PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851423

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851423
Waste To Energy (WTE) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Waste To Energy Market size is estimated at USD 45.42 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 77.30 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.22% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
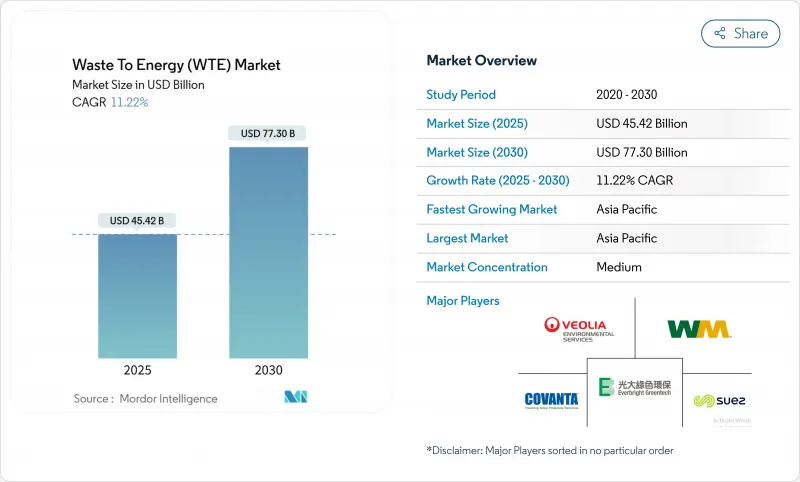
Growth rests on two converging pressures: swelling urban waste streams and the worldwide push for low-carbon power. Thermal technologies remain the backbone of capacity additions, yet investments are shifting toward advanced, lower-emission solutions such as plasma-arc and upgraded anaerobic digestion. Active carbon-price regimes in South Korea and the European Union are reshaping project economics, while landfill bans in India's Tier-2 cities accelerate feedstock availability. Strategic consolidation among utilities, environmental services firms, and technology specialists continues, and digital optimization tools are lifting operating margins and compliance performance across new and retrofit plants. Together, these forces sustain a robust pipeline of bankable projects and position the waste-to-energy market as a pivotal element of the circular economy.
Global Waste To Energy (WTE) Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Roll-out of EfW Public-Private Partnership Pipelines in China's Greater Bay Area
Investments topping CNY 35 billion are funding more than 80 projects that deploy advanced emissions monitoring and material-recovery designs. New plants form a high-capacity cluster processing over 400,000 tons daily, cementing the region's template for scalable urban waste solutions. Electricity output from clean sources, including WTE, rose 16.4% year-on-year in 2024, confirming policy momentum and investor confidence.
EU Green Taxonomy Incentives Accelerating Retrofit of Legacy Incineration Fleets
The Green Taxonomy links financing to strict energy-efficiency metrics, unlocking roughly EUR 300 million for retrofit work that couples upgraded flue-gas systems with expanded material reclamation. Operators that comply gain lower funding costs and priority grid access, reinforcing the waste-to-energy market across Western and Northern Europe.
Stricter Dioxin Emission Caps Postponing Permits for Grate-Furnace Refurbishments in Germany
The 2024 Industrial Emissions Directive tightens limits and mandates e-permits by 2035, forcing operators of older plants to redesign air-pollution-control systems. Compliance costs and protracted approvals delay capacity upgrades and dampen the waste-to-energy market in Europe's largest economy.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- National Bans on Unsegregated Landfill Triggering MSW Diversion in India's Tier-2 Cities
- Soaring Carbon Credit Prices Improving WTE Project IRRs in South Korea
- Limited Tipping-Fee Escalation Clauses Hurting Project Bankability in Indonesia
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Incineration retained 65% of the waste to energy market share in 2024, anchored by proven operational history and integration with district-heat infrastructure across Europe and East Asia. Plants above 200,000 tpa continue to deploy grate-furnace designs due to predictable runtime and established supplier networks. Nevertheless, plasma-arc capacity is forecast to log a 16% CAGR to 2030, thanks to 99% waste-to-syngas conversion efficiency and sharply lower dioxin formation. Subsidy schemes that reward lower emissions and higher metals recovery further tilt project pipelines toward plasma-arc, especially in densely populated Asian conurbations. The waste to energy market size tied to advanced thermal platforms therefore accelerates faster than the headline rate.
Hybridization trends are reshaping asset specifications: several new builds bundle front-end mechanical biological treatment with either gasification or plasma-arc to boost recycling yields before thermal conversion. Meanwhile, anaerobic digestion enjoys renewed focus in agrarian regions where high-moisture organic waste offers superior biogas yields at modest capital cost. Mechanical, thermal, and chemical pretreatments now lift methane production by 25%-190%, widening the economic sweet spot for distributed digesters. Over the forecast period, digital twins and AI-assisted combustion controls are expected to enhance thermal-island efficiency by 4%-6% on a lifecycle basis, further differentiating next-generation facilities.
Municipal solid waste accounted for 70% of the waste to energy market size in 2024, buoyed by steady collection volumes and regulatory pressure to move away from landfilling. High calorific industrial fractions and source-segregation programs in major cities sustain robust feedstock quality, supporting baseload energy output. Agricultural and agro-industrial residues, however, will post a 14% CAGR through 2030 as governments target methane mitigation in rural supply chains. Financial incentives for farmers to supply crop stover and manure unlock previously untapped energy potential and align with soil-health goals via digestate use.
Industrial waste streams featuring plastics, solvents, and high-Btu sludges present stable demand for specialized rotary-kiln and fluidized-bed systems. Sewage sludge gains visibility where stricter discharge norms require additional treatment: thermal drying coupled with mono-incineration now yields phosphorus-rich ash that can be recycled into fertilizer. Across categories, pre-processing and optical sorting technologies are raising net calorific value and reducing contaminants, a trend that supports higher plant availability and longer maintenance cycles within the waste to energy market.
The Waste To Energy (WTE) Market Report is Segmented by Technology (Physical, Thermal, and Biological), Waste Type (Municipal Solid Waste, Industrial Waste, and Others), Energy Output (Electricity, Heat, and Others), End-Users (Utilities and IPPs, Industrial Captive Plants, District Heating Operators, and Transport Fuel Distributors), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific posted 45% of 2024 revenue and will hold the pole position with a 13% regional CAGR to 2030. China alone operates over 400 plants processing 400,000 tons daily, with the capacity to climb to 700,000 tons per day by 2025. India's Tier-2 cities, guided by Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0, are issuing build-operate-transfer contracts that favor modular lines sized at 300-500 tpd. Japan sustains leadership in emissions control technologies, and South Korea's emissions-trading scheme raises modeled IRRs by up to 2.5 percentage points, broadening the waste-to-energy market in Northeast Asia.
Europe ranks second by revenue, characterized by dense district-heat integration and rigorous environmental regulation. Denmark and Sweden already surpass 75% renewable share in municipal heat networks, and the EU Green Taxonomy channels concessional capital into plant retrofits. Germany faces retrofit delays from stricter dioxin caps, while the United Kingdom's calorific-value rules redirect lower-grade RDF to domestic incinerators, creating new local capacity demand.
North America registers steady expansion anchored by utility-scale projects in the United States and biomethane investments in Canada. Covanta, Waste Management, and FCC Environmental Services vie for large municipal contracts, with recent acquisitions signaling further consolidation. South America sees biogas rollouts in Brazil's south-central sugar belt, yet feedstock-price volatility tempers project pipelines. In the Middle East and Africa, Egypt's USD 120 million solid waste-to-electricity plant illustrates rising interest, though overall deployment remains early-stage.
- Veolia Environnement SA
- Suez SA
- Waste Management Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corp.
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- Hitachi Zosen Corp.
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc.
- A2A SpA
- MVV Energie AG
- Martin GmbH fur Umwelt- und Energietechnik
- China Everbright Environment Group Ltd
- China Jinjiang Environment Holding Co.
- Xcel Energy Inc.
- Shenzhen Energy Group Co.
- Keppel Seghers
- Remondis SE & Co. KG
- FCC Servicios Medio Ambiente
- Enerkem Inc.
- Sembcorp Industries Ltd
- Green Conversion Systems LLC
- Fortum Oyj
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid roll-out of EfW public-private partnership pipelines in China's Greater Bay Area
- 4.2.2 EU Green Taxonomy incentives accelerating retrofit of legacy incineration fleets
- 4.2.3 National bans on unsegregated landfill triggering MSW diversion in India's Tier-2 cities
- 4.2.4 Soaring carbon credit prices improving WTE project IRRs in South Korea
- 4.2.5 Circular-economy led corporate power-purchase agreements (CPPAs) for biogas in Nordics
- 4.2.6 Mandatory calorific value thresholds for RDF exports in the UK post-Brexit
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stricter dioxin emission caps postponing permits for grate-furnace refurbishments in Germany
- 4.3.2 Limited tipping-fee escalation clauses hurting project bankability in Indonesia
- 4.3.3 Anaerobic-digestion feedstock price volatility undermining margins in Brazil
- 4.3.4 Community push-back against plasma-arc facilities in Australia's peri-urban regions
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Physical (Refuse-Derived Fuel, Mechanical Biological Treatment)
- 5.1.2 Thermal (Incineration/Combustion, Gasification, Pyrolysis and Plasma-Arc)
- 5.1.3 Biological (Anaerobic Digestion, Fermentation)
- 5.2 By Waste Type
- 5.2.1 Municipal Solid Waste
- 5.2.2 Industrial Waste
- 5.2.3 Agricultural and Agro-industrial Residues
- 5.2.4 Sewage Sludge
- 5.2.5 Others (Commercial, Construction, Hazardous)
- 5.3 By Energy Output
- 5.3.1 Electricity
- 5.3.2 Heat
- 5.3.3 Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
- 5.3.4 Transportation Fuels (Bio-SNG, Bio-LNG, Ethanol)
- 5.4 By End-user
- 5.4.1 Utilities and Independent Power Producers (IPPs)
- 5.4.2 Industrial Captive Plants
- 5.4.3 District Heating Operators
- 5.4.4 Transport Fuel Distributors
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Spain
- 5.5.2.5 Nordic Countries
- 5.5.2.6 Russia
- 5.5.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Colombia
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Egypt
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Veolia Environnement SA
- 6.4.2 Suez SA
- 6.4.3 Waste Management Inc.
- 6.4.4 Covanta Holding Corp.
- 6.4.5 Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.6 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- 6.4.7 Hitachi Zosen Corp.
- 6.4.8 Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc.
- 6.4.9 A2A SpA
- 6.4.10 MVV Energie AG
- 6.4.11 Martin GmbH fur Umwelt- und Energietechnik
- 6.4.12 China Everbright Environment Group Ltd
- 6.4.13 China Jinjiang Environment Holding Co.
- 6.4.14 Xcel Energy Inc.
- 6.4.15 Shenzhen Energy Group Co.
- 6.4.16 Keppel Seghers
- 6.4.17 Remondis SE & Co. KG
- 6.4.18 FCC Servicios Medio Ambiente
- 6.4.19 Enerkem Inc.
- 6.4.20 Sembcorp Industries Ltd
- 6.4.21 Green Conversion Systems LLC
- 6.4.22 Fortum Oyj
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & unmet-need assessment




