avoid nutrient depletion and waste accumulation. Ancillary services, such as cell banking, analytical testing, and viral clearance studies, round out a growing long-tail category that benefits from heightened regulatory scrutiny.
The reagents category further benefits from subscription-like purchasing patterns, as bioreactors continuously draw feed components during extended perfusion runs. Specialized vendors now market modular media kits tailored to CRISPR-engineered cell lines that exhibit unique metabolic footprints. As process intensification expands, demand for high-purity raw materials will escalate, encouraging suppliers to vertically integrate amino-acid and vitamin production. Collectively, these trends consolidate the competitive importance of consumables within the cell line development market, tightening linkages between media innovation and overall facility output.
Mammalian lines controlled 75.04% of cell line development market share in 2024, and their 11.35% CAGR underscores sustained preference for human-like post-translational modifications. Chinese hamster ovary cells remain the gold standard for monoclonal antibodies, while CRISPR knockouts that delete key glycosylation genes deliver more homogeneous glycoforms with reduced immunogenicity. Human embryonic kidney (HEK293) lines, optimized for suspension growth, underpin most adeno-associated viral vector production for gene therapies and now contribute meaningful revenue to the cell line development market size for viral applications. Non-mammalian systems, including yeast and insect lines, address niche enzyme and vaccine applications where complex glycosylation is unnecessary.
Advances in high-throughput microfluidic screening enable the rapid isolation of top-producing mammalian clones, cutting weeks from traditional limiting dilution campaigns. Novel genomic instability sensors track chromosomal aberrations in real time, allowing early culling of unstable clones. Bacterial and yeast systems still excel for simple protein products, although their overall growth lags mammalian gains. That technology mix ensures that the cell line development market maintains a diverse toolbox capable of matching specific molecular requirements with the most cost-effective cellular chassis.
The Cell Line Development Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Product (Reagent & Media, Equipment, Other Products), by Source (Mammalian Cell Line, Non-Mammalian Cell Line), by Application (Recombinant Protein Expression, Hybridomas Technology, and More. ), by End User (Biotech & Pharma Companies, Cdmos, and More. ), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America maintained 40.23% revenue share in 2024, buoyed by large-scale investments such as Eli Lilly's USD 9 billion Indiana complex and Novo Nordisk's USD 4.1 billion North Carolina expansion. The region benefits from entrenched regulatory expertise and robust venture capital, yet faces raw-material shortages and export-control uncertainties that complicate supply continuity. Canada's OmniaBio is building an AI-enabled cell therapy hub designed to halve production costs, signaling regional commitment to advanced manufacturing. Mexico attracts near-shoring interest as companies seek proximity to the United States without incurring domestic cost structures. Collectively, these dynamics ensure that the cell line development market in North America remains both innovative and capital intensive.
Asia-Pacific records the fastest 11.23% CAGR through 2030, fueled by more than USD 3 billion of 2024 biomanufacturing commitments in Singapore alone. AstraZeneca's USD 1.5 billion ADC plant and BioNTech's first ex-Germany facility exemplify the region's rise as a premium biomanufacturing destination. China and India retain cost advantages and large internal demand, yet the U.S. BIOSECURE Act proposal accelerates diversification toward Indian CDMOs, South Korean biologics clusters, and ASEAN member states. Japan and Australia complement the ecosystem through high-precision analytics and RNA therapeutics platforms, respectively. These moves collectively shift the gravitational center of the cell line development market toward Asia-Pacific while creating multipolar supply networks that mitigate geopolitical risks.
Europe experiences steady but slower expansion, supported by established pharmaceutical corridors in Germany, Switzerland, and Ireland. Government incentives for advanced therapies and cross-border regulatory harmonization preserve competitiveness, although energy costs and wage inflation narrow margins relative to Asia. The Middle East and Africa pursue strategic entry, with Saudi Arabia's National Biotechnology Strategy targeting global leadership by 2040 and the UAE positioning itself as a regional logistics node. South America, led by Brazil, taps domestic demand and emerging biosimilar opportunities, yet limited venture funding constrains rapid capacity build-out. Altogether, a rebalanced global footprint emerges in which the cell line development market relies on diverse manufacturing hubs to match local demand and de-risk supply chains.
- American Type Culture Collection
- Sartorius
- Danaher
- Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Wuxi Biologics
- Corning
- Selexis SA (JSR Life Sciences)
- Promega
- FUJIFILM
- Lonza Group
- GE HealthCare (Cell Culture)
- Samsung Group
- AGC Biologics
- Horizon Discovery (PerkinElmer)
- Charles River
- KBI Biopharma
- BioReliance (Merck)
- GenScript Biotech
- Evotec
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Biopharmaceutical Demand
- 4.2.2 Expansion of Monoclonal Antibody Pipelines
- 4.2.3 Surge in Biosimilar Production Post-patent Cliff
- 4.2.4 CAPEX Race for Continuous Bioprocessing Infrastructure
- 4.2.5 AI-guided Cell-line Optimisation Platforms
- 4.2.6 Rise of Regional Bio-CDMO Clusters in MENA & ASEAN
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent Regulatory Compliance
- 4.3.2 Lengthy Cell-line Stability Timelines
- 4.3.3 Shortage of cGMP-grade Raw-material Supply Chains
- 4.3.4 Geopolitical Export-control Risks for CHO/HEK Cell Lines
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD Million)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Reagents & Media
- 5.1.2 Equipment
- 5.1.3 Other Products
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Mammalian Cell Line
- 5.2.2 Non-mammalian Cell Line
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Recombinant Protein Expression
- 5.3.2 Hybridoma Technology
- 5.3.3 Vaccine Production
- 5.3.4 Drug Discovery & Screening
- 5.3.5 Gene & Cell Therapy Manufacturing
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Biopharma & Pharma Companies
- 5.4.2 Contract Development & Manufacturing Organisations (CDMOs)
- 5.4.3 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.4.4 Other End-users
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 American Type Culture Collection (ATCC)
- 6.3.2 Sartorius AG
- 6.3.3 Danaher Corporation (Cytiva)
- 6.3.4 Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma)
- 6.3.5 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.3.6 WuXi Biologics
- 6.3.7 Corning Incorporated
- 6.3.8 Selexis SA (JSR Life Sciences)
- 6.3.9 Promega Corporation
- 6.3.10 Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies
- 6.3.11 Lonza Group
- 6.3.12 GE HealthCare (Cell Culture)
- 6.3.13 Samsung Biologics
- 6.3.14 AGC Biologics
- 6.3.15 Horizon Discovery (PerkinElmer)
- 6.3.16 Charles River Laboratories
- 6.3.17 KBI Biopharma
- 6.3.18 BioReliance (Merck)
- 6.3.19 GenScript Biotech
- 6.3.20 Evotec SE
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




