PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1849896

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1849896
India Infrastructure Sector - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The India infrastructure sector market is valued at USD 190.7 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 280.6 billion by 2030, registering an 8.0% CAGR.
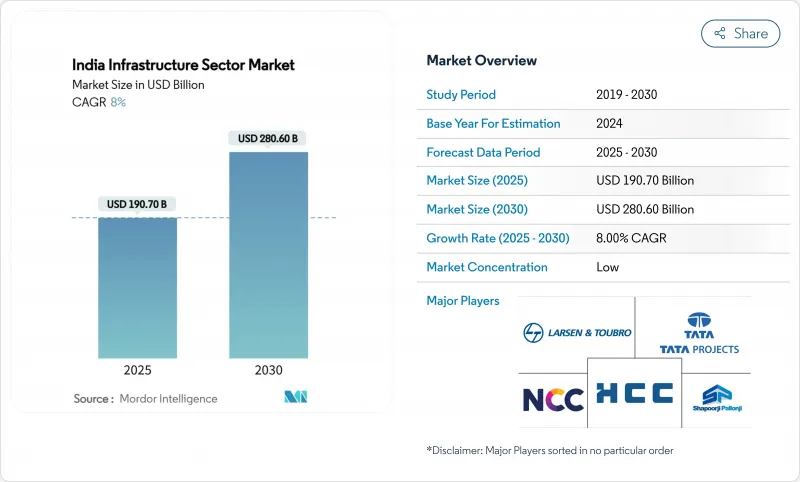
Momentum is anchored in the National Infrastructure Pipeline, which targets investments worth USD 1.34 trillion by 2025, and in the Union Budget 2025-26 that maintains capital expenditure at 3.1% of GDP. Robust spending on highways, rail corridors and urban transit is complemented by large-scale utility upgrades and fast-growing digital networks. Evolving PPP models, deeper municipal bond markets and sector-specific reforms are broadening the financing base, while technology adoption is trimming project timelines and lifecycle costs.
India Infrastructure Sector Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Urbanisation & Smart Cities Mission Fueling Capex in Tier-2 Cities
The Smart Cities Mission is reshaping 100 urban centres and is channeling USD 24.7 billion into digital-ready roads, metro-feeder links and climate-resilient public spaces. Tier-2 cities such as Indore and Surat use IoT traffic systems that have cut peak congestion by 30%, catalysing a 27% rise in commercial real-estate investment during 2024. Integrated command-and-control centres marshal live data on utilities, security and mobility, improving resource allocation and raising livability indices that attract private capital.
National Logistics Policy Accelerating Multimodal Freight Corridor Build-out
India's National Logistics Policy (NLP) is spearheading the development of multimodal freight corridors nationwide. Aimed at slashing logistics costs from the current 13-14% of GDP to single digits, the NLP seamlessly integrates rail, road, air, and waterways into a cohesive transport system. Central to this initiative are the Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs), including the fully operational Eastern DFC and the partially active Western DFC, both of which bolster rail freight capacity and speed. Furthermore, under the Logistics Efficiency Enhancement Program (LEEP), Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs) are being developed to modernize cargo movement, offering top-notch facilities for storage, handling, and intermodal transfers. These endeavors are further supported by the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, which promotes synchronized infrastructure planning and execution across various sectors. Together, these initiatives are reshaping India's logistics framework, driving economic growth, and boosting the nation's standing in global trade.
Land Acquisition Bottlenecks
Twenty-six percent of central projects face multi-year delays due to fragmented records and compensation disputes. Linear assets such as highways see 78% of projects overrun schedules because parcels remain encumbered. Digitised cadastral mapping and expedited tribunals are improving transparency, yet systemic reforms in valuation and consent remain critical.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Renewable Energy Corridor Investments Driving Grid-Scale Transmission EPC Orders
- 5G Roll-out Catalyzing Fiber Backhaul and Tower Infrastructure Expansion
- Lengthy Regulatory and Environmental Clearances
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Transportation infrastructure accounts for a 38% slice of the India infrastructure sector market size in 2024 and is projected to post a 9.2% CAGR to 2030. Expressway mileage crossed 55,000 km, while 2,031 km of new rail track and 17 pairs of semi-high-speed trains entered service in FY 2024. Flagship corridors under Bharatmala and Gati Shakti merge road, rail and inland-waterway planning, reinforcing last-mile connectivity. Investments now blend physical assets with digital signalling and integrated ticketing, improving throughput and safety. Urban metro systems in Delhi, Bengaluru and Nagpur deploy platform-screen doors and regenerative braking, lowering energy use. Growing multimodal hubs foster private logistics parks that backhaul containers directly to factories. The transport segment's expansion creates spill-over demand for bridges, flyovers and maintenance depots, anchoring allied engineering and service providers in the India infrastructure sector market.
Utilities rank second, driven by additions of renewable plants, smart grids and city gas pipelines. Hybrid solar-wind parks in Rajasthan and Gujarat connect through +-800 kV HVDC links, providing predictable power to industrial clusters. Water-supply upgrades include leak-detection sensors and supervisory control systems that curb non-revenue water. Telecom fibre overlays major highways, allowing joint trenching and lowering both capex and road-cut repairs. Social infrastructure accelerates as hospitals and education campuses adopt prefabricated modules that shorten completion cycles. Extraction assets benefit from a move to revenue-sharing terms under the March 2025 Oilfield (Regulatory and Development) Amendment Bill, spurring investment in marginal blocks and deepwater fields.
The Indian Infrastructure Market Report is Segmented by Infrastructure Segment (Transportation Infrastructure, Utilities Infrastructure, Social Infrastructure, and Extraction Infrastructure), by Construction Type (New Construction and Renovation), by Investment Source (Public and Private), and by Key Cities (Delhi NCR, Pune, and More). The Report Offers Market Size and Forecasts in Value (USD) for all the Above Segments.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Larsen & Toubro Ltd
- Tata Projects Ltd
- Hindustan Construction Company Ltd
- NCC Ltd
- Shapoorji Pallonji Engineering & Construction
- Afcons Infrastructure Ltd
- GMR Infrastructure Ltd
- IRB Infrastructure Developers Ltd
- Adani Ports & SEZ Ltd
- Reliance Infrastructure Ltd
- Dilip Buildcon Ltd
- KEC International Ltd
- Ashoka Buildcon Ltd
- JSW Infrastructure Ltd
- Kalpataru Power Transmission Ltd
- Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd
- Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- JMC Projects (India) Ltd
- GR Infraprojects Ltd
- Welspun Enterprises Ltd
- Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd
- NBCC (India) Ltd
- ITD Cementation India Ltd
- Capacit'e Infraprojects Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Insights and Dynamics
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid Urbanisation & Smart Cities Mission Fueling Capex in Tier-2 Cities
- 4.2.2 National Logistics Policy Accelerating Multimodal Freight Corridor Build-out
- 4.2.3 Renewable Energy Corridor Investments Driving Grid-Scale Transmission EPC Orders
- 4.2.4 5G Roll-out Catalyzing Fiber Backhaul and Tower Infrastructure Expansion
- 4.2.5 Expansion of Dedicated Freight Corridors Triggering Ancillary Industrial Parks
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Land Acquisition Bottlenecks
- 4.3.2 Lengthy Regulatory and Environmental Clearances
- 4.3.3 Cost Inflation & Commodity Volatility
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.4.1 Overview
- 4.4.2 Real Estate Developers and Contractors - Key Quantitative and Qualitative Insights
- 4.4.3 Architectural and Engineering Companies - Key Quantitative and Qualitative Insights
- 4.4.4 Building Material and Equipment Companies - Key Quantitative and Qualitative Insights
- 4.5 Government Initiatives & Vision 2047 Alignment
- 4.6 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.7 Technological Outlook
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.9 Pricing (Construction Materials) and Construction Cost (Materials, Labour, Equipment) Analysis
- 4.10 Comparison of Key Industry Metrics of India with Other Countries
- 4.11 Key Upcoming/Ongoing Projects (with a focus on Mega Projects)
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Infrastructure Segment
- 5.1.1 Transportation Infrastructure
- 5.1.2 Utilities Infrastructure
- 5.1.3 Social Infrastructure
- 5.1.4 Extraction Infrastructure
- 5.2 By Construction Type
- 5.2.1 New Construction
- 5.2.2 Renovation
- 5.3 By Investment Source
- 5.3.1 Public
- 5.3.2 Private
- 5.4 By Key Cities
- 5.4.1 Mumbai Metropolitan Region
- 5.4.2 Delhi NCR
- 5.4.3 Pune
- 5.4.4 Bengaluru
- 5.4.5 Hyderabad
- 5.4.6 Chennai
- 5.4.7 Kolkata
- 5.4.8 Ahemadabad
- 5.4.9 Rest of India
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Larsen & Toubro Ltd
- 6.4.2 Tata Projects Ltd
- 6.4.3 Hindustan Construction Company Ltd
- 6.4.4 NCC Ltd
- 6.4.5 Shapoorji Pallonji Engineering & Construction
- 6.4.6 Afcons Infrastructure Ltd
- 6.4.7 GMR Infrastructure Ltd
- 6.4.8 IRB Infrastructure Developers Ltd
- 6.4.9 Adani Ports & SEZ Ltd
- 6.4.10 Reliance Infrastructure Ltd
- 6.4.11 Dilip Buildcon Ltd
- 6.4.12 KEC International Ltd
- 6.4.13 Ashoka Buildcon Ltd
- 6.4.14 JSW Infrastructure Ltd
- 6.4.15 Kalpataru Power Transmission Ltd
- 6.4.16 Power Grid Corporation of India Ltd
- 6.4.17 Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- 6.4.18 JMC Projects (India) Ltd
- 6.4.19 GR Infraprojects Ltd
- 6.4.20 Welspun Enterprises Ltd
- 6.4.21 Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd
- 6.4.22 NBCC (India) Ltd
- 6.4.23 ITD Cementation India Ltd
- 6.4.24 Capacit'e Infraprojects Ltd
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook




