PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850186

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850186
China Diabetes Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The China diabetes devices market is valued at USD 3.88 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 5.74 billion by 2030, reflecting an 8.18% CAGR.
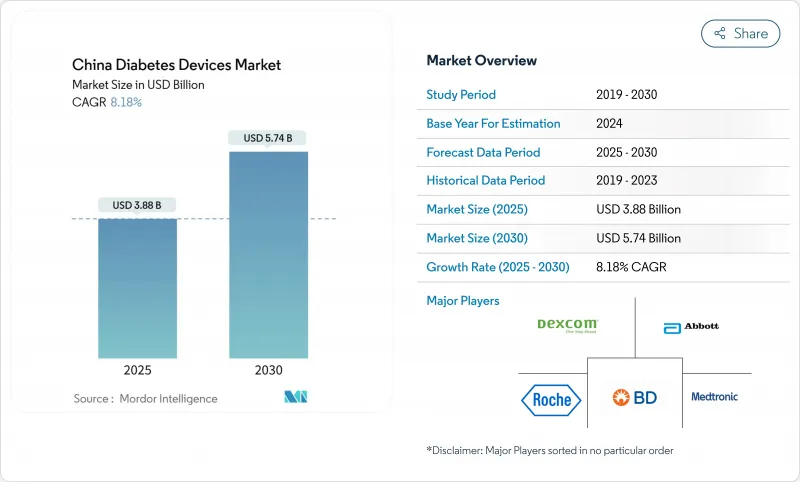
Growth is underpinned by the country's 148 million-strong adult diabetic population in 2024 and by sustained policy support through the Healthy China 2030 program, which prioritizes chronic disease management. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are displacing traditional strip-based testing, aided by domestic third-generation sensors that combine accuracy with price advantages. Broader reimbursement for diabetes medicines is spurring parallel demand for monitoring and delivery devices, while digital therapeutics platforms are improving clinical outcomes in underserved regions. Capital investment by multinational and local firms into production and R&D facilities further strengthens the supply base for the China diabetes devices market.
China Diabetes Devices Market Trends and Insights
Rising Diabetes Prevalence and Aging Population
Diabetes prevalence in China rose from below 1% in 1980 to 12.4% in 2018, and cases are projected to climb to 164 million by 2030. Urbanisation, sedentary lifestyles and an expanding older population-over 75% of older adults have at least one chronic disease-continue to enlarge the addressable pool of device users. Annual economic costs are expected to exceed RMB 360 billion within the decade, prompting both public and private investment in efficient monitoring and delivery technologies.
Government Healthcare Reforms and Insurance Coverage Expansion
National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) updates in 2024 added 15 diabetes drugs, immediately lowering out-of-pocket costs and stimulating complementary device uptake . Inclusion of dorzagliatin led to sales of RMB 255.9 million in 2024, up 234% year-on-year . Capitation payment pilots in rural counties have improved prescribing standards and redirect financial incentives toward preventive monitoring.
High Out-of-Pocket Costs for Advanced Devices
Continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pump systems remain expensive despite broader reimbursement. Annual medication costs already average RMB 12,186 (USD 1,676) for older diabetics in Beijing, leaving little room for device upgrades . Pump penetration stands at a modest 0.5%, underlining affordability constraints versus developed markets.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technological Advancements in Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Delivery
- Growing Affordability of Domestic Devices
- Limited Patient Education and Training for Device Use
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Monitoring Devices generated 60.21% of revenue in 2024, cementing their status as the backbone of the China diabetes devices market. CGM sales are forecast to jump from RMB 899 million in 2020 to RMB 5.032 billion by 2030, registering an 18.8% CAGR. The China diabetes devices market size for Monitoring Devices therefore expands faster than the overall market, driven by consumer preference for real-time insights and by clinical evidence linking CGM adoption to improved HbA1c. Self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) devices remain essential for routine testing, especially in cost-conscious cohorts, but their growth plateaus as CGM costs fall.
Management Devices are set to grow at 9.10% CAGR between 2025 and 2030. Insulin pump penetration is expected to rise from 0.5% to 1.5% by 2030, still below developed-market norms but indicative of latent demand. Foreign brands presently hold more than 70% share, yet local manufacturers have begun integrating Bluetooth connectivity and CGM compatibility into pumps, positioning for quicker gains. In select hospital pilots, pairing sensor-augmented pumps with algorithm-guided dosing cut hypoglycemic episodes by double-digit percentages, further stimulating adoption.
The China Diabetes Devices Market Report is Segmented Into Device Category (Management Devices and Monitoring Devices), End User (Hospital and Clinics, Home-Care Settings, Retail Pharmacies & Diabetes Centers), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and E-Commerce / Online Pharmacies). The Market Provides the Value (in USD) and (in Units) for the Above-Mentioned Segments.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Roche
- Abbott Laboratories
- Sinocare
- Yuwell-Jiangsu Yuyue Medical
- Medtronic
- Dexcom
- Johnson & Johnson
- Novo Nordisk
- Beckton Dickinson
- Ascensia
- Arkray
- MicroTech Medical
- Lepu Medical
- Tianjin MinFound Medical
- Sanofi
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Diabetes Prevalence and Aging Population in China
- 4.2.2 Government Healthcare Reforms and Insurance Coverage Expansion
- 4.2.3 Technological Advancements in Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Delivery
- 4.2.4 Growing Affordability of Domestic Devices
- 4.2.5 Increasing Adoption of Digital Health and Telemedicine
- 4.2.6 Expanding Private and Public Hospital Infrastructure
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Out-of-Pocket Costs for Advanced Devices
- 4.3.2 Limited Patient Education and Training for Device Use
- 4.3.3 Stringent and Lengthy Regulatory Approval for Novel Devices
- 4.3.4 Competition from Low-Cost Unregulated Products
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory & Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Device Category
- 5.1.1 Monitoring Devices
- 5.1.1.1 Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose (SMBG) Devices
- 5.1.1.1.1 Glucometers
- 5.1.1.1.2 Test Strips
- 5.1.1.1.3 Lancets
- 5.1.1.2 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Devices
- 5.1.1.2.1 Sensors
- 5.1.1.2.2 Durables (Receivers & Transmitters)
- 5.1.2 Management Devices
- 5.1.2.1 Insulin Delivery Devices
- 5.1.2.1.1 Insulin Pump Devices
- 5.1.2.1.2 Insulin Disposable Pens
- 5.1.2.1.3 Insulin Cartridges in Re-usable Pens
- 5.1.2.1.4 Insulin Syringes & Jet Injectors
- 5.1.1 Monitoring Devices
- 5.2 By End User
- 5.2.1 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.2.2 Home-Care Settings
- 5.2.3 Retail Pharmacies & Diabetes Centers
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.3.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.3.3 E-commerce / Online Pharmacies
6 Market Indicators
- 6.1 Type-1 Diabetes Population
- 6.2 Type-2 Diabetes Population
7 Competitive Landscape
- 7.1 Market Concentration
- 7.2 Strategic Moves
- 7.3 Market Share Analysis
- 7.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 7.4.1 Roche Diagnostics
- 7.4.2 Abbott Laboratories
- 7.4.3 Sinocare Inc.
- 7.4.4 Yuwell-Jiangsu Yuyue Medical
- 7.4.5 Medtronic plc
- 7.4.6 Dexcom Inc.
- 7.4.7 Johnson & Johnson (LifeScan)
- 7.4.8 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.4.9 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 7.4.10 Ascensia Diabetes Care
- 7.4.11 ARKRAY Inc.
- 7.4.12 MicroTech Medical
- 7.4.13 Lepu Medical Technology
- 7.4.14 Tianjin MinFound Medical
- 7.4.15 Sanofi
8 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 8.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




