PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844620

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844620
Submarine - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The submarine market size is worth USD 26.39 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to climb to USD 32.37 billion in 2030, advancing at a steady 4.17% CAGR.
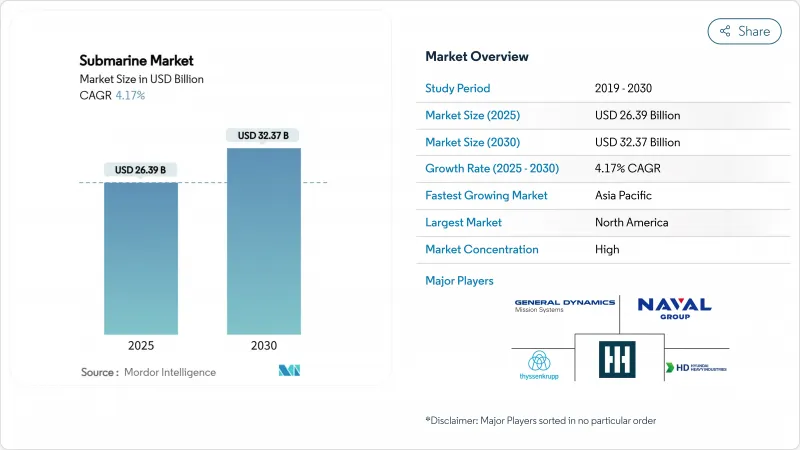
This controlled expansion reflects the capital-intensive nature of submarine acquisition, where each boat carries a multi-billion-dollar price tag and remains in service for 30 years or more. Australia's commitment to nuclear-powered submarines under the AUKUS pact has redrawn procurement priorities, forcing allied yards to realign capacity and technology roadmaps. Intensifying maritime frictions in the Indo-Pacific sustain procurement momentum, especially as China races toward an 80-boat fleet by 2035, prompting neighbors to accelerate underwater modernization. Diesel-electric boats still dominate through their cost advantages, yet nuclear units enjoy the fastest sales trajectory, mirroring a strategic tilt toward long-range deterrence. North America retains spending leadership on the back of the US Navy's USD 213.9 billion procurement pipeline. Still, the Asia-Pacific is the growth engine as regional navies scale investments to match the evolving threat picture.
Global Submarine Market Trends and Insights
Rising Defense-Modernization Budgets Among Tier-1 Navies
Expanding budgets across major sea powers underpin a visible upcycle in the submarine market. The US Navy alone has USD 213.9 billion earmarked for nuclear boats over the next decade. Parallel commitments are evident in Europe, where Germany approved EUR 800 million (USD 945.3 million) for fleet upgrades and the Netherlands allotted EUR 2.2 billion (USD 2.6 billion) for Barracuda-class replacements. India's Project 75(I) and Australia's AUKUS program add multi-billion-dollar pipelines that keep order books healthy. Because submarine contracts span 7-10 years from award to commissioning, these allocations give prime contractors long-term cash-flow visibility and justify investments in new dry-docks, modular construction lines, and research into low-observable materials.
Escalating Indo-Pacific Maritime Tensions
China's projected rise to 80 submarines by 2035, including Type 095 SSNs and Type 096 SSBNs, amplifies competitive pressure across the Indo-Pacific. Japan's Taigei-class, South Korea's KSS-III, and Australia's future SSNs form the backbone of an allied counterweight. The region is now the largest source of new-build demand, with yards in the United States, South Korea, and Australia pushing capacity to absorb overlapping orders. Forward-deployed US attack submarines rotate through Western Pacific bases more frequently, a trend intensifying pressure to sustain throughput in depot-level maintenance cycles.
Ultra-High Acquisition and Lifecycle Costs
A new Virginia-class boat now costs USD 4.8 billion, while each Columbia-class SSBN eclipses USD 15.2 billion, tightening naval capital budgets. Lifecycle burdens are equally daunting: the refueling-overhaul of USS Boise came to USD 1.2 billion, a figure rivalling the price of an export-grade conventional submarine. Budget-constrained navies often trade fleet size for capability, trimming hull counts to fund maintenance, training, and munitions. Escalating per-unit price tags remain the single largest brake on the submarine market expansion over the long term.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Fleet-Replacement Cycles in Legacy Nuclear Operators
- Adoption of AIP and Li-ion Batteries Extending Submerged Endurance
- Skilled Labor Bottlenecks in Submarine Yards
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Nuclear submarines represent the fastest-growing slice, advancing at 5.45% CAGR, while diesel-electric designs still hold the numerical lead with 56.23% of 2024 revenue. The AUKUS decision redirected supply-chain focus toward highly enriched fuel cores and reactor modules. The submarine market size for nuclear-powered craft is set to enlarge noticeably as Australia joins the United States, United Kingdom, France, Russia, China, and India in the nuclear operator club. Yet conventional boats remain indispensable in constrained, shallow theaters where smaller navies prize affordability and stealth. Advanced lithium-ion and fuel-cell solutions stretch submerged endurance, giving diesel-electric hulls a second wind in cost-sensitive procurements. Manufacturers now routinely offer common combat-system architectures across propulsion types to ease future technology transfers and life-cycle support.
Fleet planners weigh mission profiles rather than price alone when selecting propulsion. Nuclear boats offer unmatched strategic reach for deterrence patrols, special-forces insertion, and high-end anti-submarine warfare. Conventional boats thrive in chokepoints and littorals, leveraging smaller acoustic signatures to evade detection. As great-power competition intensifies, dual-track demand ensures balanced growth across both categories, broadening the revenue base for prime contractors while cushioning market volatility linked to single-program delays.
Attack submarines captured 49.12% revenue share in 2024 by their multi-mission flexibility. However, ballistic-missile boats deliver the most momentum with a 6.23% CAGR to 2030. The Columbia-class, China's Type 096, and India's S4-class collectively account for a surge in SSBN backlog. Therefore, the submarine market size for ballistic-missile platforms is on an upswing, reflecting renewed emphasis on secure second-strike capabilities. While fewer in number, guided-missile units remain essential for conventional prompt-strike options without breaching nuclear thresholds, giving navies escalatory flexibility.
Strategic doctrines are shifting: nuclear-armed states prioritize continuous-at-sea deterrence, anchoring force-posture credibility on submerged ballistic assets. In tandem, attack submarines become workhorses for day-to-day intelligence gathering, carrier escort, and anti-ship missions. The resulting portfolio mix encourages shipbuilders to adopt modular designs that can be configured for both roles, trimming R&D expense and shortening development cycles.
The Submarine Market Report is Segmented by Propulsion Type (Nuclear-Powered and Diesel-Electric Submarines), Combat Role (Attack, Ballistic-Missile, and More), Displacement Class (Less Than 2, 000 Tons, 2, 000 To 4, 000 Tons, and More), Component (Hull and Structural Modules, Propulsion Systems, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America holds 36.36% of global expenditure thanks to the US Navy's front-loaded SSN and SSBN pipeline. Although congressional appropriations remain stable, production stresses at Electric Boat and Huntington Ingalls lengthen delivery schedules, tempering near-term volume growth. AUKUS adds external demand, with Australian personnel training in American yards and British designers collaborating on reactor layouts. Canada, meanwhile, weighs a requirement for up to 12 new boats, but decision timelines extend beyond 2025.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest riser, showing a 5.92% CAGR, with China, Japan, South Korea, India, and Australia soaring in orders. Japan commissioned its fourth Taigei-class in March 2025, validating lithium-ion safety and endurance gains. India advances its Kalvari-class build schedule and pushes Project 75(I) toward contract award, structuring terms around technology transfer to state-owned yards. South Korea's Baltic Sea trials for KSS-III underscore its blue-water aspirations and export credibility. The submarine market size for Asia-Pacific is expected to close the decade, nearly matching the North American value.
Europe records measured, replacement-driven growth. German Navy life-extension work, the Dutch Barracuda deal, and Greece's Papanikolis upgrade keep regional yards occupied. Poland's Orka tender and Turkey's exploratory SSN concept studies add competitive bidding opportunities. NATO interoperability requirements continue to shape combat-system baselines, ensuring shared upgrade pathways and supplier overlap that reduce long-run sustainment costs for alliance members.
- General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc. (General Dynamics Corporation)
- Huntington Ingalls Industries, Inc.
- BAE Systems plc
- Naval Group
- thyssenkrupp Marine Systems GmbH (thyssenkrupp AG)
- HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd.
- Hanwha Corporation
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Saab AB
- NAVANTIA, S.A., SME
- Fincantieri S.p.A.
- United Shipbuilding Corporation
- China State Shipbuilding Corporation
- Jiangnan Shipyard
- ASC Pty Ltd.
- PT PAL Indonesia
- SIMA PERU S.A.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising defense-modernization budgets among Tier-1 navies
- 4.2.2 Escalating Indo-Pacific maritime tensions
- 4.2.3 Fleet-replacement cycles in legacy nuclear operators
- 4.2.4 Adoption of AIP and Li-ion batteries extending submerged endurance
- 4.2.5 AUKUS pact triggering allied fleet expansion
- 4.2.6 Need to secure subsea data-cable infrastructure
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Ultra-high acquisition and lifecycle costs
- 4.3.2 Arms-control and nuclear-proliferation treaties
- 4.3.3 Skilled labor bottlenecks in submarine yards
- 4.3.4 Supply-chain scarcity of marinized semiconductors
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Propulsion Type
- 5.1.1 Nuclear-Powered
- 5.1.2 Diesel-Electric (Conventional and AIP)
- 5.2 By Combat Role
- 5.2.1 Attack (SSN/SSK)
- 5.2.2 Ballistic-Missile (SSBN)
- 5.2.3 Guided-Missile (SSGN)
- 5.3 By Displacement Class
- 5.3.1 Less than 2,000 tons
- 5.3.2 2,000 to 4,000 tons
- 5.3.3 Greater than 4,000 tons
- 5.4 By Component
- 5.4.1 Hull and Structural Modules
- 5.4.2 Propulsion Systems
- 5.4.3 Combat and Sensor Suites
- 5.4.4 Energy Storage (Batteries, AIP)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Israel
- 5.5.5.1.2 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc. (General Dynamics Corporation)
- 6.3.2 Huntington Ingalls Industries, Inc.
- 6.3.3 BAE Systems plc
- 6.3.4 Naval Group
- 6.3.5 thyssenkrupp Marine Systems GmbH (thyssenkrupp AG)
- 6.3.6 HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Hanwha Corporation
- 6.3.8 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- 6.3.9 Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 6.3.10 Saab AB
- 6.3.11 NAVANTIA, S.A., SME
- 6.3.12 Fincantieri S.p.A.
- 6.3.13 United Shipbuilding Corporation
- 6.3.14 China State Shipbuilding Corporation
- 6.3.15 Jiangnan Shipyard
- 6.3.16 ASC Pty Ltd.
- 6.3.17 PT PAL Indonesia
- 6.3.18 SIMA PERU S.A.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




