PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850981

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850981
Gigabit Ethernet Test Equipment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
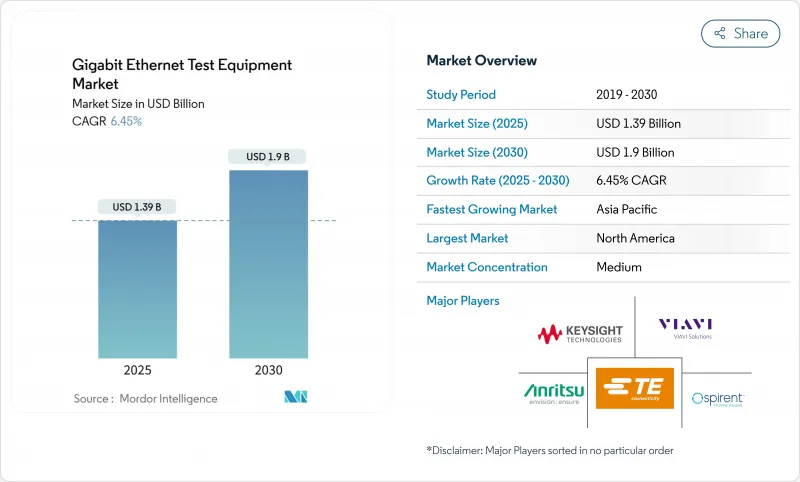
The Gigabit Ethernet test equipment market reached USD 1.39 billion in 2025 and is forecast to climb to USD 1.90 billion by 2030, advancing at a 6.45% CAGR.
Rising adoption of artificial intelligence workloads is redefining bandwidth expectations, forcing validation teams to move beyond 400G and embrace emerging 800G and 1.6T standards. Data center operators are reallocating budgets from legacy bit error rate tools to high-precision solutions that evaluate packet spray, forward error correction, and RoCEv2 latency under real-world congestion. Hyperscalers now request fully automated test beds that blend traffic generation, network emulation, and machine-learning-driven analytics to shorten development cycles. Supply bottlenecks for PAM4 optics and a shortage of 224 Gbps channel-design experts keep delivery lead times long and price points high, yet vendors that can guarantee early access to 1.6T capability are commanding premium contracts.
Global Gigabit Ethernet Test Equipment Market Trends and Insights
AI Cluster Infrastructure Drives 800G Testing Demand
Key Highlights
- Artificial intelligence training pushes bandwidth requirements beyond conventional 400G, compelling operators to adopt 800G and 1.6T links that demand fresh validation strategies. Current clusters need 1 Tbps per xPU, stressing SerDes designs that shift from NRZ to PAM4 modulation, which in turn mandates eye-opening precision for signal-to-noise ratio analysis. Vendors now bundle high-speed oscilloscopes with automated de-embedding software so engineers can characterize sub-10-ps unit intervals in minutes rather than days. The Ultra Ethernet Consortium is finalizing v1.0 specifications that extend beyond IEEE 802.3, adding congestion management tests never seen in legacy Ethernet. Early movers that deliver 1.6T capability are winning multi-year framework deals with hyperscalers eager to future-proof AI fabrics. These projects accelerate revenue for companies able to link optics, traffic generation, and analytics into a single orchestration layer.
Cloud Services Expansion Accelerates Multi-Speed Testing
Cloud providers deploy mixed 100G, 400G, and 800G topologies to balance performance and cost across variable workloads, creating a need for test rigs that validate several speeds concurrently. Forward error correction, particularly RS-FEC, is essential at those rates, so solutions must monitor real-time parity blocks without masking latent defects. Emulation engines now replay days of traffic logs to reproduce microburst congestion while maintaining sub-microsecond latency metrics. Operators request programmable APIs that integrate with CI/CD toolchains, enabling daily regression of network upgrades. The result is rising demand for virtualized test labs that cut hardware capex yet still provide deterministic performance baselines.
Technical Expertise Shortage Constrains Market Expansion
Moving from NRZ to PAM4 demands engineers competent in de-skewing, symbol error plotting, and 224 Gbps channel modeling, skills still rare across global labor pools. Many service providers rely on automated algorithms to interpret eye height and jitter budgets, yet complex failures still need human insight. Fiber inspection campaigns such as "Inspect Before You Connect" show how deficit skills inflate installation error rates. Training pipelines lag behind technology roadmaps, compelling vendors to embed AI-driven wizards that configure instruments based on minimal user input. Nevertheless, advanced troubleshooting of PAM4 crosstalk, skew, and FEC margin remains a manual discipline, keeping project timelines vulnerable to talent shortages.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Manufacturing Ethernet Adoption Creates Industrial Testing Opportunities
- Legacy Infrastructure Upgrades Drive Multi-Gigabit Testing
- Measurement Accuracy Limitations Impede High-Speed Validation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The 10 GbE category retained 42% of the Gigabit Ethernet test equipment market share in 2024, underscoring its entrenched presence in enterprise switching backbones. Yet 800 GbE and 1.6 TbE rigs are set to grow at 21.5% CAGR to 2030, the fastest pace of any speed grade, fueled by AI cluster architectures that need line-rate validation at 224 Gbps per lane. Keysight's AresONE platform streams 6.4 Tbps of test traffic, marking a leap that positions the Gigabit Ethernet test equipment market size for ultra-high-speed gear at USD 490 million by 2030, according to Keysight. Meanwhile 25/40/50 GbE and 100 GbE serve as cost-efficient stepping-stones, especially where legacy optics ecosystems lower migration risk. Semiconductor vendors such as Marvell accelerate the shift by sampling 3 nm PAM4 DSPs that drop module power by 20%, extending cooling envelopes inside dense chassis.
Buyers weigh upgrade timing against standards maturity. 400 GbE enjoys mature RS-FEC profiles, so projects chasing rapid returns still favor it. Conversely, engineering labs evaluating 1.6 T are ordering mixed-speed chassis that combine 800 G blades for immediate needs and empty cages ready for future 1.6 T pluggables. This flexibility stabilizes capital planning while protecting early adopters from obsolescence. As hyperscalers roll out fabric upgrades in six-month sprints, vendors that ship field-upgradeable hardware and perpetual software licenses gain recurring revenue streams. The transition compresses product lifecycles, shifting competitive focus from hardware bill-of-materials to programmable feature velocity.
Telecommunications captured 36.5% of 2024 revenue due to 5G backhaul rollouts, yet data centers and cloud providers are expanding at an 18% CAGR to 2030, overtaking telcos in absolute spending by 2027. AI workload density drives data centers to validate lossless packet spraying, sub-microsecond jitter, and RoCEv2 congestion control concurrently, all of which exceed traditional telco metrics. Automotive and transport OEMs ramp Ethernet compliance to support driver assistance and autonomous stacks, creating demand for rugged oscilloscopes and EMI chambers capable of 10GBASE-T1 characterization.
Meanwhile, manufacturing outfits accelerate Ethernet-APL pilots within hazardous zones, requiring intrinsically safe testers that double as power loop analyzers. A&D integrators need equipment that withstands vibration, temperature extremes, and electromagnetic pulse, compelling suppliers to adapt military-grade enclosures. Utilities and healthcare specify deterministic fail-safe protocols, pushing test plans to verify zero-loss protection switching and cyber-hardened firmware. These cross-sector nuances pressure vendors to offer modular platforms that slot vertical-specific compliance packages on demand, a strategy that tempers R&D overhead while addressing divergent regulatory frameworks.
The Gigabit Ethernet Test Equipment Market Report is Segmented by Type (1 GbE, 10 GbE, and More), End-User Industry (Telecommunications, Data Centers and Cloud, and More), Application (R&D/Lab, Manufacturing/Production, and More), Test Type (Functional / Traffic Generation, Performance / Stress, Compliance / Conformance, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
North America holds 33% revenue thanks to concentrated semiconductor R&D and aggressive AI cluster deployments that mandate 800G qualification in record time. United States cloud providers anchor most orders, but Canada gains traction through broadband revitalization and industrial Ethernet upgrades. Mexico leverages nearshoring trends to expand automotive harness manufacturing, raising demand for T1 compliance kits. Low energy costs in some states attract additional data center builds, yet the high power draw of 800G rigs prompts sustainability audits that may influence procurement cycles.
Asia Pacific leads growth at 10.25% CAGR on the back of China's hyperscale expansion and localized 1.6 T optics supply chains. Japan's auto sector champions deterministic Ethernet stacks that require stringent EMC validation, while Korea pushes semiconductor fabs into 3 nm class, needing ultra-fast jitter and crosstalk probes. ASEAN states deploy 5G backhaul and smart factory pilots, generating orders for multi-rate handheld analyzers. India's policy incentives spur telco equipment manufacturing and software defined network labs, though patchy infrastructure and a talent shortfall temper near-term adoption.
Europe charts steady gains with German OEMs formalizing in-vehicle Ethernet test plans and industrial operators embracing Ethernet-APL inside process plants. The United Kingdom modernizes fiber backbone networks, fueling demand for portable OTDRs and BERTs. France and Spain invest in renewable energy grid upgrades that require deterministic sub-station Ethernet testing. The Middle East channels oil revenues into greenfield data centers in the Gulf, while African miners commission ruggedized PoE testers for harsh environments. South America remains modest but stable, driven by Brazilian telco upgrades and Argentine automotive wire harness exports.
- Keysight Technologies Inc.
- Anritsu Corp.
- VIAVI Solutions Inc.
- Spirent Communications plc
- EXFO Inc.
- Rohde and Schwarz GmbH and Co KG
- Teledyne LeCroy (Xena)
- Yokogawa Test and Measurement
- VeEX Inc.
- GL Communications Inc.
- Trend Networks
- GigaNet Systems
- Xinertel Technology
- Apposite Technologies
- NetScout Systems Inc.
- Te Connectivity Ltd.
- Aquantia (Marvell)
- GAO Tek Inc.
- IDEAL Industries Inc.
- Veryx Technologies
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growth in mobile backhaul
- 4.2.2 Adoption of cloud services and big data
- 4.2.3 Increased Ethernet use in manufacturing
- 4.2.4 2.5 / 5 GbE upgrades on legacy cabling
- 4.2.5 AI cluster demand for 800G/1.6T testing
- 4.2.6 RoCEv2-driven ultra-low-latency validation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Lack of technical expertise
- 4.3.2 Complex measurement accuracy limits
- 4.3.3 Energy and thermal constraints in 800G rigs
- 4.3.4 Supply-chain bottlenecks for PAM-4 optics
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 1 GbE
- 5.1.2 10 GbE
- 5.1.3 25/40/50 GbE
- 5.1.4 100 GbE
- 5.1.5 400 GbE
- 5.1.6 800 GbE and 1.6 TbE
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Telecommunications
- 5.2.2 Data Centers and Cloud
- 5.2.3 Manufacturing
- 5.2.4 Automotive and Transport
- 5.2.5 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.2.6 Others (Utilities, Healthcare)
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 RandD/Lab
- 5.3.2 Manufacturing/Production
- 5.3.3 Field Service and Installation
- 5.3.4 Certification and Compliance
- 5.4 By Test Type
- 5.4.1 Functional / Traffic Generation
- 5.4.2 Performance / Stress
- 5.4.3 Compliance / Conformance
- 5.4.4 Network Emulation
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 UAE
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Keysight Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.2 Anritsu Corp.
- 6.4.3 VIAVI Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.4 Spirent Communications plc
- 6.4.5 EXFO Inc.
- 6.4.6 Rohde and Schwarz GmbH and Co KG
- 6.4.7 Teledyne LeCroy (Xena)
- 6.4.8 Yokogawa Test and Measurement
- 6.4.9 VeEX Inc.
- 6.4.10 GL Communications Inc.
- 6.4.11 Trend Networks
- 6.4.12 GigaNet Systems
- 6.4.13 Xinertel Technology
- 6.4.14 Apposite Technologies
- 6.4.15 NetScout Systems Inc.
- 6.4.16 Te Connectivity Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Aquantia (Marvell)
- 6.4.18 GAO Tek Inc.
- 6.4.19 IDEAL Industries Inc.
- 6.4.20 Veryx Technologies
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




