PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850296

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850296
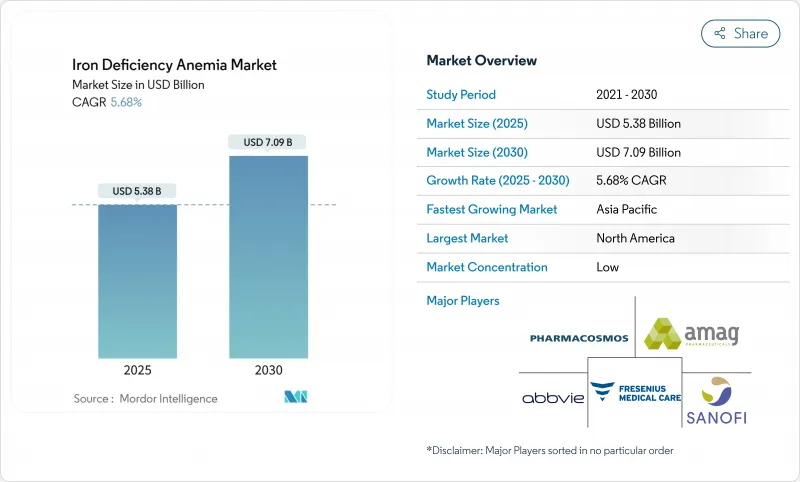
Iron Deficiency Anemia - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Iron Deficiency Anemia Market size is estimated at USD 5.38 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 7.09 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.68% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Strong clinical evidence for intravenous iron in heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and oncology, coupled with widespread screening programs, continues to lift demand. Record numbers of women of reproductive age and children now meet diagnostic criteria for deficiency, and this epidemiological pressure is translating directly into higher treatment volumes. Hospitals are favoring single-visit total-dose infusions that reduce chair time, while digital platforms are guiding dose decisions remotely. On the supply side, new oral technologies that wrap iron in protective matrices are improving adherence and opening consumer-centric sales channels that were once inaccessible to parenteral products.
Global Iron Deficiency Anemia Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Global Iron-Deficiency Anemia Prevalence
Nearly 29.9% of women aged 15-49 and 39.8% of children worldwide live with iron deficiency anemia, equating to close to 2 billion potential therapy candidates. National surveys in South and Southeast Asia place prevalence for women as high as 63% in the Maldives. Rapid urbanisation has shifted diets toward lower iron density, while infectious disease loads continue to impede absorption. The resulting clinical burden sustains baseline demand for the iron deficiency anemia market, even before accounting for chronic disease comorbidities. Longer-term demographic trends indicate sustained growth in high-risk groups, meaning underlying prevalence will remain the most powerful volume driver across forecast years.
Integration of Iron Therapy into Standard Care Pathways for Chronic Diseases
Cardiology, nephrology, and oncology guidelines now mandate ferritin screening and proactive replenishment, materially enlarging the treated population. The IRONMAN trial confirmed significant haemoglobin gains among heart-failure patients receiving ferric derisomaltose versus standard care. Similar momentum is visible in oncology, where intravenous ferric carboxymaltose achieved 52.1% haemoglobin response in solid-tumour patients compared with 32.9% for usual care. These recommendations create predictable, protocol-driven purchasing that supports premium formulations and stabilises reimbursement.
Safety and Tolerability Concerns Discouraging Long-Term Adherence
Gastrointestinal side effects still cause dropout for legacy ferrous salts, and hypersensitivity events, though rare, remain front of mind with intravenous products. Real-world audits show hypersensitivity in 3.1% of ferric derisomaltose recipients. Advanced oral options such as ferric maltol reduce discontinuations to under 5%, yet payer awareness is still catching up. The development of nano-encapsulated and transdermal delivery systems aims to remove these tolerability hurdles, but until such formats scale, adverse-event reluctance will weigh on uptake.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Anemia-Elimination Programmes
- Digitalised IV-Dosing Protocols Reducing Clinic Time
- Stringent Pharmacovigilance for Parenteral Iron
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Parenteral iron delivered 61.32% of iron deficiency anemia market size in 2024, reflecting hospital reliance on total-dose infusions for severe cases. Total-dose options such as ferric carboxymaltose enable complete repletion in a single visit, which aligns with value-based care metrics that reward shorter length of stay. Ongoing hospital formulary expansions, alongside protocol integration for heart failure and oncology, anchor this dominance. However, raw-material tightness for ferric derisomaltose APIs has sparked selective shortages, highlighting latent vulnerability on the supply side.
Oral products post the swiftest expansion at a 7.54% CAGR. Ferric maltol and iron-whey-protein microspheres drive this upswing by slashing common gastrointestinal complaints that once undermined adherence. As adherence rates exceed 80% in recent trials, payers are reconsidering step-therapy rules that previously required failure on generic ferrous sulphate. This policy shift could accelerate volume migration toward premium oral brands over the forecast horizon, diversifying revenue streams inside the iron deficiency anemia market.
The Iron Deficiency Anemia Market is Segmented by Therapy Type (Oral Iron Therapy (Ferrous Salts, and More), and Parenteral Iron Therapy (Ferric Carboxymaltose, Ferric Derisomaltose and More)), Age Group (Pediatric, Adults and Geriatric), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Channels and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 37.45% of global revenue in 2024, buoyed by comprehensive reimbursement that covers both standard infusions and newer oral brands. Widespread adoption of single-visit ferric carboxymaltose and ferric derisomaltose regimens has reduced outpatient visits, freeing capacity in overstretched clinics. Canada's recent authorisation of ferric carboxymaltose for paediatric use extends addressability across the life course. Mexico's public-health insurers are piloting bundled anaemia management packages, though infrastructure limits infusion penetration outside metropolitan hubs.
Asia Pacific posts the fastest regional CAGR at 7.47%. Japan showcases sophisticated dosing algorithms that have shifted clinicians from saccharated ferric oxide to ferric carboxymaltose for efficiency gains. Australia's primary-care lobby estimates Medicare coverage for GP-led infusions could save USD 124 million in system costs, a proposal now under active review.
Europe maintains steady expansion on the back of guideline harmonisation and supply-security strategies that favour multiple API sources. Germany, France, and the Nordic markets deploy national registries to monitor infusion safety, reinforcing physician confidence in parenteral solutions. Eastern European countries, supported by EU health-equity funds, are scaling up paediatric supplement programs, creating new frontiers for the iron deficiency anemia market even as mature Western states focus on chronic-disease integration.
- Abbvie
- Akebia Therapeutics
- AMAG (-Covis)
- Daiichi Sankyo
- Pharmacosmos
- Sanofi
- Johnson & Johnson
- Fresenius SE
- Vifor Pharma
- Rockwell Medical
- Shield Therapeutics
- American Regent
- Nicholas Piramal
- Cosmo Pharma
- PharmaNutra
- Cipla
- Alkem Laboratories
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing global iron-deficiency anemia prevalence
- 4.2.2 Integration of iron therapy into standard care pathways for chronic diseases (CKD, oncology, obstetrics)
- 4.2.3 Government anaemia-elimination programmes
- 4.2.4 Digitalised IV-dosing protocols reducing clinic time
- 4.2.5 Emergence of trans-mucosal & transdermal delivery
- 4.2.6 Guideline shift to mandatory ferritin screening in HF surgery
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Safety and tolerability concerns (GI intolerance, hypersensitivity) discouraging long-term adherence
- 4.3.2 Stringent pharmacovigilance for parenteral iron
- 4.3.3 Diagnostic ambiguity between functional and absolute iron deficiency hindering appropriate therapy
- 4.3.4 API supply bottlenecks for ferric derisomaltose
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Therapy Type
- 5.1.1 Oral Iron Therapy
- 5.1.1.1 Ferrous salts
- 5.1.1.2 Ferric and polysaccharide complexes
- 5.1.1.3 Enhanced-absorption or lipophilic
- 5.1.2 Parenteral Iron Therapy
- 5.1.2.1 Ferric carboxymaltose
- 5.1.2.2 Ferric derisomaltose
- 5.1.2.3 Iron sucrose
- 5.1.2.4 Others
- 5.1.1 Oral Iron Therapy
- 5.2 By Age Group
- 5.2.1 Pediatric
- 5.2.2 Adults
- 5.2.3 Geriatric
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.3.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.3.3 Online Channels
- 5.3.4 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 Japan
- 5.4.4.3 India
- 5.4.4.4 Australia
- 5.4.4.5 South Korea
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 GCC
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.2 Akebia Therapeutics
- 6.3.3 AMAG (-Covis)
- 6.3.4 Daiichi Sankyo
- 6.3.5 Pharmacosmos
- 6.3.6 Sanofi
- 6.3.7 Johnson & Johnson
- 6.3.8 Fresenius SE
- 6.3.9 Vifor Pharma
- 6.3.10 Rockwell Medical
- 6.3.11 Shield Therapeutics
- 6.3.12 American Regent
- 6.3.13 Nicholas Piramal
- 6.3.14 Cosmo Pharma
- 6.3.15 PharmaNutra
- 6.3.16 Cipla
- 6.3.17 Alkem Labs
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




