PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1849984

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1849984
Genetic Testing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
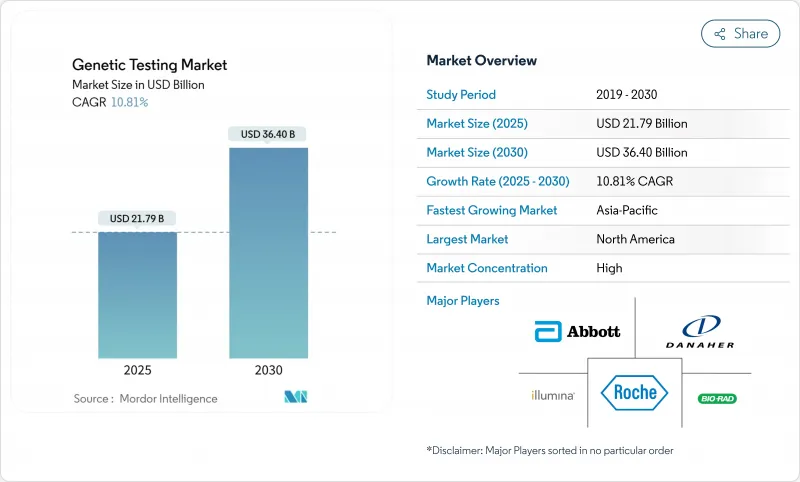
The genetic testing market is valued at USD 21.79 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 36.40 billion by 2030, advancing at a robust 10.81% CAGR.
Recent breakthroughs-AI-powered interpretation that compresses reporting cycles to 7-9 hours and sub-USD 100 whole-genome sequencing-are redefining clinical cost paradigms and accelerating global uptake. National health systems are embedding genomic services into routine care, as shown by the United Kingdom's GBP 650 million newborn DNA-testing program announced in June 2025 . Regulatory alignment, especially new FDA companion-diagnostic mandates for oncology, further normalizes test ordering across specialties. The genetic testing market now benefits from record venture funding, a wave of platform acquisitions, and widening employer health-plan coverage that jointly expand test accessibility while driving price compression.
Global Genetic Testing Market Trends and Insights
Integration of Genomic Sequencing into Standard Prenatal Care
Healthcare agencies are moving prenatal testing from a specialized referral service to routine screening. The June 2025 UK initiative allocates GBP 650 million to sequence every newborn, aiming to detect more than 200 rare disorders at birth nhs.uk. Pilot studies show that non-invasive prenatal testing plus ultrasound reaches 88.24% sensitivity for complex chromosomal anomalies, far surpassing conventional protocols. By flagging actionable findings earlier, health systems expect lifetime treatment savings and improved developmental outcomes. The approach simultaneously amasses population databanks that enrich reference genomes and fuel downstream research collaborations. As national insurers codify reimbursement pathways, prenatal genomic panels will likely become default obstetric practice in developed economies.
AI-Powered Variant Interpretation Reducing Turnaround Time
Machine-learning algorithms now triage millions of variants and annotate clinically significant findings within hours. Oxford Nanopore's rapid sequencing pipeline delivers same-day results-transformative for neonatal intensive-care and infectious-disease settings. GeneDx's 2025 purchase of Fabric Genomics integrates deep-learning decision support that trims manual curation costs and lifts diagnostic yields in rare-disease exome testing. These productivity gains permit laboratories to scale volumes without proportional staffing increases, easing backlogs created by the global shortage of certified genetic counselors. AI also unlocks long-tail applications-such as forensic analysis of degraded DNA-by improving amplification success rates in challenging samples.
Data-Privacy Legislation Proliferation (GDPR, CCPA, India DPDP)
A growing mosaic of privacy statutes complicates cross-border data flows essential for large-scale genomic research. Since 2023, more than 30 class actions have alleged improper DNA data handling under state genetic-privacy laws in the United States, exposing offenders to penalties up to USD 15,000 per deliberate breach. The European Union's GDPR obliges explicit consent and mandates data-minimization, curbing secondary analytics revenue for direct-to-consumer firms. India's 2025 Digital Personal Data Protection Act imposes local-storage requirements that raise infrastructure costs for multinational labs. Compliance spending diverts capital from R&D and slows multi-regional clinical-trial enrollment, tempering the genetic testing market's immediate growth trajectory.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Falling Costs of Whole-Genome Sequencing Below USD 100
- Oncology Companion-Diagnostic Mandates by Regulators
- Reimbursement Gaps for Multigene Panels Outside Oncology
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Next-Generation Sequencing currently accounts for 50.57% of genetic testing market revenue, underscoring its central role in high-throughput clinical workflows. The segment benefits from multiplexed panels such as Illumina's 500-gene TruSight Oncology Comprehensive kit, which condenses tumor profiling into a single run. In contrast, PCR systems, led by innovations like Seegene's dual-priming oligonucleotides, are projected to grow at 11.23% through 2030 as hospitals adopt rapid respiratory-pathogen panels that report within 80 minutes. Although microarrays and Sanger sequencing retain niche utility-validation and small gene targets respectively-laboratories increasingly deploy hybrid workstreams that pair NGS discovery with PCR confirmation. Falling reagent prices and integrated analytics platforms help smaller clinics launch in-house genomics, pushing the genetic testing market size for PCR-based tools wider even where capital budgets are constrained.
Sanger sequencing's accuracy keeps it relevant in confirmatory testing for hereditary cancer variants that require single-nucleotide discrimination. Fluorescence in situ hybridization remains indispensable for detecting oncogenic translocations in hematological malignancies. Yet the long-term trajectory clearly favors NGS and AI-optimized PCR as health systems prioritize comprehensive coverage, faster turnaround, and cost per megabase advantages. Vendor roadmaps also reveal converging technology stacks, such as ONT flowcell chemistries compatible with upstream PCR enrichment, pointing to an integrated future where sequencing modality choices become workflow agnostic.
The Genetic Testing Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Technology (Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and More ), by Application (Cancer Diagnosis & Prognosis, Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis, and More), by End User (Hospitals & Clinics, Diagnostic Laboratories and More), and Geography (North America, Europe and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America anchors the genetic testing market through well-funded healthcare systems, sophisticated payer frameworks, and an active M&A environment. Employer-sponsored genetic benefits now cover 44% of U.S. firms for family-history testing, with oncology panels seeing the strongest utilization uptick. Canada advances universal reimbursement pilots, while Mexico's private insurers slowly broaden coverage for hereditary cancer screens. Workforce shortages, however, remain acute: just 6% of rural residents live within a 30-minute drive of a certified genetic counselor, a distribution gap that limits equitable expansion.
Europe combines strong public-sector funding with rigorous data-protection oversight. The United Kingdom's GBP 650 million newborn sequencing investment not only funds clinical roll-out but also augments the UK Biobank resource-already the world's largest linked phenome-genome dataset nhs.uk. Germany and France integrate multigene oncology panels into statutory insurance, whereas Italy channels PNRR recovery funds into regional genomic labs. GDPR's consent mandates pose compliance hurdles, yet they also create a high-trust environment that encourages citizen participation in longitudinal research.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing territory for the genetic testing market, driven by population genomics programs across China, India, Singapore, and Australia. China's hospital networks routinely deploy combined germline and somatic assays, exemplified by a 768-patient hearing-loss study that achieved a 65.2% diagnostic yield with whole-exome sequencing. India's 10,000-genome dataset supplies ancestry-aligned references that significantly improve variant pathogenicity calls. Singapore's mid-2025 nationwide screen for familial hypercholesterolemia demonstrates how compact nations can integrate genomics into preventive cardiology workflows. Japan and South Korea supplement regional capacity with advanced assay development, while Australia grapples with clinician education gaps that slow comprehensive uptake outside tertiary centers.
- 23andMe
- BGI
- Illumina
- Myriad Genetics
- Roche
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- QIAGEN
- Laboratory Corporation of America (Labcorp)
- Quest Diagnostics
- Natera
- Invitae
- Ambry Genetics
- Color Health
- Centogene
- Eurofins
- NeoGenomics
- GeneDx
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- Genetron Health
- Exact Sciences (Genomic Health)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Integration of genomic sequencing into standard prenatal care
- 4.2.2 AI-powered variant interpretation reducing turnaround time
- 4.2.3 Falling costs of whole-genome sequencing below US$100
- 4.2.4 Oncology companion-diagnostic mandates by regulators
- 4.2.5 Employer-sponsored genetic-benefit plans in the U.S.
- 4.2.6 Bio-bank driven population genomic projects in Asia
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Data-privacy legislation proliferation (GDPR, CCPA, India DPDP)
- 4.3.2 Reimbursement gaps for multigene panels outside oncology
- 4.3.3 Shortage of certified genetic counsellors
- 4.3.4 Persistent scepticism over DTC health-risk tests' clinical utility
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Technology (Value)
- 5.1.1 Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- 5.1.2 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- 5.1.3 Microarray
- 5.1.4 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
- 5.1.5 Sanger Sequencing
- 5.1.6 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Application (Value)
- 5.2.1 Cancer Diagnosis & Prognosis
- 5.2.2 Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis
- 5.2.3 Neurological Disorder Diagnosis
- 5.2.4 Ancestry & Wellness
- 5.2.5 Other Applications
- 5.3 By End User (Value)
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.3.2 Diagnostic Laboratories
- 5.3.3 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.3.4 Direct-to-Consumer Companies
- 5.3.5 Other End Users
- 5.4 By Geography (Value)
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 Australia
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 GCC
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 23andMe
- 6.3.2 BGI Group
- 6.3.3 Illumina
- 6.3.4 Myriad Genetics
- 6.3.5 F. Hoffmann-La Roche
- 6.3.6 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.3.7 QIAGEN
- 6.3.8 Laboratory Corporation of America (Labcorp)
- 6.3.9 Quest Diagnostics
- 6.3.10 Natera
- 6.3.11 Invitae
- 6.3.12 Ambry Genetics
- 6.3.13 Color Health
- 6.3.14 Centogene
- 6.3.15 Eurofins Scientific
- 6.3.16 NeoGenomics
- 6.3.17 GeneDx
- 6.3.18 Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- 6.3.19 Genetron Health
- 6.3.20 Exact Sciences (Genomic Health)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & unmet-need assessment




