PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851349

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851349
Modular Construction - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Modular Construction Market size is estimated at USD 91.25 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 122.24 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.02% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
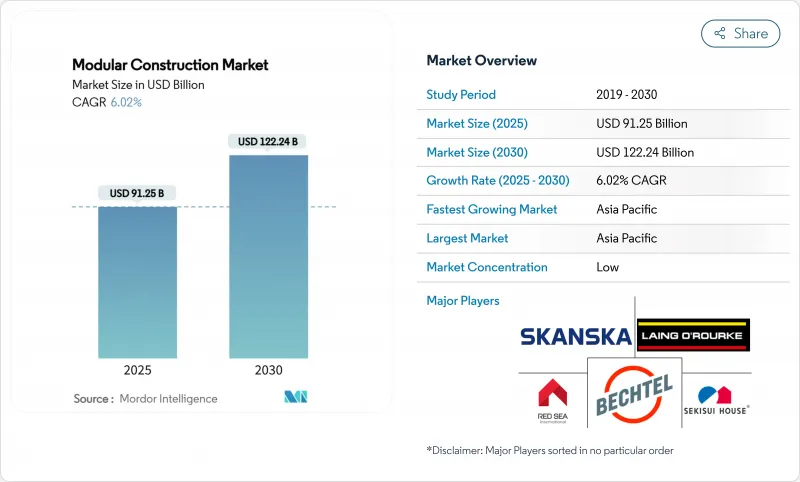
Rising labor shortages, supportive regulations, and the visible success of factory-built housing projects are repositioning modular methods from niche solutions to primary construction options across many regions. Asia-Pacific commands a 47% revenue share, powered by rapid urbanization, long-running affordable-housing mandates, and a deep manufacturing base that supplies modules to domestic and export projects. Permanent solutions account for 67% of the modular construction market, reflecting broad acceptance that factory-assembled buildings can meet durability and aesthetic expectations equal to site-built structures. Steel frameworks remain the backbone of production with an 84% share, favored for structural strength, dimensional stability, and well-established supply chains. Institutional owners-particularly education and healthcare operators-lead demand because off-site fabrication minimizes disruption, accelerates occupancy, and compresses overall project schedules.
Global Modular Construction Market Trends and Insights
Developed Economies Embrace Modular Solutions
High household demand collides with shrinking construction workforces across North America and Western Europe. In Sweden, 84% of detached homes now originate from factory lines, establishing a mature reference point that policymakers elsewhere study. Japanese builders also sustain high adoption levels, while the United States remains below 4% of its housing output but records strong momentum in healthcare, education, and multi-family projects. The visibility of successful Scandinavian and Japanese case studies reassures investors that modular construction market risk is manageable. Builders in Australia and Canada replicate similar models for social-housing pipelines, reinforcing a global learning loop that spreads expertise and reduces first-mover uncertainty.
Government Initiatives Catalyze Market Growth
Public authorities are increasingly writing modular requirements into housing and infrastructure programs. Queensland's 2024-25 budget earmarked AUD 2.8 billion (USD 1.85 billion) to deliver 600 modular homes that can be placed on-site in 3 months, versus the lengthy schedules of conventional builds. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development issued 90 new or revised manufactured-home standards in 2024, modernizing a code base that had been largely static for three decades. These steps streamline approvals, reassure lenders, and nudge specifiers to evaluate a modular approach first, thereby expanding the modular construction market.
High Initial Investment Creates Market Entry Barriers
Setting up a dedicated factory, automation lines, and a certified quality-control system requires sizable capital outlays before revenue flows. Several well-funded start-ups, including Katerra, failed despite clear product-market fit because operations ramped slower than capital was burned. Rising energy costs and inflation magnify those cash-flow stresses. Established contractors often respond through joint ventures that share risk, but the basic hurdle remains: entrants need scale almost immediately to amortize fixed assets, limiting the pool of viable new competitors and slowing overall growth of the modular construction market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Temporary Structures Drive Market Flexibility
- Accelerated Project Timelines Transform Industry Economics
- Regulatory Variations Complicate Cross-Border Expansion
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Permanent modular formats delivered 67% of 2024 revenue. Within that share, residential high-rise projects such as 147 St. Felix in Brooklyn illustrate architectural flexibility that dismisses lingering perceptions of "boxy" units. The modular construction market size for permanent solutions is forecast to expand alongside digital design tools that knit mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems into repeatable chassis, reducing re-work during assembly.
Institutional clients prize the diminished disruption that off-site fabrication delivers. Fifteen-story dormitory schemes erected in half the usual time frame help universities like California Polytechnic State University secure student revenue faster. Developers also value factory-controlled quality, which meets or exceeds code for structural integrity and fire resistance, supporting premium valuations in the modular construction market.
Steel claimed 84% of 2024 material volume due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and global availability. The modular construction market size for steel-based modules benefits from predictable torsional rigidity, allowing taller configurations without material changes. Insurance carriers often reduce premiums for non-combustible frames, tipping whole-life costs further in steel's favor.
A 20-year lifecycle study comparing a typical 10,000 ft2 project pegged total outlay at USD 350,000 for steel modules versus up to USD 1.1 million for traditional builds, underscoring economic resilience. Emerging engineered-wood technologies, such as cross-laminated timber, are penetrating niche mid-rise projects, but steel's mature supply chain and recycling value maintain its dominance in the modular construction market.
The Modular Construction Market Report Segments the Industry by Construction Type (Permanent Modular and Relocatable Modular), Material (Steel, Concrete, and More), End-User Sector (Residential, Commercial, and Industrial/Institutional), Service Stage (New Construction and After-Sales Maintenance and Refurbishment (Renovation)), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominated with 47% modular construction market share in 2024. China's vast manufacturing footprint enables low-cost module production, while Japan's pioneers such as Sekisui House sustain a reputation for high-precision factory homes. Australia's import of USD 330 million of prefab components over five years highlights robust cross-border trade, and state budgets earmark modular stock to ease social-housing backlogs. Urbanization pressures, supported by government grants, assure continued regional leadership.
North America holds significant expansion potential between 2025 and 2030. The United States faces a deficit of skilled construction labor amid a 7 million-home supply gap, so factory processes that decouple labor intensity from site location appeal strongly. HUD's 2024 code overhaul and pending Federal legislation encourage wider adoption. Canada's national housing strategy explicitly references prefabricated solutions, with senior ministers advocating modular supply to improve affordability.
Europe shows varied maturity by sub-region. Nordic countries display seasoned off-site ecosystems; Sweden builds 45% of homes in factories, offering proven technical and commercial templates for neighboring markets. The United Kingdom targets 25% modular penetration by 2030 and funds risk assessments to accelerate take-up. Southern Europe lags due to fragmented supply chains and complex permitting, yet rising carbon-reduction goals and labor scarcity are likely to converge in favor of the modular construction market.
- ACS Group
- Algeco UK Limited (Modulaire Group)
- Alta-Fab Structures Ltd.
- ATCO Ltd
- Balfour Beatty
- Bechtel Corporation
- Bouygues Construction
- CIMC Modular Building
- Daiwa House Industry Co. Ltd
- Fluor Corporation
- Guerdon, LLC.
- Laing O'Rourke
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- Lendlease Corporation
- Red Sea International
- Sekisui House Ltd
- Skanska
- Stack Modular
- Wernick Group
- WillScot Holdings Corporation
- Zekelman Industries
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Demand for Modular Construction from Developed Economies
- 4.2.2 Supportive Government Initiatives for Modular Construction
- 4.2.3 Rising Demand for Temporary/Portable Structures
- 4.2.4 Significantly Reduced Project Timelines
- 4.2.5 Solution to Skilled Labor Shortage
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Initial Investment
- 4.3.2 Design Limitations
- 4.3.3 Regulatory and Code Variations Across region
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 Segmentation by Construction Type
- 5.1.1 Permanent Modular
- 5.1.2 Relocatable Modular
- 5.2 Segmentation by Material
- 5.2.1 Steel
- 5.2.2 Concrete
- 5.2.3 Wood
- 5.2.4 Plastic
- 5.3 Segmentation by End-user Sector
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Commercial
- 5.3.3 Industrial/Institutional
- 5.4 Segmentation by Service Stage
- 5.4.1 New Construction
- 5.4.2 After-sales Maintenance and Refurbishment (Renovation)
- 5.5 Segmentation by Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Australia
- 5.5.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Nordics
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Chile
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.4 South Africa
- 5.5.5.5 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/ Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 ACS Group
- 6.4.2 Algeco UK Limited (Modulaire Group)
- 6.4.3 Alta-Fab Structures Ltd.
- 6.4.4 ATCO Ltd
- 6.4.5 Balfour Beatty
- 6.4.6 Bechtel Corporation
- 6.4.7 Bouygues Construction
- 6.4.8 CIMC Modular Building
- 6.4.9 Daiwa House Industry Co. Ltd
- 6.4.10 Fluor Corporation
- 6.4.11 Guerdon, LLC.
- 6.4.12 Laing O'Rourke
- 6.4.13 Larsen & Toubro Limited
- 6.4.14 Lendlease Corporation
- 6.4.15 Red Sea International
- 6.4.16 Sekisui House Ltd
- 6.4.17 Skanska
- 6.4.18 Stack Modular
- 6.4.19 Wernick Group
- 6.4.20 WillScot Holdings Corporation
- 6.4.21 Zekelman Industries
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 Green and Sustainable Construction Demand
- 7.2 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




