PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851055

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851055
China Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The China Waste Management Market is valued at USD 177 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 238 billion by 2030, advancing at a 6.10% CAGR.
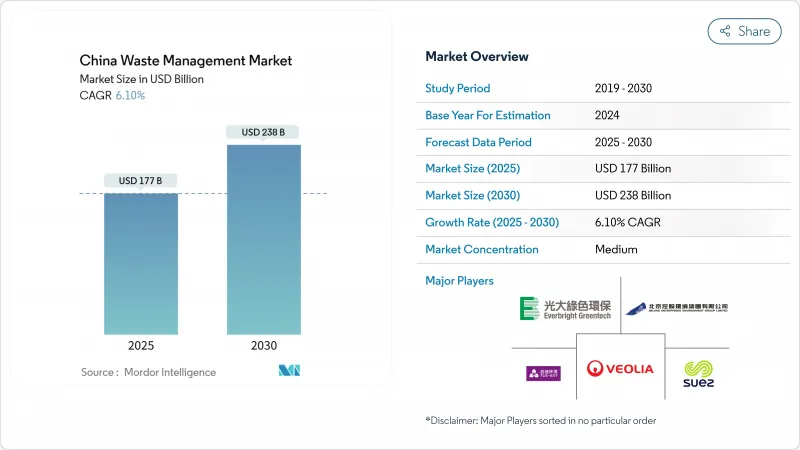
Policy commitments embedded in the Beautiful China blueprint and the national carbon-neutrality timetable are converting waste streams into revenue sources, as shown by waste-to-energy plants that now account for almost half of global installed capacity. Urbanization in tier-2 and tier-3 cities, corporate ESG mandates, and capital-market appetite for environmental public-private partnerships are reinforcing steady demand for integrated solutions. Standardized frameworks introduced through the zero-waste city program are improving project bankability, while digital technologies such as AI-enabled route planning and blockchain waste tracking strengthen operational performance. International expansion by domestic operators into Southeast Asia and the Middle East reveals a shift from a purely municipal service model toward an export-oriented, technology-rich resource recovery industry.
China Waste Management Market Trends and Insights
Expansion of Waste-to-Energy Capacity Backed by Feed-in Tariffs
More than 1,010 incineration plants form almost half of global capacity, yet many run below design load because of uneven feedstock supply. The 2025 reform moves feed-in tariffs toward market-based pricing while integrating green electricity certificates. Facilities achieving 70.9% thermal efficiency show payback periods near 4.8 years, enabling profitability with limited subsidies. Overcapacity is driving Chinese firms to invest in Vietnam and the Gulf states, exporting turnkey plants and O&M expertise.
Urbanization-driven MSW Volume Surge in Tier-2 and Tier-3 Cities
Rapid migration is lifting municipal solid waste output faster than infrastructure can keep pace. The 2024 National Development and Reform Commission report confirms 90% rural collection coverage, yet urbanizing districts still face capacity shortfalls. Demand is rising for scalable, asset-light systems that combine smart bins with modular transfer stations. Central and Southern cities are adopting waste-to-energy as a dual solution for waste and electricity, supported by a national goal of 100% safe disposal in all urban areas by 2030. Technology suppliers benefit from contracts that bundle equipment with digital O&M services, accelerating deployment cycles and reducing upfront capital risks.
Local-Government Fiscal Constraints Limiting PPP Payments
Budget pressures restrict the ability of mid-sized cities to guarantee PPP annuities, delaying project execution and raising counterparty risk. Developers respond with asset-light service models and revenue-sharing arrangements that reduce municipal cash outlay yet preserve service standards. Blended-finance vehicles incorporating green bonds and carbon credits are emerging to close funding gaps.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate ESG Mandates Driving Industrial Waste Outsourcing
- Zero-Waste City Program Scaling Nationwide
- Community Opposition to Incinerator Siting in Dense Provinces
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Residential waste contributed 40.8% of the Chinese waste management market in 2024, cementing its role as the backbone for collection network planning. Continuous urban household formation and rising consumer spending push bin-to-truck volumes upward, compelling municipalities to deploy IoT-enabled smart bins that trigger pickups only when 80% full, lifting route efficiency by 30%. Commercial waste, propelled by e-commerce packaging and food delivery trends, is forecast to register an 11.6% CAGR to 2030, the fastest among all sources. Retail fulfillment centers in Guangdong and Jiangsu have already contracted third-party operators for dedicated cardboard baling and plastics shredding, illustrating how service specialization follows waste-stream concentration.
Enhanced residential segregation rules require four-stream sorting that separates recyclables, food, hazardous, and residual waste at the doorstep. This regulatory push spurs demand for color-coded container fleets and AI vision systems that verify sorting accuracy at transfer stations. Urban neighborhood PPPs bundle collection, outreach, and data reporting under single contracts, creating multi-year revenue visibility for private firms. In parallel, industrial clusters outsource hazardous waste management to certified handlers offering cradle-to-grave manifest traceability, expanding service scope beyond household waste.
The Chinese Waste Management Market Report is Segmented by Source (Residential, Commercial, and More), by Service Type (Disposal/Treatment and More), by Waste Type (Municipal Solid Waste, Industrial Hazardous Waste, and More), and by Region (Eastern China, Northern China, and More). The Report Offers Market Size and Forecasts in Value (USD) for all the Above Segments.
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Veolia Environment SA (Veolia China)
- China Everbright Environment Group Ltd.
- Suez SA (SUEZ NWS)
- Beijing Enterprises Environment Group Ltd.
- Tus-Sound Environmental Resources Co., Ltd.
- Capital Environment Holdings Ltd.
- Canvest Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd.
- Grandblue Environment Co., Ltd.
- Dynagreen Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd.
- Shanghai Environment Group Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen Energy Environmental Co., Ltd.
- China Jinjiang Environment Holding Co., Ltd.
- Weiming Environmental Protection Co., Ltd.
- CITIC Envirotech Ltd.
- Sound Global Ltd.
- Guangxi Bossco Environmental Protection Co., Ltd.
- Hangzhou Jinjiang Group Co., Ltd.
- Anhui Shengyun Environment-Protection Group Co., Ltd.
- C&G Environmental Protection Holdings Ltd.
- Resou Resources Recovery Co., Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Urbanization-Driven MSW Volume Surge in Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities
- 4.2.2 Zero-Waste City Pilot Program Scaling Nationwide
- 4.2.3 Expansion of Waste-to-Energy Capacity Backed by Feed-in Tariffs
- 4.2.4 Corporate ESG Mandates Driving Industrial Waste Outsourcing
- 4.2.5 E-commerce Packaging Waste & Single-Use Plastic Ban Enforcement
- 4.2.6 Capital-Market Preference for Environmental PPPs Lowering Cost of Capital
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Local-Government Fiscal Constraints Limiting PPP Payments
- 4.3.2 Community Opposition to Incinerator Siting in Dense Provinces
- 4.3.3 SME Non-Compliance with Hazardous-Waste Manifest System
- 4.3.4 Fragmented Recycling Logistics Inflating Reverse-Haul Costs
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Logistics Support & Development in Chinese Waste Management
- 4.9 Strategies of Rising Start-ups in Chinese Waste Management
- 4.10 Technological Innovation in Effective Waste Management
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, In USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Source
- 5.1.1 Residential
- 5.1.2 Commercial (Retail, Office, etc.)
- 5.1.3 Industrial
- 5.1.4 Medical (Health and Pharmaceutical)
- 5.1.5 Construction & Demolition
- 5.1.6 Others (Institutional, Agricultural, etc.)
- 5.2 By Service Type
- 5.2.1 Collection, Trasportation, Sorting & Seggregation
- 5.2.2 Disposal / Treatment
- 5.2.2.1 Landfill
- 5.2.2.2 Recycling & Resource Recovery
- 5.2.2.3 Incineration & Waste-to-Energy
- 5.2.2.4 Others (Chemical Treatment, Composting, etc.)
- 5.2.3 Others (Consulting, Audit & Training, etc.)
- 5.3 By Waste Type
- 5.3.1 Municipal Solid Waste
- 5.3.2 Industrial Hazardous Waste
- 5.3.3 E-waste
- 5.3.4 Plastic Waste
- 5.3.5 Biomedical Waste
- 5.3.6 Construction & Demolition Waste
- 5.3.7 Agricultural Waste
- 5.3.8 Other Specialized Waste (Radio Active, etc.)
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 Eastern China
- 5.4.2 Northern China
- 5.4.3 Central China
- 5.4.4 Southern China
- 5.4.5 Others
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Veolia Environment SA (Veolia China)
- 6.4.2 China Everbright Environment Group Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Suez SA (SUEZ NWS)
- 6.4.4 Beijing Enterprises Environment Group Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Tus-Sound Environmental Resources Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Capital Environment Holdings Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Canvest Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Grandblue Environment Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Dynagreen Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Shanghai Environment Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Shenzhen Energy Environmental Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.12 China Jinjiang Environment Holding Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Weiming Environmental Protection Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.14 CITIC Envirotech Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Sound Global Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Guangxi Bossco Environmental Protection Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Hangzhou Jinjiang Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Anhui Shengyun Environment-Protection Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.19 C&G Environmental Protection Holdings Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Resou Resources Recovery Co., Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




