PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844655

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844655
China Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Monosodium Glutamate market size in China is estimated at USD 3.03 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow to USD 3.94 billion by 2030, registering a steady CAGR of 5.39% during 2025-2030.
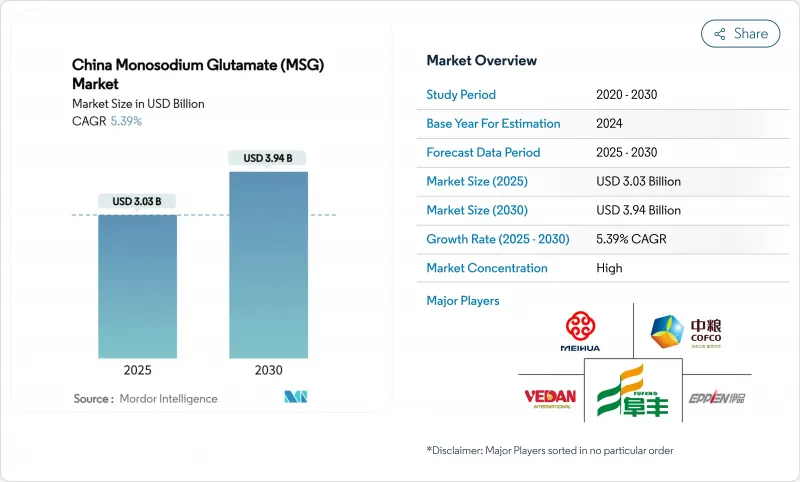
This growth is primarily driven by China's dominant role as the largest global producer and consumer of monosodium glutamate. Despite growing health concerns around food additives, the demand for monosodium glutamate remains strong. Food manufacturers rely on it to deliver a consistent umami flavor, which is highly sought after in the food industry, while also helping to reduce sodium content in products at a relatively low cost. This dual functionality makes it an indispensable ingredient for many processed foods. The market is heavily influenced by raw material availability, with corn starch being the dominant input, although cassava is emerging as a potential alternative. Natural fermentation processes continue to dominate production methods, ensuring high-quality output. In terms of applications, traditional uses of monosodium glutamate in processed foods drive the majority of demand, but innovation is expanding its reach into new product categories. China's monosodium glutamate market is highly concentrated, with an oligopolistic structure where the top five suppliers control over 80% of the country's production capacity.
China Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) Market Trends and Insights
Growing demand for flavor enhancers in packaged foods
The growing demand for flavor enhancers in China's packaged food industry is playing a key role in driving the monosodium glutamate (MSG) market. According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China, the total retail sales of consumer goods in May reached 3,921.1 billion yuan, highlighting the expanding market potential . Manufacturers are increasingly relying on monosodium glutamate due to its ability to enhance the umami flavor while reducing sodium content by up to 40%, aligning with health-conscious reformulation goals. Unlike table salt, which contains 39% sodium, monosodium glutamate has only 12%, as reported by the Center for Food Safety, making it an effective solution for sodium reduction. New formulations now feature fermentation-derived monosodium glutamate, which caters to clean-label preferences and meets the growing consumer demand for natural ingredients. Advances in synthetic biology have further enabled the production of purer, "naturally fermented" monosodium glutamate variants, allowing food brands to position their products as premium offerings.
Rising consumption of instant noodles and other processed food items
The growing popularity of instant noodles and other processed foods is significantly driving the demand for monosodium glutamate in China. This is largely due to its ability to maintain flavor stability during high-temperature processing and its compatibility with long-shelf-life products. According to the World Instant Noodles Association, China and Hong Kong recorded the highest global consumption of instant noodles in 2024, with 43,802 million servings . This highlights the essential role of monosodium glutamate in preserving flavor and ensuring product durability. Rapid urbanization and the increasing preference for convenient, on-the-go meals among younger professionals are further boosting monosodium glutamate usage. Manufacturers aiming to expand in export markets rely on monosodium glutamate's cost-effectiveness to stay competitive, especially amid rising freight costs and trade restrictions. Monosodium Glutamate helps deliver consistent taste across a variety of dehydrated and shelf-stable food categories.
Health concerns related to excessive monosodium glutamate consumption
Concerns about excessive monosodium glutamate consumption continue to limit market growth, particularly among urban and health-conscious consumers. Although global regulatory bodies like the FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives have confirmed monosodium glutamate's safety within acceptable intake limits, many consumers remain skeptical. Studies, such as intake modeling from ScienceDirect, show that children aged 3-6 years in high-exposure groups may consume up to 97.2% of the Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI), raising concerns among parents and public health advocates. Outdated myths like "Chinese Restaurant Syndrome" persist, fueled by misinformation on social media, despite being scientifically debunked. In response to these challenges, premium food brands, especially in tier-1 Chinese cities, are introducing monosodium glutamate-free or "all-natural umami" product lines. These cleaner-label alternatives are gaining traction, redirecting some market value away from traditional monosodium glutamate products and pushing manufacturers to innovate and meet evolving consumer preferences.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Abundant raw-material supply supports local monosodium glutamate production
- Monosodium Glutamate offers cost-effective taste enhancement for manufacturers
- Rising popularity of natural and clean-label foods
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Corn-starch formulations captured 61.22% of the China Monosodium Glutamate market share in 2024 because well-established wet-milling hubs in Heilongjiang and Jilin deliver steady, low-cost feedstock to adjacent fermentation plants. The same logistics networks channel finished monosodium glutamate into coastal seasoning factories, reinforcing corn's position at the heart of domestic supply chains. Cassava-based monosodium glutamate remained smaller but benefited from Guangxi's expanding crop base and Thai-linked import routes that secure year-round material flow. Sugar-beet molasses and other niche substrates held marginal shares, serving regional plants that capitalize on local by-product streams.
Looking ahead to 2030, cassava/tapioca-based monosodium glutamate is expected to grow at a faster rate, with a projected CAGR of 6.53%, outpacing other substrates. This growth is driven by advancements in fermentation technology, which are reducing detoxification costs, and by Guangxi's increasing cassava acreage to meet rising demand. Corn-starch-based monosodium glutamate will continue to expand, albeit at a slower pace, as large integrated producers focus on balancing capacity utilization with environmental regulations. Meanwhile, sugar-beet and other specialty feedstocks are likely to see modest growth, primarily supporting research and development efforts and catering to niche markets that require differentiated texture or higher purity grades.
The China Monosodium Glutamate Market Report is Segmented by Raw Material (Corn Starch, Sugar-Beet Molasses, Cassava/Tapioca, and Other Substrates), Source (Natural/Fermentation-Based and Synthetic/Chemically Derived), and Application (Noodles, Soups and Broth, Meat Products, Seasonings and Dressings, and Other Applications). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Fufeng Group Limited
- Meihua Holdings Group Co. Ltd
- COFCO Corporation
- Lotus Health Group
- Ajinomoto Co. Inc.
- Ningxia Eppen Biotech
- Henan Brilliant Biotech Co., Ltd.
- Starlake Bioscience Co., Inc. Zhaoqing
- Shandong Qilu MSG Group
- Fujian Province Jianyang Wuyi MSG Co. Ltd
- Vedan International (Holdings) Ltd
- Xinle MSG Co.
- Foodchem International Corporation
- Gremount International Company Limited
- Shandong Shenghua MSG
- Guangzhou ZIO Chemical Co.,Ltd
- Xinjiang Longyu (Shenghua) MSG
- Hainan Yeedok Industry Co. Ltd.
- The TNN Development Limited.
- Linghua Group Limited
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing demand for flavor enhancers in packaged foods drives demand
- 4.2.2 MSG offers cost-effective taste enhancement for manufacturers
- 4.2.3 Expansion of foodservice and quick-service restaurant chains boosts demand
- 4.2.4 Rising consumption of instant noodles and other processed food items drives Growth
- 4.2.5 Abundant raw material supply supports local monosodium glutamate production
- 4.2.6 Technological advancements improve yield and production efficiency surges Demand
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Health concerns related to excessive monosodium glutamate consumption
- 4.3.2 Rising popularity of natural and clean label foods hinders demand
- 4.3.3 Regulatory restrictions on monosodium glutamate in certain applications
- 4.3.4 Competition from natural umami sources like yeast extract
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Raw Material
- 5.1.1 Corn Starch
- 5.1.2 Sugar-beet Molasses
- 5.1.3 Cassava/Tapioca
- 5.1.4 Other Substrates
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Natural Fermentation-Based
- 5.2.2 Synthetic/Chemically Derived
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Noodles, Soups, and Broth
- 5.3.2 Meat Products
- 5.3.3 Seasonings and Dressings
- 5.3.4 Other Applications
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Fufeng Group Limited
- 6.4.2 Meihua Holdings Group Co. Ltd
- 6.4.3 COFCO Corporation
- 6.4.4 Lotus Health Group
- 6.4.5 Ajinomoto Co. Inc.
- 6.4.6 Ningxia Eppen Biotech
- 6.4.7 Henan Brilliant Biotech Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Starlake Bioscience Co., Inc. Zhaoqing
- 6.4.9 Shandong Qilu MSG Group
- 6.4.10 Fujian Province Jianyang Wuyi MSG Co. Ltd
- 6.4.11 Vedan International (Holdings) Ltd
- 6.4.12 Xinle MSG Co.
- 6.4.13 Foodchem International Corporation
- 6.4.14 Gremount International Company Limited
- 6.4.15 Shandong Shenghua MSG
- 6.4.16 Guangzhou ZIO Chemical Co.,Ltd
- 6.4.17 Xinjiang Longyu (Shenghua) MSG
- 6.4.18 Hainan Yeedok Industry Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.19 The TNN Development Limited.
- 6.4.20 Linghua Group Limited
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




