PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850976

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850976
Asia-Pacific Ready-to-Eat Food - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Asia-Pacific ready-to-eat food market size stands at USD 227.54 billion in 2025 and is on course to reach USD 298.56 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.58% CAGR.
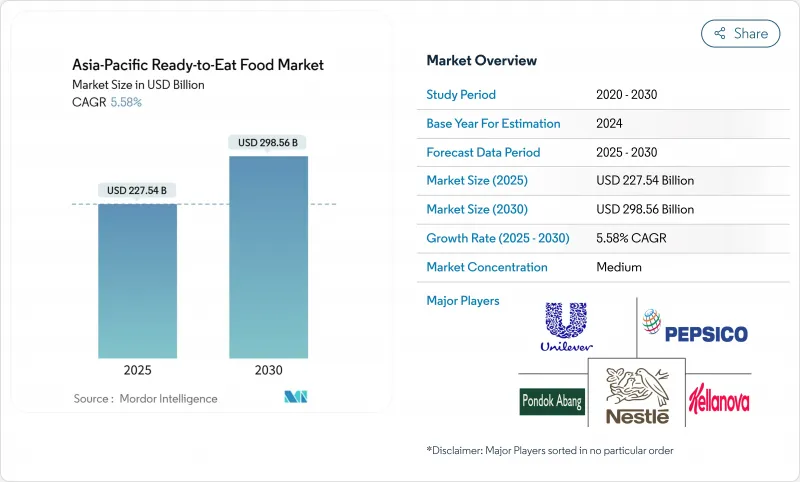
Rapid urbanization, expanding middle-income populations, and busier lifestyles underpin this steady climb, especially in metropolitan hubs where dual-earner families rely on convenient yet nutritious meal solutions. Manufacturers are responding with products that balance flavor, shelf life, and clean-label credentials, while retailers invest in technology-enabled cold chains to maintain quality during distribution. Digital commerce is reshaping consumer access as online platforms widen product choice and shorten delivery windows. In parallel, government incentives from China's infrastructure programs to India's Production Linked Incentive Scheme are catalyzing capacity upgrades across processing, packaging, and logistics.
Asia-Pacific Ready-to-Eat Food Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Popularity of Western Diets Is Encouraging Ready-to-Eat Food Adoption
Urban millennials and Gen Z are increasingly adopting Western meal formats, like single-serve entrees and breakfast bars, into their routines. Exposure to global cuisines through streaming media and travel has heightened demand for diverse flavors in the Asia-Pacific ready-to-eat (RTE) food market. Brands are localizing sauces and seasonings to suit regional tastes while ensuring convenience for time-conscious consumers. Economic growth, urbanization, and globalization in Asia have shifted diets from traditional staples to Western ones, featuring processed sauces, meats, and oils. The rise of dual-income households and longer work hours has boosted demand for quick Western-style meals like pizza and pasta. Local producers are innovating with Western and ethnic fusion RTE products to meet evolving consumer preferences.
Growth in Dual-Income Households Is Driving Demand for Time-Saving Meals
In the Asia-Pacific, the rise of dual-income households is driving demand for quick meal solutions that retain nutrition and taste. In Japan, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications reported 13 million dual-income households in 2024 . This trend is prominent in urban areas, where long commutes and demanding jobs limit time for traditional cooking. Changing gender roles and increased female workforce participation further fuel this demand. Companies are introducing premium ready-to-eat meals, often using locally sourced ingredients and traditional recipes, to rival home-cooked dishes. Consumers are willing to pay a premium for convenient, high-quality options, supported by rising incomes and a shift in cooking perceptions, especially among younger urban professionals.
Growing Health Consciousness Is Limiting the Appeal of Processed Ready-To-Eat Food
In the Asia-Pacific region, growing health consciousness is challenging traditional ready-to-eat food products, especially those seen as overly processed or less nutritious than fresh options. This trend, driven by access to nutritional information, social media influence, and government health campaigns, emphasizes the link between diet and chronic disease prevention. Consumers now scrutinize ingredient lists, nutritional data, and processing methods, demanding transparency that many traditional products struggle to provide. Products high in sodium, sugar, or artificial ingredients conflict with evolving health standards. Companies are responding by reformulating products, reducing sodium, removing artificial preservatives, and adding functional ingredients like probiotics, fiber, and plant-based proteins. However, reformulation requires significant research and development investment and must balance health-focused branding with taste profiles critical for consumer acceptance.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge In Organic and Vegan Ready-To-Eat Food Launches Boosts Its Demand
- Product Innovation and Variety Are Attracting a Broader Consumer Base
- Concerns Over Preservatives and Additives Are Affecting Consumer Trust
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Ready meals contributed 39.12% of the Asia-Pacific ready-to-eat food market in 2024, reflecting the broad acceptance of full-plate solutions that only require reheating. Packaging innovations, from microwave-ready trays to self-heating pouches, reinforce leadership by offering restaurant-style experiences at home. Instant soups and snacks, though smaller in absolute terms, are on track to post an 8.05% CAGR from 2025 to 2030 as consumers seek nutritious, portion-controlled options for intermittent snacking occasions. Functional enrichments, such as high-protein lentil bases or collagen-fortified broths, give these lines a health halo that resonates strongly with young professionals and fitness enthusiasts across the Asia-Pacific ready-to-eat food market.
The diversification of cereals and breakfast bars aligns with the increasing demand driven by early-morning time constraints. Premium breakfast SKUs now incorporate organic oats, reduced sugar, and probiotic infusions, enabling higher average selling prices and maintaining strong profit margins. Baked goods continue to gain traction by leveraging localized flavors, such as pandan-flavored cakes in Southeast Asia and matcha sponge rolls in Japan. In contrast, meat-based ready meals face growing environmental scrutiny, prompting processors to adopt hybrid meat-plant formulations.
The APAC Ready-To-Eat Food Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Instant Breakfast/Cereals, Instant Soups and Snacks, and More), Distribution Channel (Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Convenience/Grocery Stores, and More), and Country (China, Japan, Australia, India, Indonesia, South Korea, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Nestle S.A.
- PepsiCo Inc.
- Unilever PLC
- Kellanova
- General Mills Inc.
- McCain Foods Ltd.
- Beyond Meat Inc.
- Ajinomoto Co. Inc.
- CJ CheilJedang Corp.
- Nissin Foods Holdings
- Samyang Foods Co.
- Maruha Nichiro Corp.
- Thai President Foods PLC
- Kraft Heinz Co.
- Marico Ltd.
- ITC Ltd.
- Tingyi (Cayman Islands) Holding Corp
- Uni-President Enterprises Corp
- Orion Corporation
- MTR Foods Pvt. Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Popularity of Western Diets Is Encouraging Ready-To-Eat Food Adoption
- 4.2.2 Growth In Dual-Income Households Is Driving Demand for Time-Saving Meals
- 4.2.3 Surge In Organic and Vegan Ready-To-Eat Food Launches Boosts Its Demand
- 4.2.4 Product Innovation and Variety Are Attracting a Broader Consumer Base
- 4.2.5 Busy Lifestyles and Long Working Hours Are Promoting Convenient Eating Habits
- 4.2.6 Growth In E-Commerce Platforms Is Fuelling Online Ready-To-Eat Food Purchases
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Growing Health Consciousness Is Limiting the Appeal of Processed Ready-To-Eat Food
- 4.3.2 Concerns Over Preservatives and Additives Are Affecting Consumer Trust
- 4.3.3 Inconsistent Cold Chain Logistics Hinder Product Distribution in Rural Areas
- 4.3.4 Cultural Preference for Freshly Cooked Meals Reduces Ready-To-Eat Food Adoption
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE, USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Instant Breakfast/Cereals
- 5.1.2 Instant Soups and Snacks
- 5.1.3 Ready Meals
- 5.1.4 Baked Goods
- 5.1.5 Meat Products
- 5.1.6 Other Product Types
- 5.2 By Distribution Channel
- 5.2.1 Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
- 5.2.2 Convenience/Grocery Stores
- 5.2.3 Speciality Stores
- 5.2.4 Online Retail Stores
- 5.2.5 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 China
- 5.3.2 India
- 5.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.4 Australia
- 5.3.5 Indonesia
- 5.3.6 South Korea
- 5.3.7 Thailand
- 5.3.8 Singapore
- 5.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nestle S.A.
- 6.4.2 PepsiCo Inc.
- 6.4.3 Unilever PLC
- 6.4.4 Kellanova
- 6.4.5 General Mills Inc.
- 6.4.6 McCain Foods Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Beyond Meat Inc.
- 6.4.8 Ajinomoto Co. Inc.
- 6.4.9 CJ CheilJedang Corp.
- 6.4.10 Nissin Foods Holdings
- 6.4.11 Samyang Foods Co.
- 6.4.12 Maruha Nichiro Corp.
- 6.4.13 Thai President Foods PLC
- 6.4.14 Kraft Heinz Co.
- 6.4.15 Marico Ltd.
- 6.4.16 ITC Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Tingyi (Cayman Islands) Holding Corp
- 6.4.18 Uni-President Enterprises Corp
- 6.4.19 Orion Corporation
- 6.4.20 MTR Foods Pvt. Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




