PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851334

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851334
Vibration Sensor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The vibration sensor market size is valued at USD 6.10 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 8.60 billion by 2030, reflecting a 7.10% CAGR during the period.
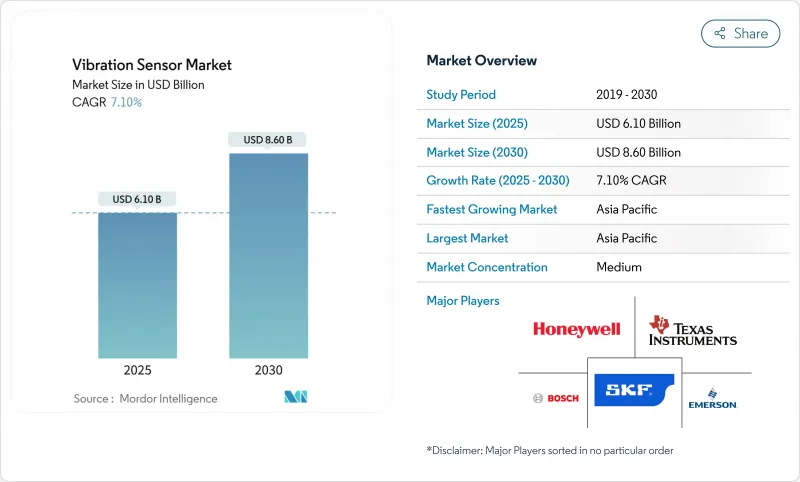
Continued investment in predictive maintenance programs, miniaturized MEMS designs, and stricter machinery-health regulations accelerated adoption across factories, wind farms, and vehicle plants. Asia-Pacific manufacturers, wind turbine owners, and automotive assemblers directed much of this spending, aided by falling sensor prices and local semiconductor capacity expansions. Wireless connectivity reduced installation costs, and edge-AI firmware cut data traffic, making sensors viable for remote or hazardous sites. Meanwhile, supply-chain diversification gained urgency after China's 2025 export controls on rare-earth inputs used in ceramic sensing elements.
Global Vibration Sensor Market Trends and Insights
Proliferation of Predictive Maintenance Programs in Continuous Process Industries
Asia-Pacific plant operators used predictive maintenance to reduce unplanned downtime costs by up to 50%, relying on dense sensor grids that stream high-frequency data to analytics engines. Early projects such as the Nordic Sugar steam-dryer retrofit demonstrated 13-day fault-prediction windows, validating payback for large chemical and steel sites. Continuous monitoring displaced periodic walk-by inspections, and edge-computing chips embedded in nodes lowered latency to millisecond levels. Chinese stimulus for Industry 4.0 upgrades-maintained momentum, embedding thousands of devices per facility. Consequently, the vibration sensor market gained long-run recurring demand from maintenance budgets rather than capital expenditure cycles.
Rise of Wireless MEMS Sensors for Hazardous Oil and Gas Sites
Offshore platforms and refineries adopted certified wireless nodes that eliminated costly cable runs through ATEX zones. Battery lives exceeded three years, and piezoelectric energy harvesters further prolonged service intervals. Operators valued retrofit capability without shutting down throughput that could otherwise cost USD 50,000 per hour. Embedded FFT processing in each sensor produced actionable bearing-wear metrics, reducing the need for on-site vibration analysts. These benefits widened the addressable base and lifted the vibration sensor market in hydrocarbon economies that historically lagged digital-maintenance adoption.
Calibration Drift of Piezoelectric Sensors at Extreme Temperatures
Piezoelectric elements experienced output deviations above 110 °C, with errors hitting 1.06% at moderate heating rates. Frequent recalibration raised lifecycle costs in turbines and aerospace engines where thermal cycling was routine. High-temperature single-crystal alternatives operated reliably beyond 600 °C but commanded premium pricing. Developers explored compensation circuits and dual-sensor configurations, yet complex designs limited mass-market appeal. The resulting performance-price trade-off slowed deployments in harsh-duty niches of the vibration sensor market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Edge-AI Enabled Diagnostics in Automotive Assembly
- Mandatory ISO 20816 Compliance in EU and North America
- Data-Security Concerns in Cloud-based Analytics (Defense)
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Accelerometers generated 54.4% revenue in 2024, underpinning the vibration sensor market size of USD 6.10 billion through their tri-axial versatility in vehicles, smartphones, and factory motors. Wireless velocity devices, though smaller in value, led growth at 9.1% CAGR to 2030 as refinery and pipeline engineers valued velocity's direct correlation with bearing health.
The miniaturization push spurred next-generation accelerometers such as Bosch Sensortec's BMA580, which reduced package volume by 76% while meeting sensitivity targets for hearables. Edge filtering in these chips cuts outbound data by transmitting only anomalies, conserving bandwidth in mesh networks. Parallel advances in energy harvesting prolonged node life, enabling five-year maintenance intervals on remote assets. Together, these enhancements allowed the vibration sensor market to broaden into wearables and condition-based lubrication systems previously constrained by power or size limits.
Piezoelectric elements retained a 46.3% share in 2024 thanks to low-frequency sensitivity, but MEMS shipments expanded at a 10.3% CAGR as semiconductor fabs delivered wafer-level economies. The vibration sensor market benefited from single-die integration that collapsed discrete analog front-ends into compact system-on-chip packages.
Texas Instruments' ultrasonic lens-cleaning demo highlighted MEMS versatility, using programmable vibrations to remove contaminants from automotive cameras. Foundry advances enabled multi-axis arrays measuring sub-g vibrations suitable for structural-health monitoring. Meanwhile, piezoresistive and capacitive designs served ultra-low-power wearables where duty cycles were sparse. This diversified portfolio allowed OEMs to choose architectures based on bandwidth, cost, and power, expanding overall penetration of the vibration sensor market.
Vibration Sensor Market is Segmented by Product Type (Accelerometers, Velocity Sensors, Displacement Sensors, and More), Technology (Piezoelectric, Piezoresistive, Capacitive, Strain-Gauge, and MEMS), Material (Quartz, Piezoelectric Ceramics, Doped Silicon, and Others), End-Use Industry (Automotive, Aerospace and Defense, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led with a 34.2% share in 2024 as China's wind-turbine roll-outs and India's semiconductor design centers lifted local demand. The region's 8.3% CAGR also out-paced global averages, preserving its leadership through 2030. Japanese precision-machinery firms ordered high-resolution sensors for robotics, further enlarging the vibration sensor market in the bloc.
North America followed, driven by ISO compliance in chemical plants and aerospace programs requiring radiation-tolerant devices. US defense retrofits favored edge-processed units that remained air-gapped, mitigating cybersecurity exposure. Canadian miners installed ruggedized wireless mesh networks across remote pits where wired runs were impractical, adding niche demand to the vibration sensor market.
Europe exhibited advanced maturity, exemplified by BMW's sensor-equipped robo-dogs patrolling engine plants. Nordic offshore wind farms fitted high-channel-count systems on 15 MW turbines to monitor yaw and blade harmonics. Strict worker-safety directives assured steady upgrades, keeping the vibration sensor market resilient despite macroeconomic headwinds.
South America and the Middle East/Africa remained emerging but dynamic. Brazilian miners and agribusiness processors began installing condition-monitoring kits, aided by falling MEMS costs. Gulf-region NOCs embraced ATEX-rated wireless sensors for flare stacks and compressors, quickly expanding the vibration sensor market footprint in hazardous-area deployments.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- SKF AB
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Analog Devices Inc.
- TE Connectivity Ltd
- Bosch Sensortec GmbH
- Texas Instruments Inc.
- National Instruments Corp.
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- Parker Hannifin Corp.
- Baker Hughes (Bently Nevada)
- Wilcoxon Sensing Technologies
- PCB Piezotronics Inc.
- Meggitt PLC (Sensing Systems)
- IMI Sensors
- ifm electronic GmbH
- Siemens AG
- Omron Corporation
- Hansford Sensors Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Proliferation of Predictive Maintenance Programs in Continuous Process Industries (Asia Pacific)
- 4.2.2 Rise of Wireless MEMS Sensors for Hazardous Oil and Gas Sites (Middle East)
- 4.2.3 Edge-AI Enabled Diagnostics in Automotive Assembly (Europe)
- 4.2.4 Mandatory ISO 20816 Compliance in EU and North America
- 4.2.5 Expansion of Wind Turbine Installations (Nordics and China)
- 4.2.6 Miniaturization Demand from Wearables and Hearables
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Calibration Drift of Piezoelectric Sensors at Extreme Temperatures
- 4.3.2 Data-Security Concerns in Cloud-based Analytics (Defense)
- 4.3.3 Shortage of Specialty Piezo-ceramic Materials (China Export Quotas)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Investment Analysis
- 4.8 Assessment of Macroeconomic Factors on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Accelerometers
- 5.1.2 Velocity Sensors
- 5.1.3 Displacement Sensors
- 5.1.4 Gyroscopes (Vibration-Grade)
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Piezoelectric
- 5.2.2 Piezoresistive
- 5.2.3 Capacitive
- 5.2.4 Strain-Gauge
- 5.2.5 MEMS
- 5.3 By Material
- 5.3.1 Quartz
- 5.3.2 Piezoelectric Ceramics
- 5.3.3 Doped Silicon
- 5.3.4 Others
- 5.4 By End-Use Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive
- 5.4.2 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.4.3 Oil and Gas
- 5.4.4 Industrial Manufacturing
- 5.4.5 Power Generation (incl. Wind)
- 5.4.6 Healthcare
- 5.4.7 Consumer Electronics and Wearables
- 5.4.8 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Taiwan
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 India
- 5.5.3.6 ASEAN
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Mexico
- 5.5.4.2 Brazil
- 5.5.4.3 Argentina
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, Funding)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.4.2 SKF AB
- 6.4.3 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.4 Analog Devices Inc.
- 6.4.5 TE Connectivity Ltd
- 6.4.6 Bosch Sensortec GmbH
- 6.4.7 Texas Instruments Inc.
- 6.4.8 National Instruments Corp.
- 6.4.9 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.10 NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- 6.4.11 Parker Hannifin Corp.
- 6.4.12 Baker Hughes (Bently Nevada)
- 6.4.13 Wilcoxon Sensing Technologies
- 6.4.14 PCB Piezotronics Inc.
- 6.4.15 Meggitt PLC (Sensing Systems)
- 6.4.16 IMI Sensors
- 6.4.17 ifm electronic GmbH
- 6.4.18 Siemens AG
- 6.4.19 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.20 Hansford Sensors Ltd
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




